Flutter vs React Native: Which Fits Your Mobile App Best?

Mobile app frameworks play a central role in modern product development. They influence cost structure, hiring flexibility, UI control, performance behavior, and long-term maintainability.
Cross-platform frameworks such as Flutter and React Native reduced dependence on fully native stacks and enabled applications to run across Android and iOS from a single codebase. This shift accelerated development cycles and changed how engineering teams structure frontend and backend workflows.
However, every technical choice introduces trade-offs. Each framework has architectural differences, ecosystem maturity levels, and performance implications that become more visible as a product scales.
According to a survey, Flutter is used by approximately 46% of developers, while React Native is used by about 32%.
Both of these frameworks offer solid frontend and backend capabilities.making them strong contenders for cross-platform development. To simplify that decision, I’ve broken down their individual strengths, limitations, and core capabilities so you can evaluate them side by side and determine which one fits your product requirements better by the end of this article.
What is the architectural difference between Flutter and React Native?
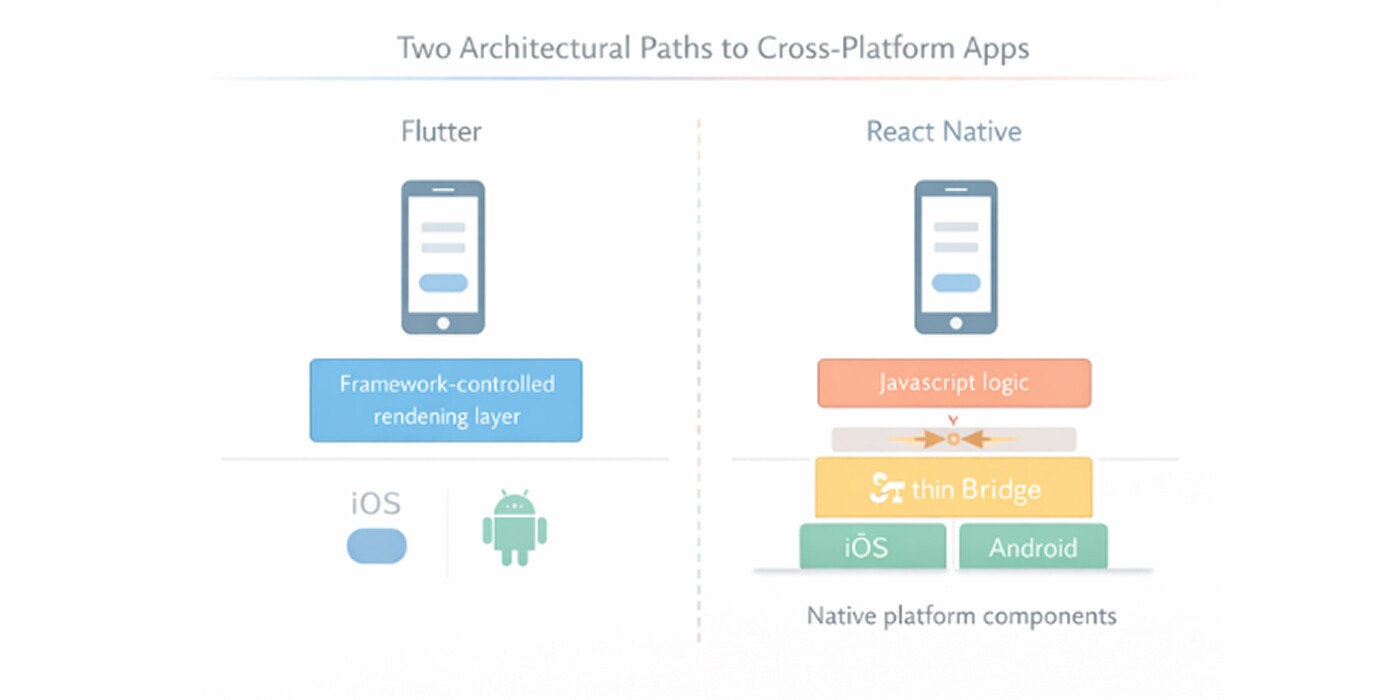
Code structure is only one aspect of a framework's internal design. It influences performance behavior, debugging complexity, UI consistency, and the amount of work needed to maintain the app over time.
Although cross-platform development is made possible by both Flutter and React Native, their underlying architectural models result in very different trade-offs in actual projects.
The architectural model of Flutter:
- Flutter uses its own rendering engine to function.
- It draws the entire interface itself rather than depending on native platform widgets.
- Flutter has strong control over visual consistency across platforms because its framework layer renders every button, animation, and layout element.
- In order to minimize runtime interpretation overhead, the framework precompiles code into native machine code.
- Teams benefit from consistent UI behavior across platforms and fewer platform-specific edge cases because flutter manages the entire rendering pipeline.
React Native’s architectural model:
- React Native takes an alternative approach to design. Instead of curating the interface itself, it uses native iOS and Android components to render UI elements.
- With this method, the application's appearance and functionality feel more in line with platform standards.
- Since JavaScript is used to run application logic, a large portion of the business layer operates outside of the native environment.
- Through an abstraction layer that connects the two worlds, JavaScript and native modules can communicate with each other.
- Depending on how heavily the app uses native APIs, this model may introduce performance issues even though it offers flexibility and makes integration with existing native code easier.
At an architectural level, Flutter emphasizes consistency and control within the framework, while React Native prioritizes alignment with native platforms. That distinction carries through every downstream decision.
How does the programming model differ?
The programming model of a framework defines how application logic is structured, how state is managed, and how the UI interacts with platform APIs.
It directly impacts development speed, debugging complexity, and long-term maintainability.
Flutter is built around Dart and follows a widget-driven architecture where everything in the UI is a composable component.
The framework controls rendering, layout, and animation within its own engine.
This creates a consistent development environment across platforms, but it requires teams to adopt Dart and Flutter-specific patterns.
React Native relies on JavaScript and follows a component-based model similar to React for the web, where state management and lifecycle behavior are handled through patterns like hooks.
This setup can feel familiar to react native experts, but performance and behavior depend on how efficiently the JavaScript layer communicates with native modules.
Which framework offers better UI consistency?
One of the most visible differences between Flutter and React Native appears in how they handle UI rendering and platform behavior.
Flutter renders every interface element using its own engine. This means the design remains visually consistent across Android and iOS because the framework controls layout, animations, and visual components internally.
Pixel-level control is possible, and UI behavior remains predictable across devices. However, because it does not rely on native platform widgets, subtle platform-specific nuances may need to be recreated manually.
React Native like other react native frameworks, renders real native UI components. A button on iOS is an actual iOS button. On Android, it maps to Android’s native equivalent.
This results in interfaces that naturally align with platform conventions. The trade-off is that maintaining identical design behavior across platforms can require additional styling and testing.
If visual consistency across platforms is a priority, Flutter offers tighter control. If adherence to native platform behavior is more important, React Native aligns more closely with that goal.
How does performance compare between Flutter and React Native?
Performance differences between Flutter and React Native usually do not surface in simple views or early builds. They become relevant as apps introduce frequent UI updates, complex animations, or tighter coupling between interface and application logic.
Understanding where overhead exists helps teams anticipate constraints before performance issues appear in production, especially when planning for cross-platform performance optimization.
The comparison below highlights where performance characteristics diverge at a structural level, helping you evaluate which model aligns better with your application’s interaction patterns and scaling expectations
Which framework has a stronger ecosystem?
Flutter ecosystem structure
- In the case of flutter , many core features are maintained or heavily influenced by Google.
- This creates consistency in tooling and documentation, but it can also mean reliance on the framework’s roadmap for certain platform integrations.
React Native ecosystem structure
- React Native benefits from the broader JavaScript ecosystem.
- It is built around React and JavaScript, it integrates naturally with web technologies and has access to a large pool of third-party libraries.
- However, library quality can vary, and some integrations depend heavily on community support rather than centralized governance.
- React Native projects may require more careful dependency management.
Which framework is easier to hire for?
Developer availability and talent pool
- Flutter applications are written in Dart. Developers familiar with object-oriented languages such as Java or C# typically adapt without difficulty.
- However, Dart has a smaller global developer base compared to JavaScript.
- Building a Flutter team may require hiring developers specifically experienced in Flutter or allocating time for internal upskilling.
- For organizations without prior Dart exposure, onboarding timelines should be factored into delivery planning.
- React Native is built on JavaScript and follows React’s component-based structure.
- Since JavaScript remains one of the most widely used programming languages globally, the available hiring pool is significantly larger , with many specialised react native development teams operating worldwide.
- We've compiled a list of performing react native expert agencies in india if you're looking to hire a resource, visit this page.
Cross-team collaboration
- React Native aligns naturally with existing web development teams using React.
- Shared architectural patterns between web and mobile projects can simplify collaboration and allow resource flexibility across projects.
- Flutter teams operate within a more specialized development environment.
- While this can create strong internal expertise, scaling across multiple teams may require more targeted hiring or training investment.
- Organizations already embedded in the JavaScript ecosystem may find React Native easier to integrate into existing CI/CD workflows and tooling environments.
- Flutter projects require alignment with Dart tooling and framework-specific conventions, which can introduce operational adjustments.
How well does each framework integrate with backend systems?
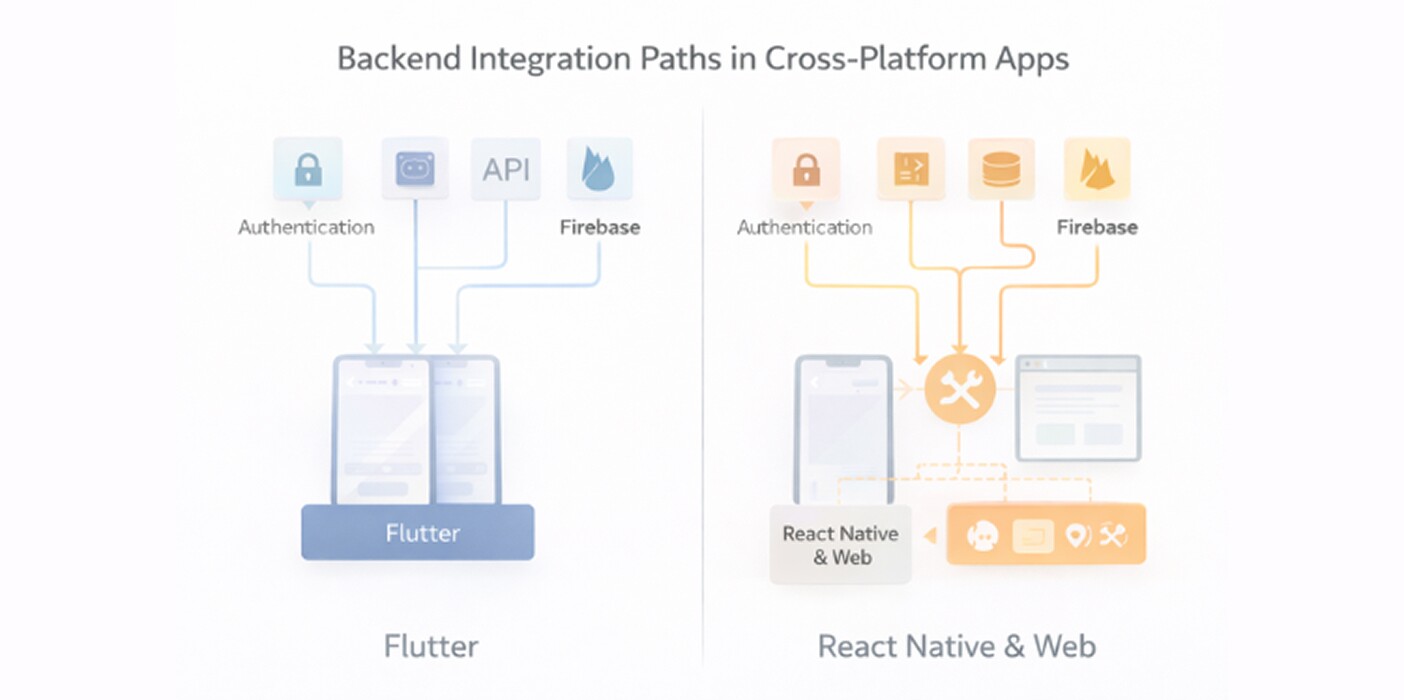
Both flutter and React native function as client-side frameworks. Backend compatibility depends primarily on API design rather than framework constraints.
Flutter supports REST, GraphQL, WebSockets, and real-time communication through standard networking libraries. Because it compiles to native code, it can integrate with platform-specific SDKs when needed.
React native communicates with backend services through JavaScript networking libraries such as fetch or Axios. native modules can be written for deeper platform integrations.
In practical terms, backend flexibility is comparable in both frameworks. Differences appear only when deep native SDK integration is required.
Integration with flutter
- Flutter’s plugin system allows developers to access device capabilities and third-party SDKs.
- If an official plugin does not exist, native modules can be written in Kotlin, Java, Swift, or Objective-C.
Integration with react native
- React Native supports native modules that bridge JavaScript with platform-specific APIs.
- Because of its longer presence in production environments, many enterprise SDKs already provide React Native support.
How much does it cost to build with each framework?
At MVP stage, React Native may be marginally more cost-efficient if the organization already uses JavaScript.
At scale, cost differences narrow. Architecture quality, backend complexity, compliance requirements, and infrastructure planning influence pricing far more than whether the app is built in Flutter or React Native.
