Crafting an Efficient CI/CD Pipeline to Streamline Your Project Development
Introduction
Automating the software development life cycle through Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CI/CD) is a proven practice that accelerates the development and release of frontend applications, enhancing speed and efficiency.
This article will explore the key components of crafting an efficient CI/CD pipeline, providing insights and examples while guiding you through setting up a basic CI/CD workflow using GitHub Actions.
Understanding CI/CD
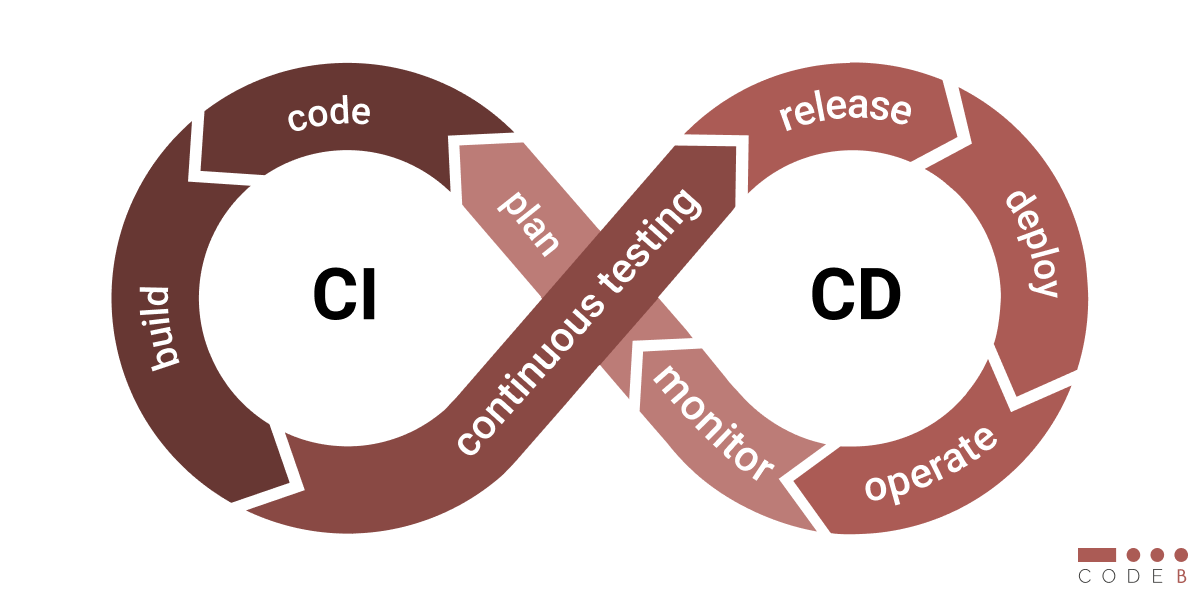
Continuous Integration (CI) is automating the integration of code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository. Continuous Delivery (CD) takes it a step further by automating the process of deploying applications to production. This seamless integration allows developers to detect and fix bugs early in the development cycle and ensures a more reliable release process.
Continuous Integration (CI):
Continuous Integration is a development practice that encourages developers to integrate their code changes into a shared repository multiple times a day. The main objective of CI is to detect and address integration issues early in the development process, rather than waiting until later stages, such as during testing or deployment.
Key principles of Continuous Integration:
- Frequent Code Integration: Developers are encouraged to integrate their code changes into a shared version control system (such as Git) regularly, typically multiple times a day.
- Automated Builds and Tests: CI relies on automated build and test processes to validate code changes. This ensures that new code integrates seamlessly with the existing codebase and does not introduce regressions.
- Early Detection of Issues: By integrating code frequently and automating tests, CI helps identify and address integration issues, bugs, or conflicts early in the development cycle, reducing the time and effort required for bug fixing.
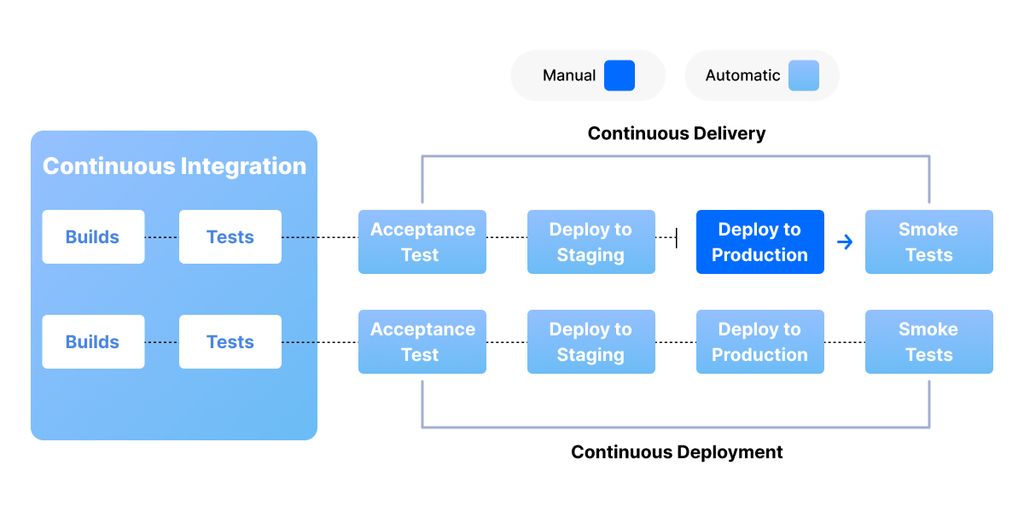
Continuous Delivery (CD):
Continuous Delivery is an extension of CI and focuses on automating the software delivery process. It involves the automation of the entire release pipeline, from building and testing to deployment and delivery to production. The goal of CD is to make the software delivery process more efficient, reliable, and repeatable.
Key principles of Continuous Delivery:
- Automated Deployment: CD emphasizes the automation of deployment processes to ensure that software can be reliably and consistently deployed to various environments, including testing, staging, and production.
- Incremental Releases: Continuous Delivery promotes the idea of delivering small, incremental changes to production regularly, making it easier to manage and reducing the risk associated with large, infrequent releases.
- Deployment Pipelines: CD often involves defining and managing deployment pipelines, which are automated workflows that orchestrate the steps involved in building, testing, and deploying the application.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
Continuous Deployment (CD) is a software development practice that extends the principles of Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) to automatically deploy code changes to production environments after passing automated tests. While Continuous Integration focuses on frequent code integration and automated testing, and Continuous Delivery emphasizes automating the software delivery process up to the staging or pre-production environment, Continuous Deployment takes the automation one step further by automatically deploying changes to the production environment without manual intervention.
Key characteristics and principles of Continuous Deployment:
- Automated Deployment: The primary feature of Continuous Deployment is the automation of the deployment process. Once code changes have passed all automated tests in the CI/CD pipeline, they are automatically deployed to the production environment without the need for manual approval.
- Immediate Release: Continuous Deployment aims to minimize the time between code changes being merged into the main branch and those changes being available to end-users. This rapid release cycle helps in delivering new features, bug fixes, and improvements to users quickly.
- Rollback Mechanism: To mitigate the risks associated with automatic deployments, Continuous Deployment pipelines often include rollback mechanisms. If an issue is detected after deployment, the system can automatically revert to the previous stable version, ensuring minimal impact on users.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous Deployment relies on continuous monitoring of applications and infrastructure in production. Monitoring helps detect and address any issues that may arise after a deployment, providing insights into system performance and user experience.
- Feature Toggles (Feature Flags): Feature toggles are often employed in Continuous Deployment to enable or disable certain features at runtime. This allows teams to release code changes to production while keeping new features hidden until they are ready to be exposed to users.
While Continuous Deployment offers numerous benefits, it may not be suitable for all types of applications or organizations. Mission-critical systems or industries with strict regulatory requirements may choose to adopt Continuous Delivery with manual approval steps for production releases to ensure additional scrutiny and control over deployments. The decision to implement Continuous Deployment depends on factors such as organizational policies, risk tolerance, and the nature of the application being developed.
Key Components of an Efficient CI/CD Pipeline
1. Source Code Management
The foundation of any CI/CD pipeline lies in robust source code management. Utilize Git, a widely adopted version control system, to track changes, manage collaboration, and maintain a reliable codebase.
Example: Initialize a Git repository for your project and create branches for feature development and bug fixes. Regularly merge changes into the main branch to ensure a cohesive codebase.
2. Automated Testing
Incorporating automated testing into your pipeline is crucial for identifying issues early in the development cycle. This includes unit, integration, and end-to-end tests to ensure code quality and reliability.
Example: Integrate a testing framework like Jest for JavaScript applications or JUnit for Java projects. Create test suites that automatically run during the CI process to catch and address potential issues.
3. Continuous Integration
Automate the process of code integration to detect and resolve conflicts early. Tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions can be employed to trigger builds upon code commits, ensuring a consistent integration workflow.
Example: Set up a GitHub Actions workflow by creating a .github/workflows/main.yml file in your repository. Define jobs and steps to execute tasks such as installing dependencies, running tests, and building artifacts (example included below).
4. Artifact Management
Efficiently manage and store build artifacts, dependencies, and release-related assets. Artifact repositories like JFrog Artifactory or Sonatype Nexus provide centralized storage for these components.
Example: Configure your CI pipeline to publish build artifacts to a designated repository, ensuring easy retrieval and consistency across different environments.
5. Continuous Deployment
Automate the deployment process to move code seamlessly through different environments, from development to testing and production.
Example: Utilize deployment tools like Kubernetes for container orchestration or Ansible for configuration management. Define deployment workflows that automatically promote code through different stages.
Benefits of a CI/CD Pipeline
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline for your project has several benefits, including:
1. Early Detection of Issues
A CI/CD pipeline facilitates automated testing, enabling early detection and resolution of issues. By catching bugs in the early stages of development, teams can significantly reduce the time and resources spent on debugging and troubleshooting later in the process.
2. Consistent Codebase
Continuous Integration ensures that code changes are regularly merged into the main branch, promoting a consistent and cohesive codebase. This practice minimizes integration conflicts and enhances collaboration among team members.
3. Efficient Collaboration
CI/CD pipelines encourage a collaborative development environment by automating repetitive tasks and providing a shared platform for code integration. This fosters effective communication and cooperation among team members, increasing productivity.
4. Accelerated Time-to-Market
Automation in the CI/CD pipeline expedites the development and deployment processes. With quick and reliable feedback from automated tests, teams can confidently release new features and updates, reducing time-to-market and staying ahead of the competition.
5. Improved Code Quality
Automated testing, a key component of CI/CD, ensures that only high-quality code is merged into the codebase. This results in a more robust and stable application, reducing the likelihood of post-release issues and enhancing overall code quality.
And many more.
All these benefits result in a smoother, faster, and more reliable delivery process, making CI/CD a crucial tool in today’s fast-paced world. Now, let’s see an example of how to set this pipeline up for a Node.js project using GitHub Actions.
Setting Up GitHub Actions for a Simple Project
Create a GitHub repository
In the project directory, use the .github/workflows command to create a workflow directory. You can have multiple workflows for your project.
Click the Actions tab of your repository. A number of preset workflows will be displayed, you can choose from there as per your requirement or create a new one from scratch.
I will create a workflow from scratch, let’s name it basic-workflow.yml
Here I have created a workflow for the Node.js project. This will get triggered when making push and pull requests on the main branch. Its work is to run test cases and it will use the Ubuntu server.
name: CI
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set Up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 18
- name: Install Dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run Tests
run: npm testBest practices for a CI/CD pipeline
1. Maintain a Clean and Readable Configuration
Keep your CI/CD configuration files clean and readable. Use descriptive names for jobs, steps, and variables to enhance clarity and make it easier for team members to understand and maintain the pipeline.
2. Automate Everything Possible
Automate as many tasks as possible within the pipeline, including testing, code analysis, and deployment. Automation reduces the risk of human error, ensures consistency, and accelerates the development process.
3. Parallelize and Distribute Builds
Parallelize build processes and distribute them across multiple agents to speed up the overall build time. This is especially important for large projects with extensive test suites.
4. Implement Incremental Builds
Optimize your CI/CD pipeline by implementing incremental builds. Only build and test the components that have changed since the last commit, reducing the overall execution time.
5. Use Immutable Artifacts
Treat build artifacts as immutable. Once an artifact is created, avoid modifying it. This ensures consistency and reproducibility across different environments.
6. Security Scanning and Compliance Checks
Integrate security scanning tools into your pipeline to identify and address vulnerabilities early in the development process. Additionally, include compliance checks to ensure that the code adheres to industry standards and best practices.
CI/CD vs DevOps
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) and DevOps represent two interrelated but distinct approaches to modern software development and delivery. CI/CD is a methodology and set of practices focused on automating the steps involved in code integration, testing, and deployment. It aims to enhance the development process by ensuring that code changes are frequently and seamlessly integrated into a shared repository, with automated testing providing quick feedback on potential issues. The continuous delivery aspect extends this automation to the entire release pipeline, allowing for rapid and reliable deployment of software changes to various environments, including production. On the other hand, DevOps is a broader cultural and organizational philosophy that transcends specific practices or tools. DevOps emphasizes breaking down silos between development and operations teams, fostering collaboration, and promoting a shared responsibility for the entire software development lifecycle. It encompasses cultural shifts, collaborative practices, and the use of automation tools across the entire spectrum of software development, from planning and coding to testing, releasing, deploying, and monitoring. While CI/CD is often a crucial component of DevOps practices, the latter represents a holistic approach to improving collaboration, efficiency, and agility throughout the software delivery process. Together, they form a powerful framework for organizations seeking to deliver high-quality software rapidly and reliably.
What are some common CI/CD tools?
Numerous CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) tools are available to help automate various stages of the software development and delivery process. These tools facilitate the implementation of CI/CD practices, ensuring faster, more reliable, and efficient software delivery. Here are some common CI/CD tools:
1. Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server widely used for building, testing, and deploying code changes. It supports the automation of various tasks and integrates with a wide range of plugins and tools.
2. GitLab CI/CD
GitLab provides built-in CI/CD capabilities as part of its integrated DevOps platform. It includes features for continuous integration, testing, and deployment.
3. Travis CI
Travis CI is a cloud-based CI/CD service that automatically builds and tests code changes in GitHub repositories. It supports various programming languages and platforms.
4. CircleCI
CircleCI is a cloud-based CI/CD platform that automates the software development process. It integrates with popular version control systems and offers customization through configuration files.
5. TeamCity
TeamCity, developed by JetBrains, is a CI/CD server that supports building and deploying code changes. It offers powerful build configuration options and integrates with various development tools.
6. Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps, part of the Microsoft Azure cloud platform, provides a set of integrated tools for CI/CD, including Azure Pipelines for build and release automation.
7. Bamboo
Bamboo, by Atlassian, is a CI/CD server that integrates with Jira and Bitbucket. It supports the automation of build, test, and deployment processes.
8. GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD and automation service provided by GitHub. It allows developers to define workflows directly in their GitHub repositories for building, testing, and deploying applications.
9. GoCD
GoCD is an open-source CI/CD server designed to handle complex workflows and pipelines. It emphasizes flexibility and supports the modeling of dependencies between different stages.
10. Drone
Drone is an open-source CI/CD platform that integrates seamlessly with popular version control systems. It uses containers to execute build and deployment steps.
11. Jira Pipelines
Jira Pipelines is part of the Atlassian suite and provides a cloud-based CI/CD service that integrates with Jira Software and Bitbucket repositories.
12. Spinnaker
Spinnaker is an open-source, multi-cloud continuous delivery platform designed for deploying and managing applications in cloud environments.
These tools offer a range of features and integrations, allowing development teams to choose the CI/CD solution that best fits their specific requirements and technology stack. The selection often depends on factors such as ease of use, scalability, integration capabilities, and the overall workflow preferences of the development team.
CI/CD in the Cloud
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) in the cloud refers to the practice of utilizing cloud computing services and platforms to implement and optimize software development workflows. Cloud-based CI/CD solutions offer numerous advantages over traditional on-premises setups, providing scalability, flexibility, and seamless integration with other cloud services. Let's explore how CI/CD aligns with some prominent cloud providers:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Scalability: AWS provides a vast array of scalable computing resources through services like Amazon EC2 and AWS Lambda. Teams can dynamically adjust resources to match the demands of their CI/CD processes.
- Integrated Services: AWS offers a comprehensive suite of services, including AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy, which seamlessly integrate to form an end-to-end CI/CD pipeline. These services can be combined with other AWS tools for monitoring, logging, and security.
2. Microsoft Azure
- Ease of Integration: Azure DevOps Services, part of the Microsoft Azure ecosystem, offers a fully integrated CI/CD platform. It supports a variety of programming languages, containerization, and deployment to various Azure services.
- Managed Services: Azure provides managed services such as Azure DevOps Pipelines, allowing teams to focus on coding while Azure handles the underlying infrastructure and maintenance tasks.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Containerization and Orchestration: GCP emphasizes containerization with services like Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Teams can easily incorporate container orchestration into their CI/CD processes, ensuring consistency across different environments.
- Serverless Options: Google Cloud offers serverless options like Cloud Functions, allowing developers to build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
4. IBM Cloud
- Enterprise-Grade CI/CD: IBM Cloud offers solutions for enterprise-grade CI/CD with tools such as IBM Cloud Continuous Delivery. This includes features for automated testing, deployment, and release management.
- Hybrid Cloud: IBM Cloud supports hybrid cloud environments, allowing organizations to integrate on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based CI/CD processes.
5. Heroku
- Simplicity and Speed: Heroku, a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) provider, offers a simple and fast way to deploy applications. Heroku Pipelines facilitates easy integration of CI/CD workflows, making it an excellent choice for startups and small to medium-sized projects.
- Fully Managed Platform: Developers using Heroku can focus solely on code and application logic, as Heroku manages the underlying platform and infrastructure.
6. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- Integration with Oracle Tools: Oracle Cloud provides CI/CD solutions that integrate with popular development tools and Oracle's cloud infrastructure services. This allows teams to leverage a variety of Oracle services in their workflows.
- Enterprise-Class CI/CD: OCI supports enterprise-class CI/CD pipelines with features for scalability, security, and compliance.
Conclusion
Implementing a robust CI/CD pipeline is essential for enhancing the efficiency of your project development. By understanding and integrating the key components discussed in this guide, you can significantly streamline your workflow.
The practical example of setting up a GitHub Actions workflow for a simple project demonstrates how easily you can incorporate CI/CD practices into your development process, paving the way for more reliable and efficient software releases.
The outlined benefits further emphasize the importance of embracing CI/CD for a more collaborative, consistent, and accelerated development lifecycle.