How AI Transforms Manufacturing with Real Use Cases and Key Trends
Why AI is shaping manufacturing today
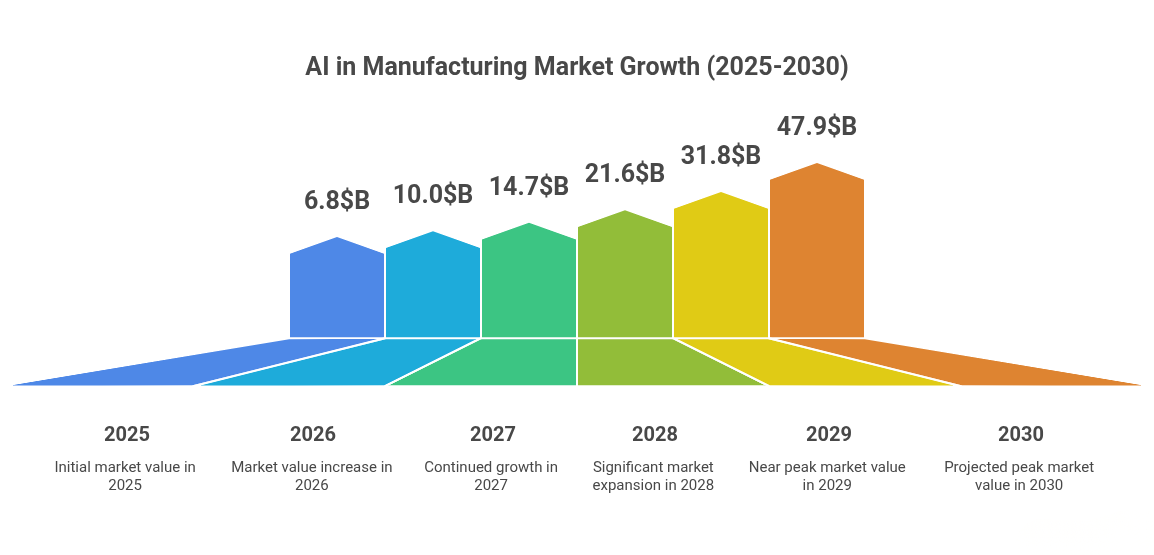
AI in manufacturing is entering a high-growth phase, driven by expanding industrial data, stronger automation needs, and pressure to stabilize production. The global market is projected to reach USD 47.88 billion by 2030 (Grand View Research), with North America, Europe, China, Japan, and India leading adoption efforts as factories push to reduce uncertainty and improve output reliability through digital tools.
Several factors are accelerating this shift through 2025–2026. Supply chains remain unpredictable, raw material and energy costs put strain on margins, and skilled labor shortages limit production capacity across major manufacturing hubs. At the same time, advances in machine learning, computer vision, and connected sensor networks have made AI systems more accessible for tasks such as equipment monitoring, quality inspection, and production planning.
This blog breaks down the technologies shaping AI in manufacturing, the use cases that deliver measurable improvements, the industries adopting these tools the fastest, and the practical steps manufacturers can take to integrate AI into their operations.
Why industrial AI is a key benefit for smart manufacturers
Manufacturers face constant challenges balancing quality, cost, and efficiency while managing supply chain pressures and equipment reliability. Industrial AI directly addresses these pain points by using machine learning and data insights to improve how factories operate day-to-day.
According to the NAM, AI adoption in the industrial sector is already delivering measurable improvements
- 72% of manufacturers report that AI has reduced operational costs and improved overall efficiency.
- 51% have gained better visibility into production processes and faster issue detection.
- 41% say AI has enhanced process control and improved production consistency.
Key advantages for smart manufacturers
Fewer defects, higher quality
AI systems identify product anomalies during production, reducing manual inspection time and helping maintain consistent quality across every batch.
Greater efficiency and throughput
Automation powered by AI streamlines repetitive operations and improves cycle times, allowing teams to focus on higher-value work.
Faster, Data-driven decisions
Manufacturers get clearer insights into equipment health, production flow, and resource usage, enabling quicker responses to disruptions or demand changes.
Lower costs and maintenance overhead
Predictive analytics cuts unplanned downtime and optimizes maintenance schedules, preventing unnecessary stoppages and expensive emergency repairs.
Smarter use of energy and resources
AI-driven monitoring helps track machine performance and energy consumption, supporting sustainability goals while lowering utility expenses.
Core AI technologies used in manufacturing
AI in manufacturing is powered by several key technologies. Each one contributes to specific improvements across maintenance, inspection, production, and shop-floor operations. Understanding these foundations makes it easier for manufacturers to plan where AI fits in their workflows.
Machine learning & predictive analytics
Machine learning examines equipment, production, and sensor data to identify patterns that signal early signs of drift or stress. These insights help maintenance teams plan work before an issue halts production.
How manufacturers use it
A model trained on vibration, pressure, and temperature readings identifies unusual patterns that typically appear before bearing failure. The team schedules service during a planned stop instead of reacting after a breakdown.
Why does it improve daily operations?
Predictive insights reduce stoppages and help technicians focus on machines that need attention instead of following fixed maintenance calendars.
Setting up the groundwork
Choose one asset category and gather a clean baseline dataset. The first model should aim to detect deviation rather than classify every fault type. This speeds adoption and delivers early wins.
Computer Vision for inspection and line Control
Computer vision uses cameras trained with AI models to inspect products and support equipment used in assembly or packing tasks. It increases inspection precision at speeds difficult for manual checks.
How does it fit into production?
A vision system evaluates electronic components as they move down the line, flagging soldering faults or missing parts without slowing production.
Direct impact on quality
Better detection accuracy means fewer defective units reach later stages of assembly. This saves materials, cuts rework time, and improves consistency across batches.
What should teams prepare for?
Gather images that reflect actual production conditions—lighting, angles, shadows, and surface textures. Good data improves early model accuracy and reduces the need for repeated retraining.
Robotics and Autonomous systems
AI-enabled robots support tasks where consistency and controlled movement matter. They assist with assembly, packaging, pallet movement, and machine tending while working alongside human operators.
How do manufacturers apply it?
A guided robot arm tightens fasteners with steady torque, allowing operators to handle tasks that require judgment or skill. In larger plants, mobile equipment carries materials between stations to reduce manual transport.
Operational advantages
Robotic assistance reduces delays caused by repetitive tasks, supports continuous production flow, and helps teams avoid fatigue-related errors.
What to validate during setup?
Test movement paths, gripping force, and cycle timing in a controlled cell before connecting robots to the main line. This helps refine the workflow and ensures safe interaction with human operators.
Digital Twins and simulation models
A digital twin is a virtual model of a machine, cell, or line that uses operational data to show how equipment performs under different conditions. It allows teams to evaluate changes before applying them to the physical setup.
Where does this create impact?
A twin of a molding process evaluates how adjustments in temperature or cycle timing influence the final output. Engineers identify the best configuration without interrupting production.
Why do manufacturers rely on it?
Simulation reduces trial-and-error on the floor and speeds decision-making when operations need to adapt to demand shifts or material constraints.
Key considerations for adoption
Start with a single machine or process. Compare simulation output with recorded performance to confirm accuracy. Build complexity only after the initial model proves reliable.
AIoT for factory monitoring
AIoT links sensors, industrial controllers, gateways, and AI models so factories can process equipment data close to where it’s generated. This supports quicker responses to unexpected patterns and reduces unnecessary data transfer.
How does it function on the floor?
A gateway beside a gearbox evaluates vibration, heat, and movement signatures locally. It sends alerts only when readings drift from normal ranges, keeping network traffic low.
What do factories gain?
Teams receive faster warnings about abnormal behavior, which supports smoother operations and more informed maintenance planning.
How to deploy it effectively?
Decide which signals need to remain close to the machine and which can move to cloud dashboards for reporting and model updates. This balance keeps systems efficient without overwhelming network bandwidth.
Key AI adoption trends in manufacturing
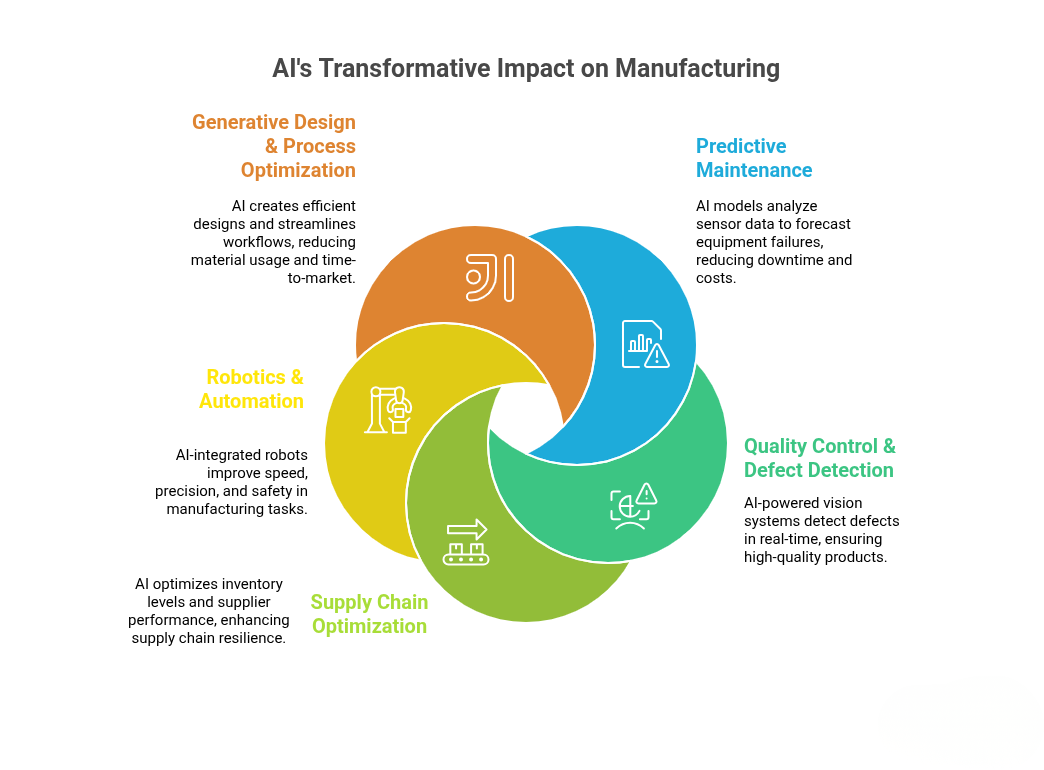
Manufacturers are using AI to fix long-standing inefficiencies in maintenance, quality control, supply chains, and production design. Adoption is growing quickly because the results are measurable, like lower downtime, fewer defects, faster output, and better cost control.
Predictive Maintenance
Equipment failures remain a major production risk. More than 75% of large manufacturers now use AI to predict mechanical issues before breakdowns occur. By analysing sensor data from machines, AI schedules maintenance at the right time, cutting downtime and saving millions in operational costs.
Quality Control and Defect Detection
Maintaining consistent quality at high speed is difficult through manual inspection. Around 60-70% of automotive and electronics factories deploy AI-based vision systems to detect defects early. These systems improve precision, reduce rework, and maintain production flow without compromising accuracy.
Supply Chain Optimisation
AI helps manufacturers respond faster to demand shifts and inventory challenges. 95% of manufacturers use AI for forecasting, inventory optimisation, and supplier management. These tools shorten lead times, reduce overstocking, and improve overall supply reliability.
Robotics and Automation
AI-driven robotics handle repetitive and precision tasks in assembly, packaging, and logistics. Manufacturers using these systems have reported up to 30% higher productivity and stronger output consistency. Automation supported by AI allows teams to focus on higher-value production tasks.
Generative Design and Process Optimisation
AI algorithms are reshaping how products are designed and built. Generative tools create lighter, more efficient components while reducing material waste. Early users report 20-25% less material usage and faster design iterations that shorten production timelines.
Leading industries using AI in manufacturing
AI adoption is accelerating across high-volume manufacturing sectors that depend on precision, consistency, and uninterrupted production. These industries are moving quickly because the gains are measurable and immediate across throughput, equipment reliability, and product quality.
Automotive Manufacturing
Automotive plants apply AI for welding inspection, assembly accuracy, defect detection, battery production optimization, and predictive maintenance on paint, stamping, and machining lines. Computer vision reduces alignment errors, while analytics help avoid costly downtime. Impact: Improved assembly consistency, fewer defects, and better production stability.
Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics production uses AI to monitor SMT lines, inspect solder joints, detect micro-defects, and trace quality issues across batches. AI models flag failures earlier than manual inspection, helping stabilize high-speed operations. Impact: Higher first-pass yield, fewer PCB defects, faster root-cause identification.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharma companies rely on AI for process control, batch consistency, quality checks, and equipment monitoring. AI models support audit trails and deviation detection across complex, regulated workflows. Impact: Stronger compliance, better quality consistency, reduced batch failures.
FMCG Manufacturing
FMCG manufacturers use AI to optimize packaging inspection, demand forecasting, production scheduling, and raw material planning. Vision systems verify labels and seals, while forecasting tools prevent shortages and excessive stock. Impact: Reduced waste, improved line speed, better alignment between demand and production.
Heavy Machinery & Industrial Equipment
Producers of heavy equipment use AI for machining optimization, welding accuracy, inventory planning, and predictive maintenance on motors, hydraulics, and high-load assemblies. Impact: Fewer equipment failures, better machining precision, and more reliable production planning.
How AI is reshaping different manufacturing sectors
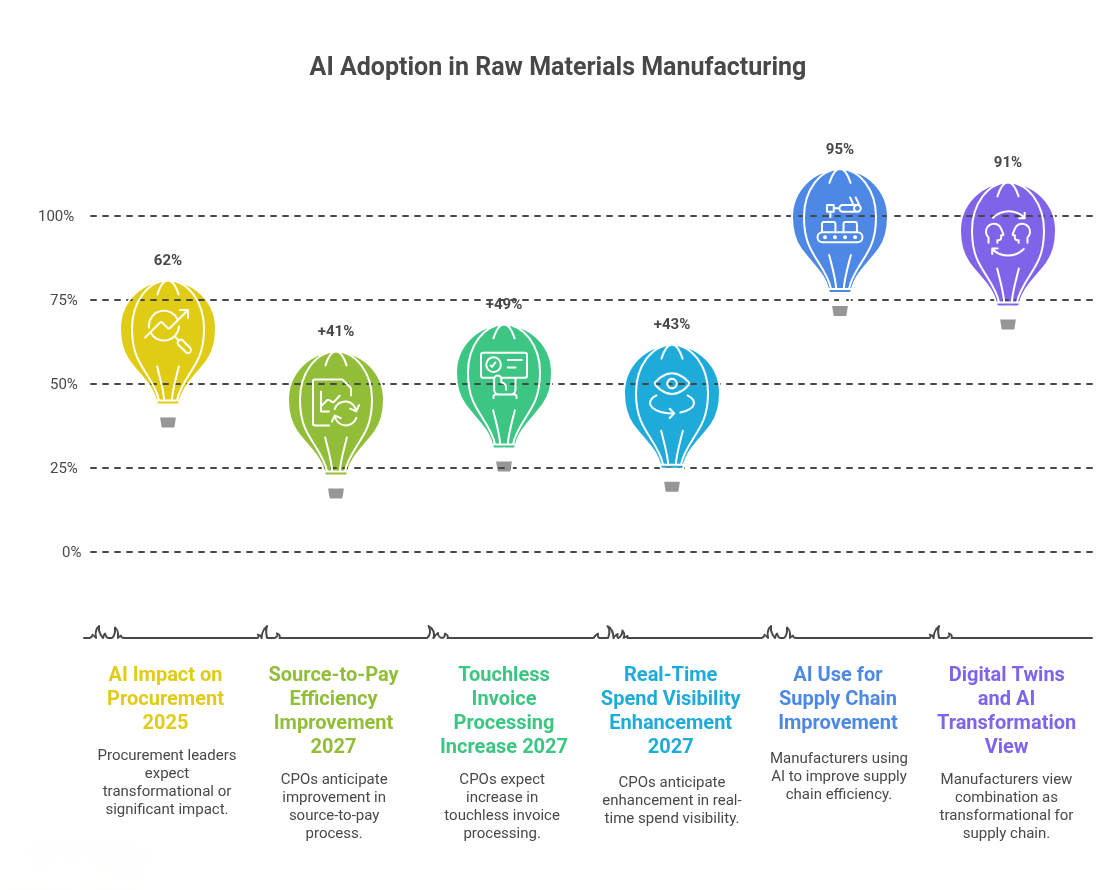
AI adoption in procurement
A 2025 study by Ardent Partners found that 62% of procurement leaders believe AI will have a "Transformational" or "Significant" impact on procurement in the next 2-3 years.
Procurement efficiency gains
Chief Procurement Officers (CPOs) anticipate a 41% improvement in source-to-pay process efficiency, a 49% increase in touchless invoice processing, and a 43% enhancement in real-time spend visibility by 2027.
AI in supply chain management
A report by Trax Technologies indicates that 95% of manufacturers are using AI to improve supply chain efficiency, with applications in inventory management, demand forecasting, and supplier collaboration.
Digital twins and AI
91% of manufacturers view the combination of digital twins and generative AI as transformational for asset performance and supply chain resilience.
AI in manufacturing operations
According to Thomasnet, AI is enhancing predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
AI in Rubber Manufacturing
AI is revolutionizing the rubber manufacturing industry by enhancing efficiency, quality, and innovation across various departments. Here's how AI is being integrated into key areas
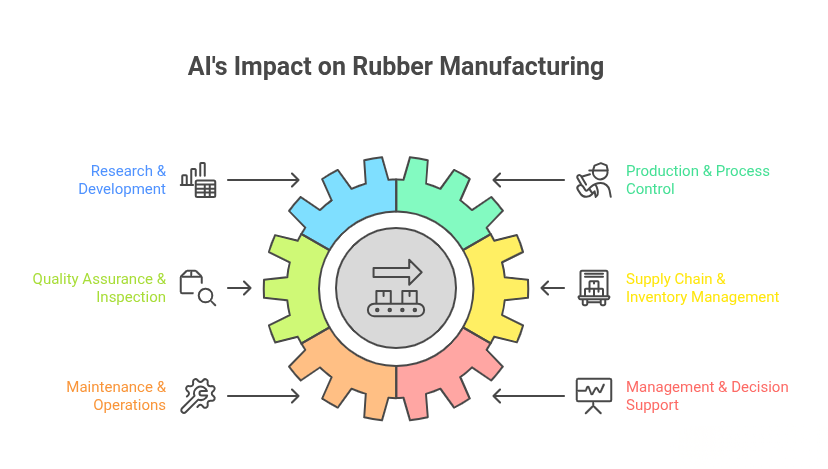
Research & Development (R&D)
- AI accelerates the development of new rubber formulations by analyzing vast datasets to identify optimal ingredient combinations.
- This data-driven approach reduces the trial-and-error process, leading to faster innovation cycles and the creation of materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
Production & Process Control
- AI systems monitor and adjust production parameters in real-time to maintain consistent product quality.
- By analyzing sensor data from machinery, AI can predict potential issues before they lead to defects, ensuring smoother operations and reducing downtime.
Quality Assurance & Inspection
- AI-powered vision systems detect surface flaws early, improving inspection accuracy and reducing rework.
- In precision industries like electronics, these tools have lowered defect rates by over 50%, proving how AI-driven quality control enhances consistency and reliability.
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
- AI optimizes supply chain operations by forecasting demand, managing inventory levels, and identifying the most efficient logistics routes.
- This leads to cost savings, reduced waste, and improved responsiveness to market changes.
Maintenance & Operations
- Predictive maintenance powered by AI analyzes equipment data to forecast failures before they occur.
- This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime, extends machinery lifespan, and reduces maintenance costs.
Management & Decision support
- AI-driven analytics provide management with actionable insights into production performance, quality metrics, and operational efficiency.
- These insights support informed decision-making, strategic planning, and continuous improvement initiatives.
AI in Plastics Manufacturing
Production & process engineering
- AI analyses machine data to stabilise production, cut idle time, and optimise energy use.
- Manufacturers using these systems report 25-30% higher productivity and 5-10% energy savings, helping plastics operations run efficiently with less waste.
Quality Control
- Computer vision systems powered by AI can detect surface flaws and structural inconsistencies that manual checks may overlook.
- Predictive algorithms also analyze historical defect patterns, enabling manufacturers to prevent recurring quality issues and maintain consistent product standards.
Maintenance & Operations
- AI-driven predictive maintenance uses sensor data to identify early signs of machine wear or failure.
- This allows teams to schedule repairs before breakdowns occur, reducing downtime, cutting maintenance costs, and extending the overall lifespan of equipment.
Research & Development
- In material innovation, AI supports the discovery and testing of new polymer blends.
- Simulation models predict how different formulations will perform, making it easier to create plastics that are durable, recyclable, and environmentally friendly.
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
- AI forecasting tools predict material demand and optimize stock levels to prevent overstocking or shortages.
- In addition, intelligent logistics planning improves supplier coordination and reduces transport delays, ensuring a more reliable supply chain.
Waste & Recycling
- AI-powered sorting systems can accurately identify various types of plastics in recycling streams.
- This improves material purity, enhances the quality of recycled plastics, and supports circular economy initiatives by reducing landfill waste.
Tailored AI strategies for manufacturing enterprises
AI adoption in manufacturing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Small, medium, and large manufacturers face different challenges, have different resources, and therefore benefit from AI in different ways.
The key is aligning AI solutions with the size and needs of the enterprise to achieve meaningful improvements in efficiency, quality, and competitiveness
Small manufacturers
Challenges small manufacturers are facing
- Limited budgets and staff for implementing complex AI systems
- Scarcity of historical data to train AI models
- Minimal in-house expertise in AI technologies
How integrating AI can work for small manufacturers
- Cloud-Based AI tools: Affordable, subscription-based AI platforms that require minimal setup.
- Lightweight predictive maintenance: Simple AI models can forecast equipment issues to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
- Collaborative learning models: Federated learning allows small businesses to benefit from AI trained on multiple datasets without sharing sensitive data.
Example: A small rubber gasket manufacturer implemented a cloud-based AI tool for predictive maintenance, resulting in a 20% reduction in unplanned downtime. - ResearchGate
Why It Works: Cloud-based AI tools are cost-effective and require minimal infrastructure, making them ideal for small manufacturers with limited resources. Predictive maintenance helps identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Medium Manufacturers
Challenges medium manufacturers are facing
- Integrating AI with existing production and management systems
- Handling and processing larger volumes of operational data
- Balancing AI investments with operational expenses
How integrating AI can work for medium manufacturers
- Edge AI computing: Processes data locally to reduce latency and improve efficiency.
- Robotic process automation (RPA): Automates repetitive tasks, freeing staff for higher-value work.
- AI-Powered quality control: Machine vision detects defects in real-time, improving product reliability.
Example: A mid-sized plastic molding company integrated an AI-powered quality control system, leading to a 15% decrease in product defects. - advantechplastics
Why It Works: AI-powered quality control systems use machine learning and computer vision to detect defects in real-time, improving product quality and reducing waste. These systems can be scaled to meet the growing needs of medium-sized manufacturers.
Large Manufacturers
Challenges large manufacturers are facing
- Disparate data sources across multiple departments create silos
- Scaling AI solutions across global operations can be complex
- Resistance from employees to adopting AI-driven processes
How integrating AI can work for large manufacturers
- Enterprise AI platforms: Centralize data from all departments to provide actionable insights.
- Advanced robotics & automation: Deploy collaborative robots and autonomous systems for consistent, high-volume production.
- AI-Driven supply chain optimization: Forecast demand, manage inventory, and streamline logistics using predictive analytics.
Example: A global rubber manufacturing leader adopted an AI-driven supply chain optimization system, resulting in a 25% improvement in inventory turnover and a 30% reduction in logistics costs. - Cornerstone
Why It Works: AI-driven supply chain optimization systems analyze vast amounts of data to forecast demand, manage inventory, and optimize logistics, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency. These systems are designed to handle the complexity of global operations.
Benefits of using AI in manufacturing
Higher operational efficiency
AI distributes workloads across machines, identifies slowdowns, and adjusts process parameters to maintain steady flow. By automating repetitive steps, teams spend less time firefighting and more time improving production.
Lower production and maintenance costs
Predictive models detect early signs of equipment deterioration, helping avoid expensive emergency repairs. Improved quality control reduces scrap and rework, and AI-assisted resource planning cuts unnecessary energy and material use.
More confident and informed decision-making
AI highlights patterns in quality trends, machine health, cycle timing, and material consumption. Leaders can test adjustments through digital simulations before making changes on the floor, reducing risk and improving accuracy.
Stronger safety across operations
AI-supported robots and guided workflows take over heavy, hazardous, or repetitive tasks. Systems can also detect unsafe behavior or equipment states, offering alerts before conditions escalate.
Improved sustainability performance
AI optimizes temperature, pressure, and material usage across lines, cutting waste and energy consumption. Forecasting tools help plants avoid overproduction and reduce landfill contributions.
Faster innovation and prototyping
Generative design tools and simulation models allow teams to evaluate multiple product or tool variations quickly. This reduces physical trial cycles and shortens the path from concept to production-ready design.
Challenges of using AI in manufacturing
Data quality and accessibility limitations
AI models rely heavily on complete and accurate datasets, but many factories work with inconsistent sensor data, limited historical logs, or unstructured quality records. These gaps reduce model reliability and slow deployment.
Integration barriers with legacy equipment
Older machines may lack sensors, connectivity, or compatible control systems. Retrofitting them requires additional hardware and planning, and in some cases, upgraded controllers or gateways are needed to extract meaningful signals.
Shortage of AI and analytics skills
Most production teams have deep domain expertise but limited experience with data interpretation or model validation. Without training, teams may misread alerts or underuse dashboards that are critical to finding operational gains.
Increased cybersecurity exposure
AI initiatives introduce more connected devices, cloud endpoints, and data flows. This expands the attack surface, requiring stronger network segmentation, device authentication, and continuous monitoring.
People and process resistance
Introducing AI often changes daily responsibilities and introduces new alert-driven workflows. If teams don’t understand why a system recommends an action, trust becomes a barrier and adoption slows.
High upfront investment and slow initial returns
AI requires sensors, data pipelines, compute resources, and technical expertise. Smaller manufacturers may struggle with budget allocation until early pilots demonstrate clear savings or efficiency improvements.
How to Successfully Implement AI in Manufacturing
Set measurable goals tied to real operational priorities
Begin with a clear problem that affects output, cost, or quality. Examples include chronic downtime on a critical asset, recurring defects on a specific line, or excessive scrap during changeovers. Defined goals keep teams aligned and make it easier to evaluate whether the project moves the needle.
Build a reliable data foundation before model development
Successful AI depends on strong data. Verify sensor coverage, evaluate data accuracy, standardize timestamps, and identify missing signals. Collect a baseline dataset long enough to show normal, stressed, and idle machine states. This preparation shortens model development cycles and improves accuracy from the beginning.
Run a focused pilot on one machine group or inspection point
Start small and in a controlled production environment. Deploy models, observe alerts, and compare results against your baseline. Use this phase to identify practical issues sensor noise, operator response time, or false positives and refine the model accordingly. A good pilot demonstrates value and builds internal confidence.
Involve operators, technicians, and production supervisors early
AI changes how teams inspect products, plan maintenance, and respond to machine behavior. Engage frontline users from the start, explain model logic, and collaborate on alert thresholds. When the people closest to the process understand how the system works, adoption becomes smoother and insights are applied consistently.
Measure outcomes with KPIs that reflect business impact
Track metrics such as downtime reduction, scrap decrease, cycle-time stability, energy use, maintenance cost savings, and first-pass yield improvements. Regular reviews help teams understand what’s working, where adjustments are needed, and whether the system is delivering results that justify expansion.
Expand gradually using a repeatable integration framework
Once a pilot shows reliable improvement, apply the same structure to similar assets or lines. Standardize integration methods, documentation, alert logic, and retraining cycles. Consistency across deployments reduces confusion and prevents misalignment between sites or departments.
Assign long-term ownership and define governance processes
AI is not a “set it and forget it” tool. Assign a dedicated owner for model monitoring, periodic tuning, and retraining triggers. Document workflows, escalation steps, and data-handling procedures. Strong governance ensures the model remains accurate as equipment ages, production changes, or new data becomes available.
Summing Up
AI is no longer a “nice-to-have” in manufacturing, it’s becoming the foundation for operational efficiency, product innovation, and supply chain resilience.
From predictive maintenance to quality control, process optimization, and supply chain analytics, AI is transforming every layer of manufacturing operations. Companies that embrace this shift will not only improve productivity but also gain a competitive edge in cost efficiency, product quality, and scalability.
To capture real value, manufacturers must go beyond experimentation. It is crucial to assess which workflows can benefit most from AI, measure potential ROI, and ensure infrastructure and workforce readiness.
By starting with strategic goals, piloting AI in high-impact areas, and scaling thoughtfully, manufacturers can turn AI into a core driver of growth, innovation, and operational excellence.
External Sources
This section drew insights and data from trusted resources:
