Understanding FinOps: Full Guide
Introduction
In today’s digital-first world, cloud computing is a backbone for businesses. With its scalability, flexibility, and on-demand resources, the cloud has become a critical component of modern IT strategies. However, managing cloud costs effectively is challenging. This is where FinOps implementation comes into play.
In this guide, we will explore the purpose, benefits, and key components of FinOps, with a focus on how it enables organizations to manage cloud finances efficiently.
What is FinOps, and Why Should You Adopt It?
FinOps, short for “Cloud Financial Operations,” is a cultural and operational practice that helps businesses manage cloud costs efficiently. The goal is to align cloud spending with business goals while enabling teams to own their cloud usage and costs.
Benefits of Adopting FinOps:
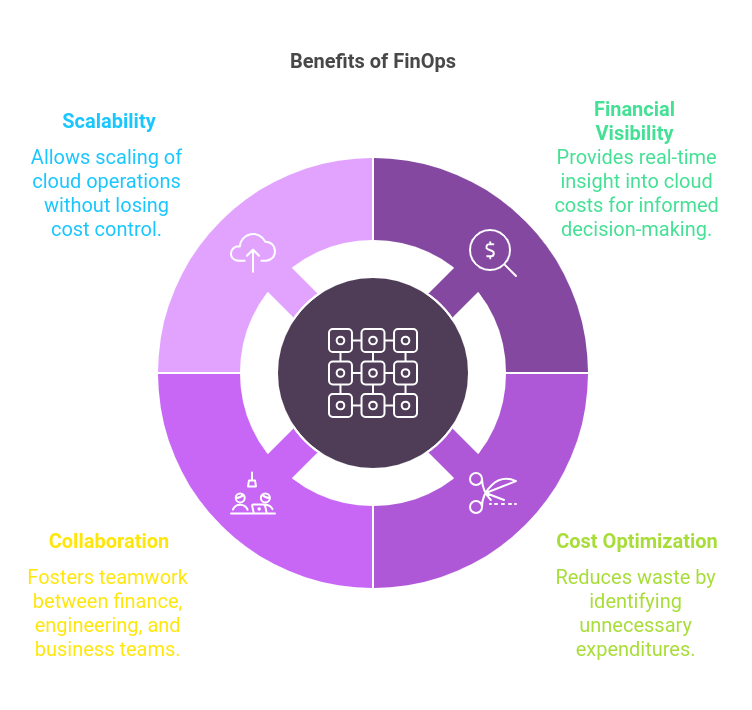
Financial Visibility in Cloud: FinOps provides real-time visibility into cloud costs, enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
Cost Optimization: By identifying unnecessary expenditures, FinOps reduces waste and ensures that cloud investments are efficient.
Collaboration: FinOps fosters a culture of collaboration between finance, engineering, and business teams.
Scalability: With a FinOps approach, organizations can scale their cloud operations without losing control of costs. Adopting FinOps not only improves cost efficiency but also ensures alignment between business objectives and IT investments. As cloud adoption grows, FinOps becomes essential for maintaining financial health while embracing digital transformation.
Why is FinOps Crucial for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments?
As businesses adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, managing cloud costs becomes increasingly complex. Different providers, pricing models, and usage patterns can quickly lead to inefficiencies. Multi-cloud FinOps and FinOps in hybrid cloud environments address these challenges by:
- Standardizing financial management practices across platforms.
- Offering consolidated reporting and analysis.
- Enabling better negotiation and pricing strategies with vendors.
- Improving governance and control over diverse cloud environments.
Managing Complexity in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Setups
Multi-cloud environments involve using multiple cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. While this approach reduces dependency on a single provider and offers flexibility, it complicates cost management.
Similarly, hybrid environments that combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources require careful financial planning to avoid unexpected costs. FinOps streamlines these processes by:
- Centralizing visibility across all platforms.
- Providing actionable insights through advanced analytics.
- Encouraging accountability among teams for their resource usage.
Core Principles of FinOps
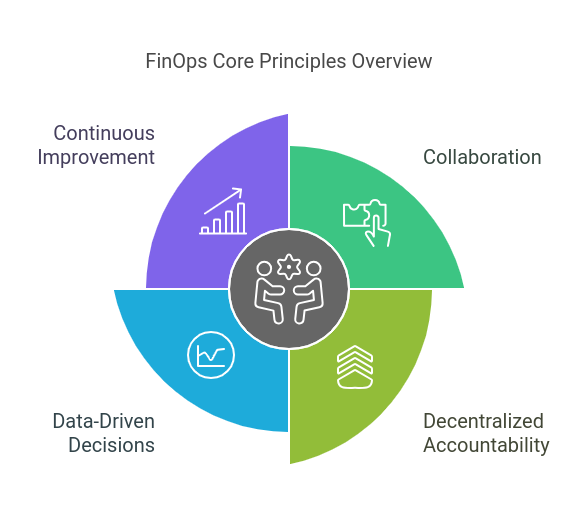
The Core Principles of FinOps serve as a foundation for effective implementation. These principles ensure that organizations can maximize the value derived from their cloud investments while maintaining cost control.
Teams Need to Collaborate: FinOps thrives on collaboration between technology, finance, and business teams. This cross-functional approach ensures alignment and better decision-making.
Decentralized Accountability: Each team is responsible for its cloud usage and associated costs. This decentralized model fosters ownership and accountability.
Decisions Driven by Data: Real-time data and FinOps metrics and KPIs guide financial decisions, enabling precise adjustments and forecasting.
Continuous Improvement: FinOps is an ongoing process that evolves with business and technology needs. Regular reviews and refinements are key to its success.
How Collaboration Drives Success
One of the unique aspects of FinOps is its emphasis on teamwork. Instead of operating in silos, engineering, finance, and operations teams work together to balance performance and cost. This collaborative culture promotes:
Faster decision-making.
Transparency in cloud spending.
Innovation without compromising budget constraints.
Reducing Unnecessary Cloud Expenditures
One of the key roles of FinOps is identifying and eliminating unnecessary cloud expenses. Cloud environments are dynamic, and without proper oversight, costs can spiral out of control. Common areas of waste include:
Over-Provisioned Resources: Resources that are larger or more numerous than needed, such as oversized virtual machines or excessive storage allocations.
Idle Resources: Resources left running when not in use, such as development environments or test servers.
Mismanaged Discounts: Underutilized reserved instances or volume discounts, leading to missed savings opportunities.
Practical Steps to Optimize Costs
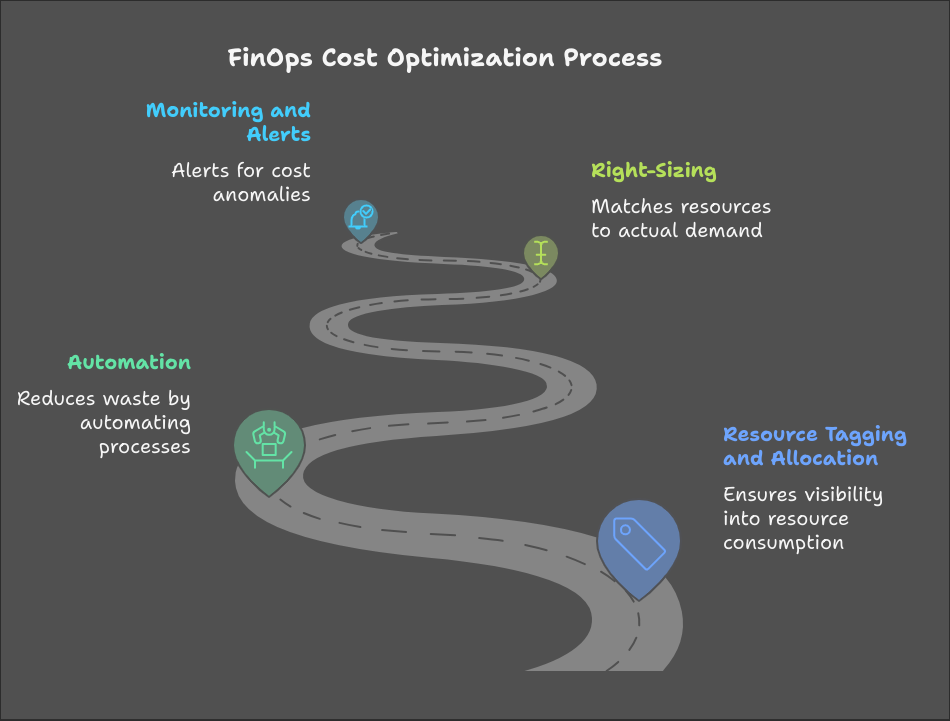
To tackle these issues, FinOps practices involve:
Resource Tagging and Allocation: Proper tagging ensures visibility into which teams or projects are consuming resources.
Automation: Automating processes like scaling and shutting down idle resources reduces manual intervention and prevents waste.
Right-Sizing: Analyzing usage patterns and resizing resources to match actual demand.
Monitoring and Alerts: Setting up alerts for cost anomalies to quickly address unexpected spikes.
FinOps Tools and Technologies
Several tools and technologies support FinOps implementation by providing visibility, optimization, and automation. These tools empower organizations to manage cloud finances effectively and ensure cost control at scale.
Categories of FinOps Tools
Cloud Cost Management Platforms: Tools like CloudHealth, CloudCheckr, and AWS Cost Explorer offer granular insights into cloud expenses. They help identify trends, anomalies, and optimization opportunities.
Automation Tools: Platforms like Terraform and Ansible automate provisioning and scaling, ensuring resources are efficiently managed and costs are minimized.
Monitoring Solutions: Tools like Datadog and New Relic monitor cloud performance, enabling teams to identify inefficiencies and optimize resources.
Dashboards and Reporting: Customized dashboards provide real-time visibility into FinOps metrics and KPIs, aiding decision-making and fostering accountability.
How to Choose the Right Tools
When selecting FinOps tools, consider:
Scalability: Can the tool handle your organization’s growth and increasing complexity?
Integration: Does it integrate seamlessly with existing systems and workflows?
Usability: Is the interface user-friendly and accessible to non-technical stakeholders?
Customization: Can you tailor the tool to meet your specific requirements?
FinOps Metrics and KPIs to Track
To measure the success of FinOps, organizations track several key metrics. These metrics provide insights into how well cloud resources are being managed and where improvements are needed.
Key Metrics and KPIs
Cloud Cost per Product/Team: Assigning costs to teams or products fosters accountability and enables precise budget tracking.
Savings Realized: Tracking cost reductions achieved through optimization efforts highlights the impact of FinOps initiatives.
Resource Utilization: Ensuring that resources are used efficiently minimizes waste and maximizes ROI.
Budget Adherence: Comparing actual spending against forecasts helps maintain financial discipline.
Anomaly Detection Rate: Measuring the frequency and resolution of cost anomalies indicates how well FinOps processes are functioning.
Time to Value: The speed at which FinOps initiatives deliver measurable results reflects their effectiveness.
Using Metrics to Drive Action
Metrics and KPIs are not just numbers—they are tools for driving action. Regularly reviewing these metrics enables organizations to:
- Identify trends and predict future spending.
- Benchmark performance against industry standards.
- Take corrective actions to address inefficiencies.
Implementing FinOps in Your Organization
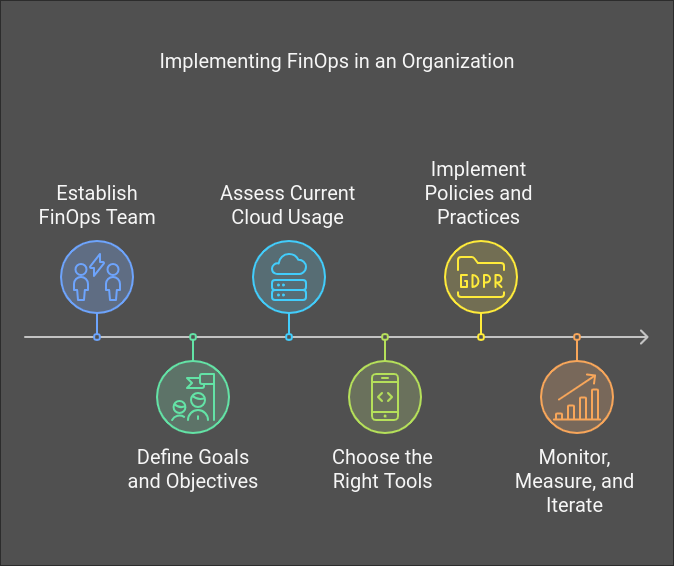
Successfully implementing FinOps requires a combination of cultural change, strategic planning, and technological adoption. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
1. Establish a FinOps Team
Form a cross-functional team comprising representatives from finance, engineering, and business units. This team will lead the FinOps initiative and drive collaboration.
2. Define Goals and Objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with FinOps, such as reducing costs, improving transparency, or optimizing resource utilization.
3. Assess Current Cloud Usage
Conduct a comprehensive audit of your cloud environment to understand spending patterns, resource utilization, and areas of waste.
4. Choose the Right Tools
Select tools and platforms that align with your organization’s needs and scale.
5. Implement Policies and Practices
Introduce policies for tagging, budgeting, and anomaly detection. Train teams to follow best practices.
6. Monitor, Measure, and Iterate
Regularly review performance metrics, gather feedback, and refine your approach to ensure continuous improvement.
FAQs
Conclusion
FinOps is a transformative approach to cloud financial management that empowers organizations to control costs, optimize resource utilization, and drive collaboration. As cloud adoption continues to grow, the importance of FinOps will only increase, especially in multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
By adhering to its core principles, leveraging the right tools, and fostering a culture of accountability, businesses can unlock the full potential of their cloud investments. Whether you are just beginning your FinOps journey or looking to refine your practices, this guide provides the foundation for sustainable and efficient cloud financial operations.
