Vision–Language Models (VLMs): The Future of Multimodal AI in 2025

Introduction

Artificial Intelligence has reached an inflection point in 2025. For years, models like GPT handled text only tasks, while systems like ResNet or YOLO specialized in image recognition. But real world information is rarely so one dimensional. When you read a newspaper, you’re processing both text and images. When you scroll through social media, you encounter memes, captions, and videos all woven together.
This is where Vision Language Models (VLMs) come in. They represent the next generation of AI: models that can not only see and read but also reason across modalities, providing richer, more context aware insights.
What Are Vision Language Models (VLMs)?
At their core, Vision Language Models (VLMs) are AI systems that combine computer vision (understanding images and videos) with natural language processing (NLP) (understanding and generating text).
)
Instead of treating vision and language as two separate silos, Vision Language Models (VLMs) fuse both domains into a single, unified system. This fusion allows them to perform a wide range of tasks that traditionally required separate models or human intervention. Some of the key tasks include:
- Generating captions for an image: VLMs can describe the contents of an image in natural language, making them useful for accessibility, digital media, and e commerce applications.
- Explaining the content of a chart: They don’t just see the visual patterns, but also interpret and communicate insights, such as trends, comparisons, or anomalies.
- Answering questions about a video: Beyond static images, VLMs can analyze frames in a video, track objects, and provide context aware answers to questions like “What is the person doing?” or “How many cars are passing by?”.
- Summarizing documents that mix text and graphics: They can combine information from tables, diagrams, and written passages into a concise summary, enabling better understanding of complex reports or presentations.
To illustrate, imagine showing a VLM a photo of a street sign written in French. The model can:
- Recognize the sign visually (computer vision),
- Translate the French text into English (language processing), and
- Provide driving instructions based on the meaning of the sign (reasoning).
All of this happens in one seamless workflow, without switching between multiple tools or systems. This integration of vision and language not only makes AI more powerful but also more practical, unlocking new possibilities across industries like healthcare, education, customer support, content creation, and autonomous vehicles.
How VLMs Combine Image Understanding with NLP
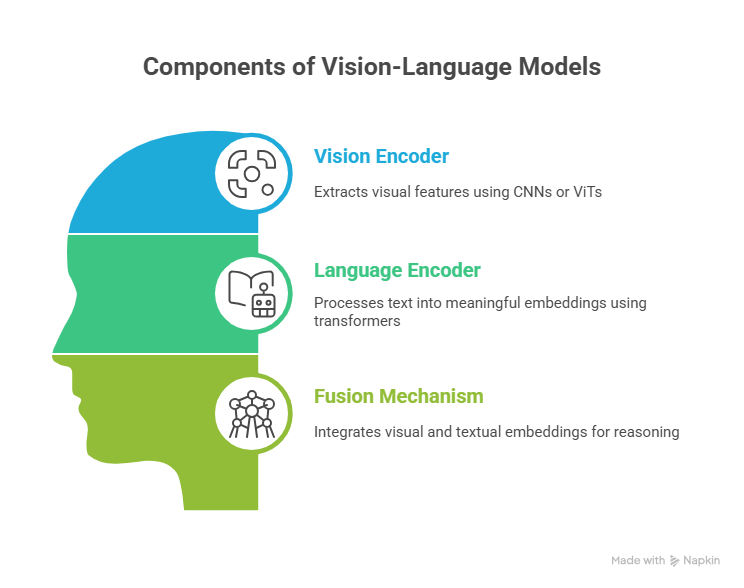
VLMs typically rely on three main components:
1. Vision Encoder
- Uses architectures like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or Vision Transformers (ViTs) to extract visual features (e.g., shapes, colors, objects).
2. Language Encoder
- Based on transformer architectures (e.g., BERT, GPT). It processes text and converts it into embeddings that capture meaning.
3. Fusion Mechanism
- Aligns and integrates visual and textual embeddings so the model can “reason” across them. Some use dual encoders (separate vision + language models with cross attention), while others employ fusion encoders (a single transformer processes both modalities together).
This fusion allows a VLM to answer questions like: “What’s happening in this photo?” or “Summarize this scientific paper with its graphs included.”
How VLMs Differ from Single Modality Models
Let’s contrast them with traditional models:
1. Text only Models (e.g., GPT 3, GPT 4):
- These models excel at generating and understanding natural language.
- They can write essays, debug code, draft emails, or even mimic creative writing styles with incredible fluency.
- However, they are blind to anything outside of text. Show them an image, chart, or video, and they won’t know what to do with it because their training data only involves words and symbols.
2. Vision only Models (e.g., ResNet, EfficientNet, YOLO):
- On the other end of the spectrum, vision models specialize in analyzing visual data.
- They can identify objects in images (like “this is a cat” vs. “this is a dog”), detect faces, or classify medical scans. But they cannot explain their reasoning or communicate insights in natural language.
- For example, a vision model might detect a “dog,” but it can’t say “this is a Labrador playing fetch in the park.”
3. Vision Language Models (e.g., GPT 5, Gemini, Claude 4):
VLMs combine the strengths of both worlds. They don’t just see and don’t just read they integrate both capabilities. Given a photo of a cat, a VLM can:
- Identify the animal and even its breed.
- Describe the scene in detail (e.g., “The cat is sitting on a wooden table beside a laptop.”).
- Connect it to broader context (e.g., “This breed is common in Japan, where it is often kept as a house pet.”).
- Answer follow-up questions (e.g., “Is this cat likely to shed a lot of fur?”).
This integration is transformative. Instead of siloed systems where one model analyzes an image and another model separately processes text VLMs create a seamless bridge. They can reason across modalities, making them more natural to interact with and more powerful in solving real-world problems.
In short:
- Text only → masters of words, but blind to visuals.
- Vision only → masters of perception, but mute in explanation.
- Vision Language Models → break the silos, enabling AI to see, understand, and communicate across both worlds.
What Makes a VLM Stand Out?
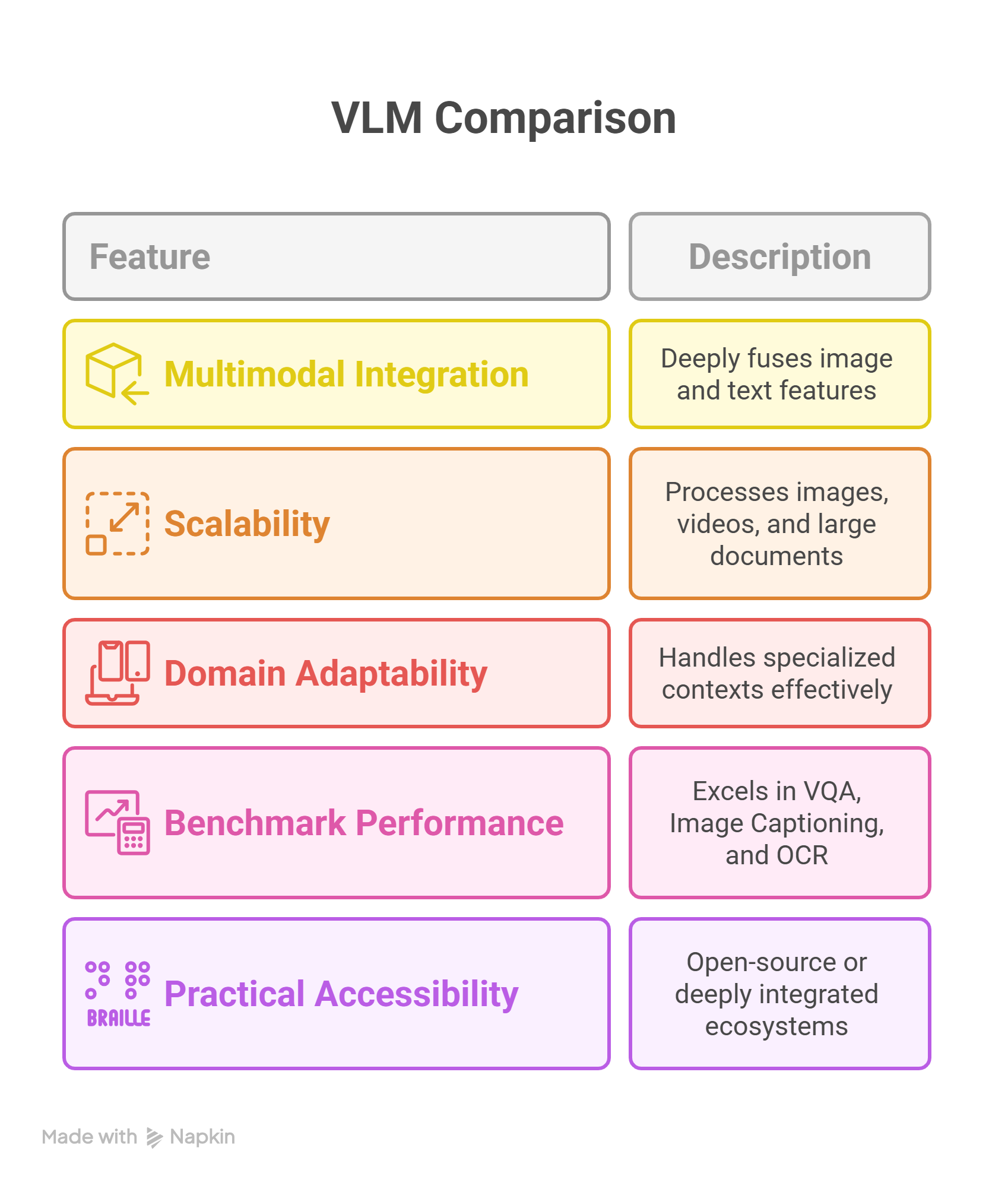
Not all VLMs are equal. The most successful models in 2025 share these traits:
- True Multimodal Integration : They don’t just “bolt on” image features to a text model, but deeply fuse both.
- Scalability : Able to process from small images to long videos and large documents with charts.
- Domain Adaptability : Can handle specialized contexts like medical scans, financial reports, or scientific data.
- Performance on Benchmarks : Excelling in tasks like Visual Question Answering (VQA), Image Captioning, and OCR.
- Practical Accessibility : Whether open source for research (like Llama 3.1) or deeply integrated into ecosystems (like Gemini in Google Docs).
Top 10 Vision Language Models in 2025
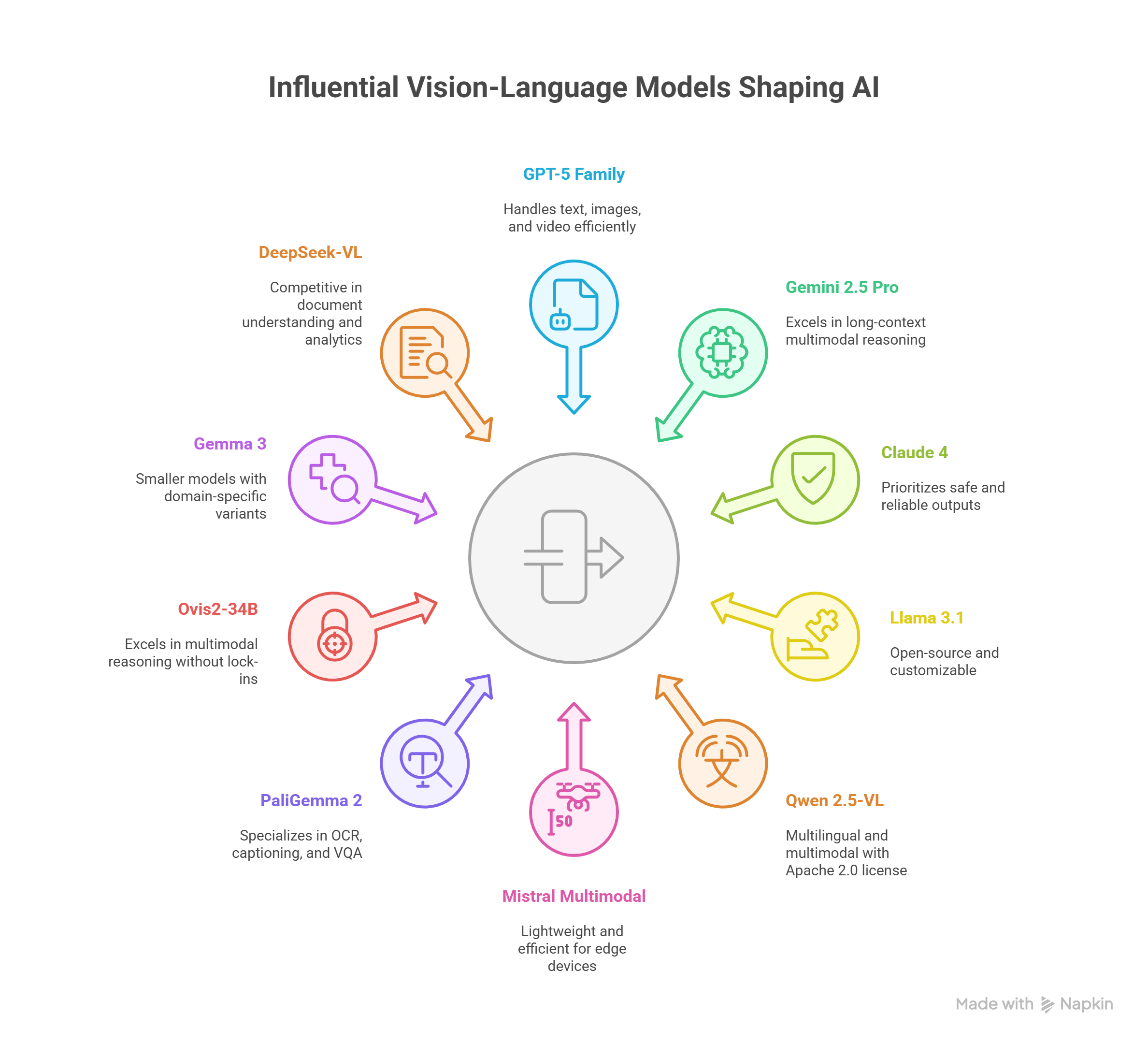
The Most Influential VLMs Shaping AI in 2025
The past year has seen a surge in powerful Vision Language Models, each bringing unique strengths to the AI ecosystem. Here are the models that are making the biggest waves in 2025:
GPT 5 Family (OpenAI)
- The successor to GPT 4, GPT 5 is a true multimodal powerhouse.
- It can seamlessly handle text, images, and even video with improved efficiency and reasoning.
- Enterprises are adopting it for workflows like automating reports, analyzing product photos, or assisting with creative design.
- Its balance of creativity and accuracy makes it a go to for industries like media, marketing, and research.
Gemini 2.5 Pro (Google DeepMind)
Google’s flagship VLM is known for long context multimodal reasoning meaning it can analyze hours of video, hundreds of pages of documents, or a combination of charts, diagrams, and text without losing track. Its deep integration with Google Workspace (Docs, Slides, Gmail) makes it a natural choice for productivity and knowledge work.
Claude 4 (Anthropic)
- Anthropic has carved out a niche by focusing on safety and reliability.
- Claude 4 is less about flashy demos and more about delivering trustworthy outputs.
- It shines in regulated industries like law, finance, and healthcare, where a hallucinated answer isn’t just inconvenient
- it could be catastrophic. Businesses that need a careful, responsible AI assistant lean toward Claude.
Llama 3.1 (Meta)
- Meta continues to push open source forward with Llama 3.1, giving startups, researchers, and smaller companies access to cutting edge VLM tech without licensing headaches.
- It’s customizable, community driven, and free to fine tune, making it especially popular in academia, AI startups, and emerging markets where proprietary models can be too expensive.
Qwen 2.5 VL (Alibaba Cloud)
- China’s Alibaba has been gaining attention with Qwen, a multilingual multimodal model released under the Apache 2.0 license.
- Unlike many closed models, Qwen is designed for global adoption, supporting multiple languages and making AI more inclusive for non English speakers.
- It’s becoming a favorite for companies targeting international audiences.
Mistral Multimodal
- Known for efficiency and portability, Mistral is carving a space for AI on edge devices and mobile platforms.
- Instead of relying on massive cloud infrastructure, Mistral’s lightweight models allow real-time image and text understanding in smaller devices think smart glasses, AR headsets, or even in car assistants.
PaliGemma 2 (Google Research)
- Specialized models still matter, and PaliGemma 2 shows why.
- It’s fine tuned for optical character recognition (OCR), image captioning, and visual question answering (VQA).
- That makes it incredibly useful for accessibility tools (screen readers, document scanners for the visually impaired) and education (interactive textbooks, visual learning apps).
Ovis2 34B (Open source)
- This 34 billion parameter model proves that open source VLMs can compete with big tech.
- Ovis2 34B excels in multimodal reasoning and is free of proprietary lock ins, making it attractive for organizations that want full control and transparency over their AI stack.
Gemma 3 (Google DeepMind)
- Gemma is part of Google’s push for smaller, domain specific VLMs.
- With sizes ranging from 1B to 27B parameters, Gemma models can be tailored to niche areas.
- A prime example is MedGemma, which focuses on healthcare applications like reading scans, assisting with diagnostics, and simplifying medical documentation.
DeepSeek VL (China)
- One of the fastest growing challengers from Asia, DeepSeek VL is tuned for document understanding and enterprise analytics.
- It’s efficient and competitive with Western models, showing how quickly the global VLM race is expanding beyond the US and Europe.
- Companies are already using it for business intelligence and enterprise search.
VLM Comparison Table
Challenges of Vision Language Models
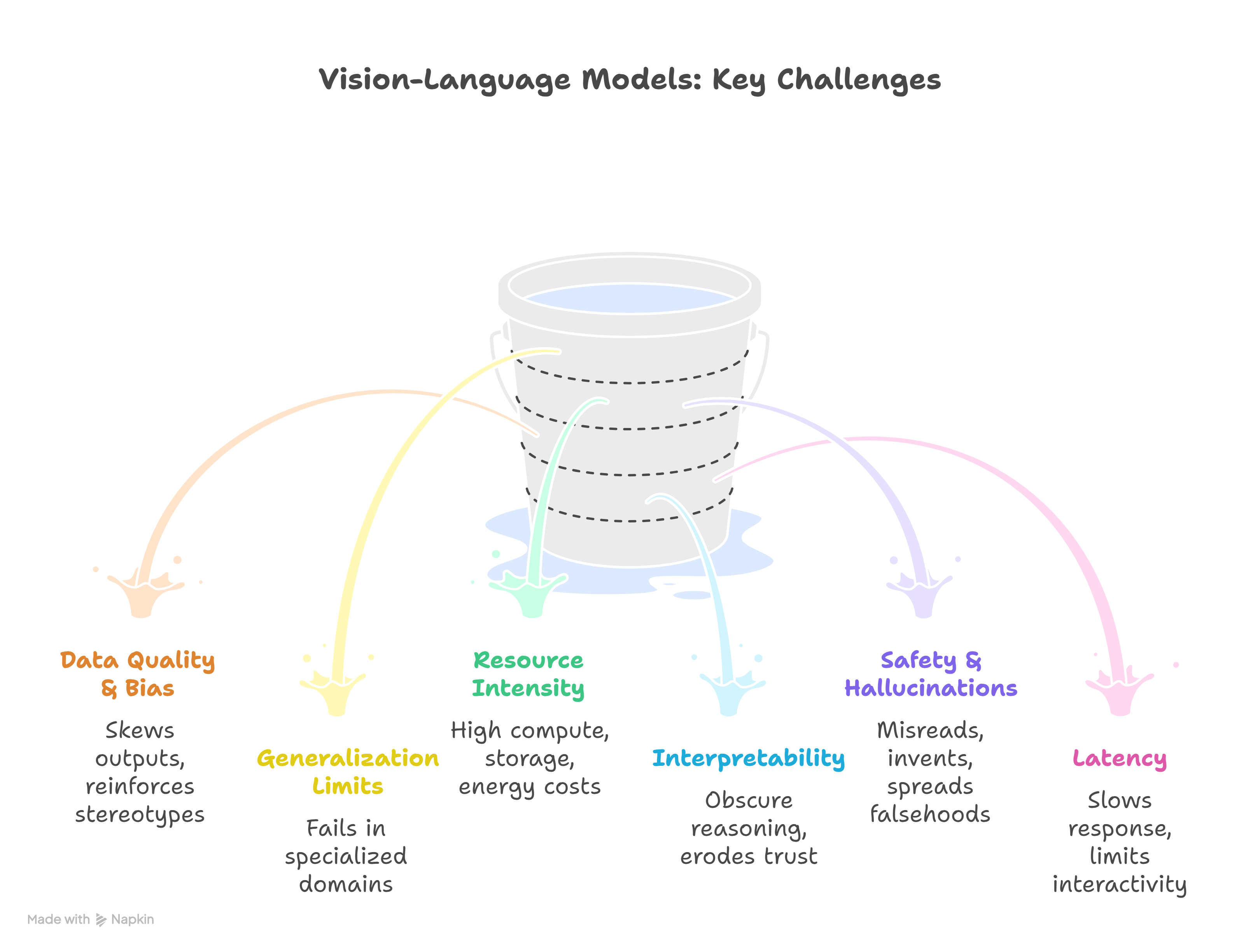
Despite rapid progress, VLMs face several hurdles:
- Data Quality & Bias : Training requires massive paired image text datasets. If biased, outputs can reflect stereotypes or misinformation.
- Generalization Limits : A model trained on news images may fail in specialized domains like medical imaging.
- Resource Intensity : Training multimodal giants is expensive in compute, storage, and energy.
- Interpretability : It’s difficult to understand how VLMs connect vision and language internally, raising trust issues.
- Safety & Hallucinations : Like text LLMs, VLMs can hallucinate (e.g., misreading charts or inventing nonexistent objects).
- Latency : Processing both images and text increases response time compared to unimodal models.
Conclusion
Vision Language Models are transforming AI from single sense specialists into multimodal generalists that see, read, and explain.
- Proprietary leaders like GPT 5, Gemini, and Claude are redefining enterprise AI.
- Open-source challengers like Llama, Qwen, and Ovis2 are democratizing access.
- Specialized variants like PaliGemma and MedGemma are revolutionizing healthcare, accessibility, and education.
As we move deeper into 2025, the key challenges will revolve around bias, transparency, efficiency, and responsible deployment. But one thing is clear: the future of AI is multimodal and VLMs are at the center of that future.
