Best Practices for Cloud Disaster Recovery

In today’s world, data and applications are key to every business. That’s why having a solid disaster recovery (DR) plan is essential to keep things running smoothly during unexpected events. Cloud solutions offer great tools for disaster recovery, but businesses must know the best practices, how Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) works, and how new technologies like AI, Machine Learning, and Blockchain can help.
1. Benefits of Cloud Disaster Recovery
Cloud-based disaster recovery offers numerous advantages, including flexibility, scalability, and reduced costs. Here are some of the key benefits:
Cost-Effective: Traditional disaster recovery solutions can be expensive, requiring businesses to invest in additional hardware and infrastructure. Cloud disaster recovery, on the other hand, allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
Scalability: Cloud environments allow businesses to scale their recovery resources up or down based on demand. If a disaster occurs, resources can be provisioned quickly to ensure operations are restored swiftly.
Faster Recovery Times: Cloud solutions typically offer faster recovery times compared to traditional methods, reducing the impact of downtime on operations.
2. Key Components of a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
A comprehensive cloud disaster recovery plan should include several essential components:
Data Backup and Replication: Backing up data in the cloud and replicating it across different regions or availability zones is critical. This ensures that if one region experiences a failure, data can still be accessed from another.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO): RTO defines how quickly an organization needs to recover after a disaster, while RPO specifies the maximum acceptable amount of data loss. Setting these objectives helps organizations determine their cloud infrastructure requirements.
Automated Failover: Automated failover ensures that if your primary system fails, operations are automatically switched to a backup system without manual intervention, minimizing downtime.
3. Multi-Cloud vs Single-Cloud Disaster Recovery Strategies
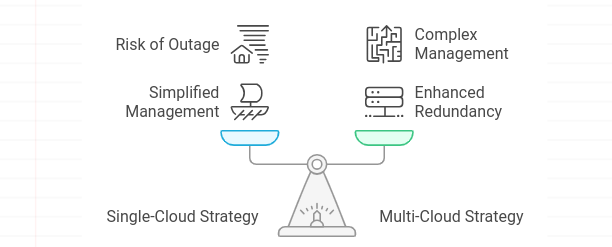
Organizations can choose between a multi-cloud or single-cloud disaster recovery strategy based on their business needs:
Single-Cloud: Using a single cloud provider for disaster recovery can simplify management but may pose risks if that provider experiences an outage.
Multi-Cloud: A multi-cloud strategy leverages services from multiple cloud providers, enhancing redundancy and reducing the risk of service disruption. It offers higher resilience but requires more complex management.
Example: An e-commerce platform using AWS and Azure for disaster recovery can switch to the other cloud provider if one experiences an outage, ensuring business continuity.
4. Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) is an increasingly popular model where businesses outsource their disaster recovery needs to a third-party provider. DRaaS offers several advantages:
Simplified Management: DRaaS providers handle the complexities of data replication, backup, and recovery, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
Cost Savings: Instead of maintaining an in-house DR infrastructure, organizations can use DRaaS to reduce costs associated with hardware, storage, and personnel.
Scalability: DRaaS can scale based on the size and needs of the business, making it an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes.
Example: A small business can rely on DRaaS to protect critical data and applications without the need for a dedicated IT team to manage the recovery process.
5. The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Disaster Recovery
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can enhance disaster recovery by predicting potential failures and automating recovery processes:
Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze system performance and identify patterns that may indicate potential failures. For example, it can detect signs of hardware degradation before it fails, allowing businesses to proactively address the issue.
Automated Failover: AI-driven automation can trigger failover processes faster than manual intervention, ensuring that recovery times are minimized.
Example: AI-driven disaster recovery systems can predict a hard drive failure and automatically switch to a backup system before the failure occurs, reducing downtime.
6. Blockchain for Cloud Disaster Recovery
Blockchain technology can be used to enhance the security and integrity of disaster recovery processes. By maintaining an immutable ledger of backup and recovery operations, businesses can ensure that their recovery data has not been tampered with.
Data Integrity: Blockchain ensures that backup data is not altered, even during the recovery process, providing a verifiable record of recovery operations.
Enhanced Security: Blockchain's decentralized nature can make it more difficult for malicious actors to compromise backup data.
Example: A healthcare provider could use blockchain to track patient data backups and ensure that the data remains secure and unaltered during recovery.
7. Zero-Downtime Disaster Recovery
Zero-downtime disaster recovery aims to ensure that critical systems remain available, even during a disaster. This is particularly important for businesses that operate 24/7, such as financial institutions or e-commerce platforms.
Continuous Operations: Zero-downtime solutions use load balancing and real-time data replication to ensure that if one system fails, another system takes over without interruption.
Minimal Disruption: With zero-downtime recovery, the user experience remains unaffected, even during disasters.
Example: A financial trading platform can use a zero-downtime disaster recovery system to ensure that trading continues without disruption, even if a primary server goes down.
8. Regular Testing and Validation of DR Plans
A disaster recovery plan is only as good as its execution. Regular testing and validation help businesses ensure their DR processes work as expected in real-world scenarios. Organizations should conduct simulated disasters and recovery drills to uncover potential weaknesses and improve their recovery strategies. This ongoing testing ensures businesses are always ready for the unexpected.
Example: A global e-commerce company can test their cloud disaster recovery plan quarterly, identifying any process bottlenecks or gaps in recovery time objectives (RTOs).
9. Customized Recovery Playbooks
A tailored recovery playbook should be created for each business. This playbook outlines the exact steps to be followed during disaster recovery, designating roles and responsibilities, identifying key systems and data, and ensuring the process is efficient. A customized playbook addresses business-specific needs and ensures that no vital steps are missed during recovery.
Example: A healthcare provider may customize their recovery playbook to prioritize patient data restoration and minimize disruption to critical healthcare services during a disaster.
10. Ransomware Protection as a Service (RPaaS)
Ransomware attacks are becoming a significant threat to cloud environments. Ransomware Protection as a Service (RPaaS) provides businesses with advanced security measures, including real-time monitoring and detection to protect against ransomware threats. By implementing RPaaS, organizations can prevent potential disruptions to their recovery systems, ensuring that data remains secure during a disaster recovery event
Example: A financial services firm can implement RPaaS to detect and stop ransomware attacks before they affect their cloud-based disaster recovery systems, ensuring business continuity.
11. Regulatory Compliance in Cloud Disaster Recovery
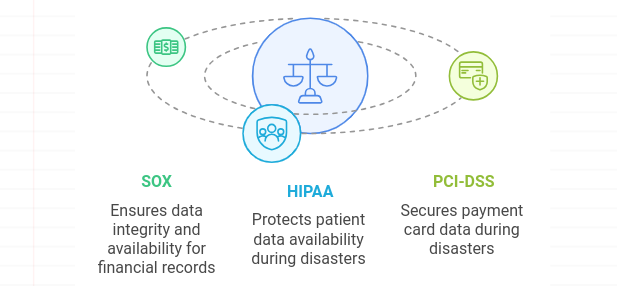
Organizations must ensure that their cloud disaster recovery plans comply with industry regulations such as SOX, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. These regulations require businesses to protect sensitive data and ensure that it is available even during disasters.
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): Requires businesses to maintain data integrity and availability, particularly for financial records.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Requires healthcare organizations to protect patient data and ensure its availability during disasters.
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Requires businesses that process payment card data to ensure data security and availability during disasters.
Example:A healthcare organization using cloud disaster recovery must ensure that patient data is encrypted, backed up, and recoverable in compliance with HIPAA.
12. Consequences of Not Having a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
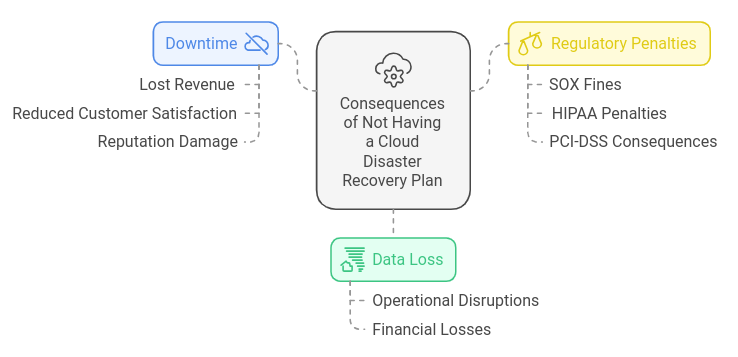
The consequences of not having a cloud disaster recovery plan can be severe:
Data Loss: Without proper data backup and recovery systems, businesses risk losing critical data during a disaster, leading to operational disruptions and financial losses.
Downtime: Extended downtime can result in lost revenue, reduced customer satisfaction, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with regulations like SOX, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
Example:A financial services company experiences a cyberattack that compromises its cloud infrastructure. Without a disaster recovery plan in place, they lose access to critical customer transaction data. The downtime lasts three days, causing significant financial losses, frustrated clients, and a $250,000 penalty for non-compliance with PCI-DSS regulations. This incident severely damages the company’s reputation and trust among its customers.
FAQs
Final Thoughts
Cloud-based disaster recovery is essential for businesses that rely on digital data and applications. By adopting best practices such as multi-cloud strategies, automated failover, AI-driven recovery, and blockchain for data integrity, businesses can minimize downtime and ensure business continuity. Additionally, compliance with industry regulations ensures that businesses meet legal requirements while protecting sensitive data. By investing in cloud disaster recovery, businesses can safeguard their operations against unforeseen disruptions and ensure long-term resilience.
