Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines

Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines
Text-to-Speech (TTS) is a technology that converts written text into spoken words. It works by analyzing text, determining pronunciation and tone, and then generating speech using synthetic or AI-based voices. TTS is widely used in screen readers, voice assistants, audiobooks, and language learning tools. Modern TTS engines use deep learning to produce natural, human-like speech. This makes it useful for both accessibility and interactive digital experiences.
 Engines Workflow.png)
Why Open-Source TTS?
Open-source TTS engines have revolutionized the way we interact with digital content. Unlike commercial tools, they offer:
With advancements in AI and machine learning, many open-source TTS tools now deliver natural and expressive speech. Whether you're a developer, researcher, or hobbyist, these tools are powerful, customizable, and freely accessible.
The 9 Best Open Source Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines
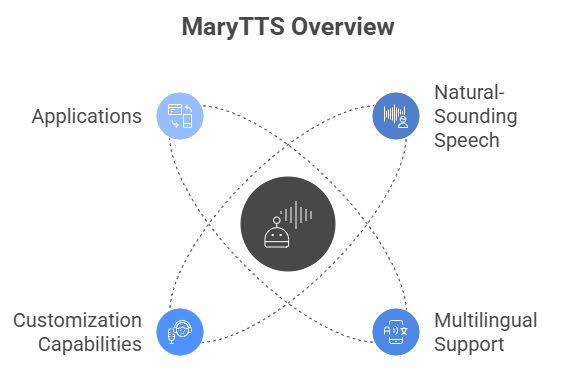
MaryTTS – Open Source Java-Based TTS Engine
MaryTTS is a powerful, open-source Text-to-Speech engine developed in Java. It's widely appreciated for its natural-sounding speech, multilingual support, and customization capabilities. Suitable for both developers and researchers, it’s used in various applications like screen readers, e-learning tools, and conversational interfaces.
Multilingual Support
- MaryTTS supports several languages including English, German, Russian, Turkish, Telugu, and more.
Flexible Input Formats
- It accepts plain text, tokenized text, and MARY XML for more control over how the text is processed and spoken.
Voice Options
- MaryTTS provides both unit selection and diphone synthesis voices, offering more natural-sounding speech in supported languages.
Easy Integration
- The engine can be integrated directly into Java applications using its API or run as a standalone server.
Voice Import Tool
- It comes with a tool that allows you to build your own custom voices using recorded audio data.
Open Source
- MaryTTS is free to use, modify, and distribute under the LGPL (Lesser General Public License).
MaryTTS is an excellent choice for projects involving voice output, including accessibility tools, educational applications, and AI-driven systems.
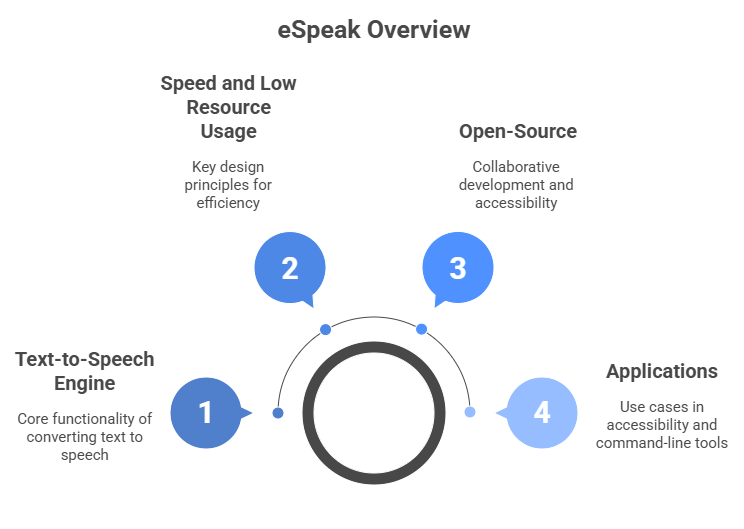
eSpeak
eSpeak is a lightweight, open-source text-to-speech engine written in C. It is designed for speed and low resource usage, making it ideal for embedded systems and devices with limited hardware capabilities. While its voice quality is more robotic compared to modern neural TTS engines, eSpeak is still widely used for accessibility, command-line tools, and language research.
Multilingual Support
- eSpeak supports more than 40 languages, including English, Spanish, French, Hindi, and Chinese.
Compact and Fast
- It has a small footprint and runs efficiently even on low-power devices like Raspberry Pi or microcontrollers.
Cross-Platform
- eSpeak works on Windows, Linux, macOS, and even Android (via wrappers or native ports).
Customizable Voices
- Users can adjust pitch, speed, and voice characteristics using configuration files or command-line options.
Integration and Scripting
- It can be easily used in scripts, embedded in applications, or called from the terminal with simple commands.
Open Source
- eSpeak is free to use, modify, and distribute under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
eSpeak is a solid choice for projects where size, speed, and multilingual support matter more than highly realistic voice output.
Festival – Versatile and Modular TTS Engine
Festival is a general-purpose, open-source Text-to-Speech system developed by the University of Edinburgh. It is written in C++ and Scheme and provides a full framework for building and experimenting with speech synthesis systems. Festival is widely used in research, academic projects, and speech-enabled applications.
Multilingual Support
- Festival supports multiple languages, with English and Spanish being the most developed. Additional languages can be added with language-specific modules.
Full TTS Framework
- It includes text analysis, linguistic processing, and waveform generation — offering both command-line tools and a programmable API.
Modular and Extensible
- Festival’s architecture allows customization at every level, including pronunciation rules, prosody, and voice models.
Voice Variety
- It supports different synthesis techniques, such as diphone-based and limited unit selection voices. Custom voices can also be built and added.
Integration Options
- Festival can be used standalone via command-line or integrated into applications through its APIs or server mode.
Open Source
- Festival is distributed under a permissive open-source license, making it free to use, study, and modify.
Festival is best suited for educational use, research, and custom voice synthesis tasks where full control and flexibility are important.
Flite – Fast, Lightweight TTS Engine
Flite (Festival Lite) is a small, fast, open-source Text-to-Speech engine developed by Carnegie Mellon University. It is a lighter version of the Festival Speech Synthesis System, designed specifically for resource-constrained environments like embedded systems and mobile devices.
Compact and Efficient
- Flite is highly optimized for speed and low memory usage, making it ideal for devices with limited hardware such as IoT gadgets, wearables, or microcontrollers.
Simple Architecture
- Unlike Festival, Flite is written entirely in C and has no external dependencies, making it easy to compile and deploy on various platforms.
Built-in Voices
- Flite includes a few prebuilt voices and supports basic voice customization, though it doesn’t offer the same variety or naturalness as larger TTS engines.
Cross-Platform Support
- It runs on Linux, Windows, macOS, Android, and various embedded systems.
Command-Line and API Access
- Flite can be used directly via command-line or integrated into applications through its simple C-based API.
Open Source
- Flite is free to use and modify under a permissive BSD-style license.
Flite is an excellent choice when you need a fast, lightweight TTS engine for real-time or embedded applications with minimal resources.

Mimic – Lightweight TTS Engine by Mycroft AI
Mimic is an open-source, fast, and lightweight Text-to-Speech engine developed by Mycroft AI. It is based on Flite and optimized for speed and offline use, making it ideal for voice assistants, embedded devices, and privacy-focused applications.
Offline and Privacy-Friendly
Natural Sounding Speech
- Compared to Flite, Mimic provides improved voice quality and supports custom voice building using speech datasets.
Optimized for Mycroft
- Mimic is designed to work seamlessly with the Mycroft open-source voice assistant but can also be used independently in any application.
Custom Voice Support
- Users can train their own voices with Mimic (especially with Mimic 2), allowing for more natural and personalized speech.
Fast and Lightweight
- It is built to run quickly on devices with limited resources, such as Raspberry Pi and other ARM-based systems.
Open Source
- Mimic is released under a permissive open-source license, allowing free use, modification, and distribution.
Mimic is a great choice for developers needing a fast, offline, and customizable TTS engine for smart devices, assistants, or privacy-first projects.
Pico TTS – Lightweight TTS Engine for Embedded Devices
Pico TTS is a simple, fast, and compact Text-to-Speech engine developed by SVOX and later made open source by Google. It is best known for its use in Android devices and is ideal for embedded systems and mobile applications due to its small size and efficiency.
Small and Efficient
- Pico TTS is highly optimized for speed and low memory usage, making it perfect for resource-constrained environments like smartphones, wearables, and embedded systems.
Basic Voice Quality
- While the voice output is not as natural as modern neural TTS engines, it is clear, intelligible, and sufficient for simple applications like navigation and notifications.
Multilingual Support
- It supports several languages, including English, German, French, Italian, and Spanish.
Offline Use
- Pico TTS works completely offline, with no need for network access, ensuring privacy and low-latency performance.
Easy Integration
- It is commonly used in Android systems and can be integrated into custom apps and firmware with minimal setup.
Open Source
- Pico TTS is open source and freely available for use, modification, and redistribution.
Pico TTS is ideal for developers needing a tiny, reliable TTS engine for offline use on mobile or embedded platforms.
Mozilla TTS – Deep Learning-Based Text-to-Speech Engine
Mozilla TTS is an open-source, neural network-based Text-to-Speech engine developed by Mozilla. It produces high-quality, natural-sounding speech using deep learning models and is built with PyTorch. Mozilla TTS is designed for researchers, developers, and voice AI projects that require expressive and realistic synthetic voices.
High-Quality Neural Voices
- Mozilla TTS uses advanced models like Tacotron 2, Glow-TTS, and HiFi-GAN to generate speech that sounds very close to human speech.
Custom Voice Training
- You can train your own voice models using your own dataset, making it suitable for branded voice assistants, accessibility tools, and content creation.
Multilingual Support
- Supports various languages and is easy to extend by training on new language datasets.
Flexible and Configurable
- Offers extensive configuration options for voice tuning, training parameters, and output quality.
Real-Time Inference
- With optimized vocoders like HiFi-GAN, Mozilla TTS can generate speech in real time on modern hardware.
Open Source
- Released under an open-source license, it is free to use, modify, and extend for both academic and commercial projects.
Mozilla TTS is ideal for developers and researchers seeking high-fidelity, customizable TTS in modern AI-driven applications.
ESPnet-TTS – End-to-End Neural Speech Synthesis Toolkit
ESPnet-TTS is part of the larger ESPnet (End-to-End Speech Processing Toolkit) project and focuses on state-of-the-art neural Text-to-Speech synthesis. Built using PyTorch, it supports cutting-edge models and is widely used in research and advanced AI projects.
Advanced Neural Models
- ESPnet-TTS supports top-performing models like Tacotron 2, FastSpeech, Transformer TTS, and VITS, allowing for highly natural and expressive speech output.
End-to-End Training
- The entire pipeline—text processing, acoustic modeling, and vocoding—can be trained in a single framework, making experimentation easier and more efficient.
Multilingual and Multispeaker Support
- Supports training and inference in multiple languages and voices, including speaker adaptation and voice cloning.
Research-Grade Quality
- Designed for flexibility, ESPnet-TTS is ideal for academic and industrial research with reproducible experiments and pre-trained models.
Real-Time and Offline Inference
- Supports both fast offline synthesis and near real-time performance using optimized vocoders like Parallel WaveGAN and HiFi-GAN.
Open Source
- Freely available under a permissive license and backed by an active research community.
ESPnet-TTS is best suited for researchers and developers who need high-performance, customizable TTS solutions powered by the latest in deep learning.
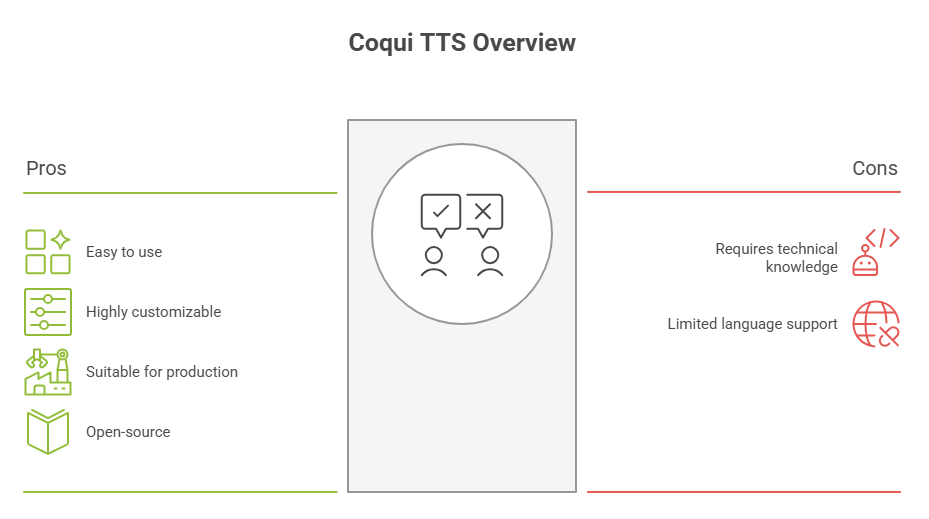
Coqui TTS – Powerful Open-Source Neural Text-to-Speech Toolkit
Coqui TTS is a modern, open-source deep learning-based Text-to-Speech engine developed by the creators of Mozilla TTS. It is designed to be easy to use, highly customizable, and suitable for production, research, and personal voice projects.
High-Quality Speech
- Coqui TTS uses state-of-the-art models like Tacotron 2, FastSpeech2, Glow-TTS, and VITS, producing highly realistic and expressive speech output.
Easy to Use
- Comes with pre-trained models and simple CLI tools for synthesis, training, and fine-tuning, making it accessible to both beginners and advanced users.
Custom Voice Training
- Supports multilingual and multispeaker voice cloning. You can train custom voices using your own dataset with minimal setup.
Real-Time Inference
- Compatible with fast neural vocoders like HiFi-GAN, enabling real-time speech generation on modern hardware.
Modular and Scalable
- Designed for flexibility, it supports plug-and-play model components and is production-ready with REST API options and cloud deployment support.
Open Source
- Released under a permissive open-source license, Coqui TTS is free to use, extend, and deploy commercially.
Coqui TTS is ideal for developers, startups, and researchers building high-quality, customizable, and deployable TTS solutions.