A Comprehensive Guide on Large Action Models (LAMs)
Introduction: From Large Language Models to Large Action Models
Over the past few years, artificial intelligence has captured the imagination of researchers, businesses, and everyday users alike. Much of the attention has gone to Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT, Claude, and Gemini systems that excel at generating and understanding human-like text.
But AI is not just about conversation anymore. A new frontier has emerged: Large Action Models (LAMs). Unlike LLMs, which focus on predicting and producing text, LAMs are designed to take meaningful actions in the real or digital world. Think of them as AI agents that don’t just talk about solving problems, but actually go out and execute the solution whether that means navigating software systems, automating workflows, operating robots, or making decisions in complex environments.
This guide will break down what LAMs are, how they work, their architecture, where they’re being applied, real-world examples, the challenges they face, and where the future might take them.
How LAMs Work: The Core Idea
At its heart, a Large Action Model is an AI system trained not only on data about language, images, or code, but also on action patterns. While an LLM might generate instructions on how to use Excel, a LAM can actually open Excel, create the file, apply the formulas, and send the report.
Here’s how the workflow generally looks:
- Input/Goal Understanding – The user provides a request (“Book me the cheapest flight to Mumbai next week”).
- Contextual Reasoning – The LAM interprets intent, breaks the problem into actionable steps, and decides which tools or APIs to call.
- Execution – It carries out the sequence of actions: querying flight APIs, comparing prices, booking the ticket, and sending confirmation.
- Feedback Loop – It validates whether the actions succeeded, and if not, retries or adjusts the approach.
- Output/Result – The user receives not just an answer, but a completed task.
In short, while LLMs are great “talkers,” LAMs are doers.
LAM Architecture and Technical Framework
LAMs don’t exist in isolation - they’re a blend of multiple AI and engineering components. The architecture can vary by implementation, but most share common layers:
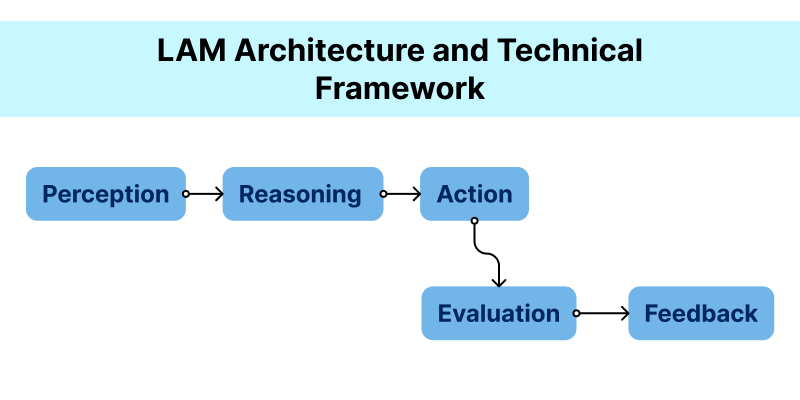
1. Perception Layer
- Handles natural language understanding, vision, or multimodal input.
- Often powered by LLMs or vision models.
- Example: Parsing “Turn on the living room lights at 7 PM every day.”
2. Reasoning and Planning Layer
- Core decision-making unit.
- Uses reinforcement learning, planning algorithms, or chain-of-thought reasoning to break goals into steps.
- Example: Translate “book flight” into a plan: search → filter → compare → purchase.
3. Action Execution Layer
- Interfaces with APIs, operating systems, robotics, or IoT devices.
- Requires connectors, toolkits, or scripts that enable the model to interact with real-world systems.
- Example: Sending a POST request to an airline API.
4. Memory and Knowledge Layer
- Stores past interactions and results for long-term learning.
- Helps adapt to preferences (“always book window seats”).
5. Feedback and Safety Layer
- Monitors actions to prevent harmful outcomes.
- Uses guardrails, human-in-the-loop verification, or error-checking routines.
Together, these layers form a loop of perception → reasoning → action → evaluation, mimicking how humans plan and act.
LLMs vs. LAMs: Key Differences
Since Large Action Models (LAMs) are often compared to Large Language Models (LLMs), it’s worth highlighting where they overlap and where they diverge.
Applications of LAMs Across Industries
LAMs are not just a futuristic concept - they’re already transforming multiple industries.
1. Business and Enterprise Automation
- Automating workflows in CRMs, ERPs, and financial systems.
- Example: A LAM that generates quarterly sales reports by pulling data from multiple databases.
2. Healthcare
- Scheduling patient appointments, processing medical records, even guiding robotic surgeries.
- Example: An AI nurse assistant that manages patient queries, retrieves test results, and books follow-ups automatically.
3. Finance
- Trading bots that adapt to live markets, fraud detection, risk management.
- Example: A LAM that monitors transactions in real-time and freezes suspicious accounts before damage spreads.
4. E-commerce & Customer Support
- End-to-end shopping assistants that compare prices, order products, track deliveries, and handle returns.
- Example: A virtual agent that not only recommends a product but buys it on your behalf.
5. Smart Homes & IoT
- Controlling devices seamlessly—lights, appliances, security.
- Example: “Set thermostat to 24°C when I’m 2 km from home.”
6. Robotics & Manufacturing
- Robotic arms guided by LAMs to manage supply chains, warehouse logistics, or assembly lines.
7. Education & Research
- Automating literature reviews, setting up experiments, or grading assignments.
Real-World Examples of LAMs in Action
While the term LAM is relatively new, early implementations are already in motion:
- AutoGPT / BabyAGI – Experimental open-source projects that link LLMs with autonomous action loops.
- Google DeepMind’s AlphaZero lineage – Though focused on games, they embody the concept of action-driven intelligence.
- OpenAI’s API with tool use – GPT models integrated with APIs that allow browsing, running code, or performing transactions hint at LAM-like behavior.
- Tesla’s Optimus Robot (prototype) – Embedding models capable of both perception and action in robotics.
- Enterprise AI agents (UiPath, Cognition Labs, Adept AI) – Startups working to build general-purpose LAMs that automate software workflows across industries.
Challenges Facing LAMs
The promise of LAMs is massive, but so are the obstacles:
- Reliability: Unlike text generation, failed actions can have real costs—booking the wrong flight or mismanaging finances.
- Safety & Ethics: How to prevent malicious use, accidents, or unsafe commands (“Delete all company records”).
- Tool Integration: The digital world is fragmented; LAMs must connect seamlessly to thousands of APIs and platforms.
- Generalization: Human environments are unpredictable—LAMs need to adapt flexibly.
- Trust & Transparency: Users need visibility into how and why actions are taken.
- Compute & Costs: Training and running LAMs with continuous monitoring is resource-intensive.
Future Trends: Where LAMs Are Headed
The next few years are likely to see rapid growth in LAM development. Some key trends to watch:
1. Deeper Tool Integration
- LAMs will be increasingly connected to enterprise apps, APIs, and IoT devices.
- Think of an AI “universal remote” for all your digital workflows.
2. Hybrid Models (LLM + LAM)
- The most powerful systems will combine strong language reasoning with action capabilities.
- Example: A customer service agent that chats naturally and refunds an order automatically.
3. Edge and On-Device LAMs
- As compute efficiency improves, smaller LAMs will run directly on devices like smartphones, cars, or home robots.
4. Safety & Governance Frameworks
- Expect stricter rules and ethical guidelines around autonomous AI actions.
- Human-in-the-loop verification will remain essential in high-stakes areas (healthcare, finance).
5. Personalized Agents
- Future LAMs will adapt to individuals, learning personal preferences, habits, and contexts.
- Imagine an AI assistant that knows not just how to book travel, but your favorite seat, airline, and meal preferences.
6.Physical World Integration (Robotics)
- Beyond software, LAMs will control machines, vehicles, and robots.
- This bridges AI from the digital world into the tangible one.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
Large Action Models represent the natural evolution of AI - from systems that describe the world to systems that can change it. They take us closer to autonomous digital and physical agents that assist with everyday life, business operations, and scientific breakthroughs.
We’re still early in this journey. Current LAMs are limited, sometimes clumsy, and in need of strong safety frameworks. But as architectures mature, integrations broaden, and trust mechanisms improve, LAMs will likely become as ubiquitous as today’s chatbots and recommendation engines.
The big picture? LLMs gave AI a voice. LAMs will give AI hands and legs.
