What is an Enterprise Software?
Enterprise software is a type of program designed to help businesses operate more smoothly. Here’s a quick overview of what it does:
Streamlines Daily Operations: It makes everyday tasks more efficient, saving time and effort.
Keeps Everything Organized: It helps manage information and activities, which is essential for handling tasks and projects effectively.
Scalable for Any Business: Whether a company is large, medium-sized, or small, enterprise software can be tailored to meet its needs and adapt as the business grows.
Provides Data Insights: Over time, it collects and analyses data to help businesses make smarter decisions based on trends and performance.
In a nutshell, enterprise software is like a powerful tool that helps businesses of all sizes stay organised, work more efficiently, and make better, data-driven decisions.
Enterprise Software Statistics :-
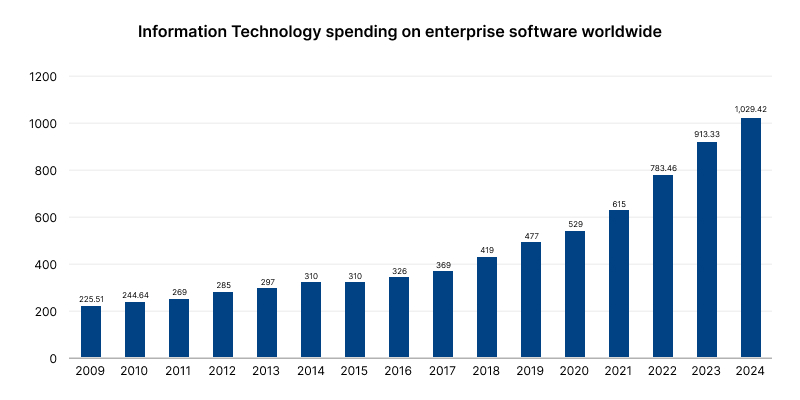
Based on the above stats we can observe the following trends :-
Steady Growth (2009-2016):
- From 2009 to 2016, there was a steady but gradual increase in spending, rising from $225.51 billion to $321 billion. The growth rate during this period was relatively modest.
Significant Increase (2016-2019):
- Between 2016 and 2019, spending increased more rapidly, jumping from $321 billion to $529 billion. This period marked the beginning of a sharper upward trend.
Sharp Surge (2019-2024):
- From 2019 onward, the growth became even more pronounced. Spending grew from $529 billion in 2019 to $783.46 billion in 2021.
- The trend is expected to continue, reaching over $1 trillion by 2024, highlighting the accelerating investment in enterprise software.
Why is Enterprise Software Important?
- Improved decision-making: Enterprise software provides access to real-time data and analytics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on facts and trends.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: By streamlining operations and providing better customer service, enterprise software can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Scalability: Enterprise software can grow with a business, accommodating changes in size and complexity.
- Cost savings: By automating tasks, reducing errors, and improving efficiency, enterprise software can help businesses save money.
- Competitive advantage: Businesses that leverage enterprise software effectively can gain a competitive edge by optimizing their operations and offering superior products and services.
- Automation of tasks: It automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added work.
- Increased efficiency and speed: By streamlining processes and providing real-time data, enterprise software helps businesses operate more efficiently and make faster decisions.
- Ease of use: Modern enterprise software is designed to be user-friendly, eliminating the need for extensive training and reducing the learning curve.
Types of Enterprise Software
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are designed to manage and enhance interactions with current and potential customers across an organization. They offer features that cover key areas such as sales, marketing, customer service, and support. Examples of CRM software include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM.
Let's take a brief overview of each one by one.
- Salesforce was founded in 1999 in the United States.
Launched:
- Salesforce is widely regarded as the leading CRM system globally, consistently ranking at the top in various industry reports due to its extensive capabilities and large user base.
Global Ranking:
- Sales cloud, service cloud, marketing cloud, and commerce cloud.
- Advanced analytics and AI-powered tools like Salesforce Einstein.
- Highly customizable platform with a vast ecosystem of third-party apps via AppExchange.
- Mobile accessibility and strong integration with other business tools.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive CRM solution covering all customer-related processes.
- Strong emphasis on innovation with regular updates and new features.
- Scalable for businesses of all sizes, from SMBs to large enterprises.
- Extensive community and support resources.
Pros:
- High costs, especially for small businesses.
- Complex setup and implementation.
- Customization requires technical expertise.
- Steep learning curve for users.
Cons:
Launched:
- HubSpot CRM was launched in 2014 as a free tool, with additional paid tiers available.
Global Ranking:
- HubSpot CRM is particularly popular among small to medium-sized businesses, praised for its user-friendly interface and inbound marketing tools. It is often ranked highly in CRM evaluations, especially for SMBs.
Key Features:
- Contact management, email marketing, sales pipeline management, and customer service tools.
- Integrates with HubSpot’s marketing, sales, and service hubs.
- Free version available with essential CRM features.
- Extensive educational resources through HubSpot Academy.
Pros:
- Easy to use and quick to set up.
- Free version available, making it accessible for startups and small businesses.
- Strong focus on inbound marketing and lead nurturing.
- Seamless integration with HubSpot’s full suite of tools.
Cons:
- Less suited for large enterprises with complex needs.
- Some advanced features are only available in paid tiers.
- Customization options are more limited compared to Salesforce.
- Reporting capabilities may be less robust than other enterprise-level CRMs.
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM was originally launched in 2003. It was rebranded and integrated into the Dynamics 365 suite in 2016.
Launched:
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM is highly regarded, particularly for its integration with other Microsoft products. It is commonly ranked among the top CRM solutions, especially in businesses already using Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Global Ranking:
- Sales, marketing, customer service, and field service modules.
- Strong integration with Microsoft Office 365, Teams, and LinkedIn.
- AI-driven insights and analytics with Dynamics 365 AI.
- Scalable and customizable for different industries and business sizes.
Key Features:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft’s suite of tools.
- Flexible and modular, allowing businesses to add or remove features as needed.
- Scalable for SMBs and large enterprises alike.
- Strong focus on data security and compliance.
Pros:
- Can be less intuitive for users not familiar with Microsoft products.
- Licensing and pricing can be complex.
- Customization and configuration may require technical expertise.
- Some users may find it less specialized in certain areas compared to niche CRM providers.
Cons:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems are designed to integrate and streamline business processes across various departments within an organization. They offer features that cover key areas such as finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, and manufacturing. Examples of ERP software include SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
SAP :
Launched:
Global Ranking:
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Launched:
- Oracle ERP was launched in 2001
Global Ranking:
- Oracle ERP is also a top-tier global ERP solution, frequently ranked alongside SAP. It is known for its strong financial and database management capabilities.
Key Features:
- Robust financial management features: Strong capabilities in accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Strong integration with Oracle's database and cloud services: Seamless integration across various business functions.
- Comprehensive and scalable solutions: Suitable for large enterprises with complex requirements.
- Regular updates and innovations: Continuous improvements, especially in cloud ERP.
Pros:
Cons:
Launched:
Global Ranking:
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Business Intelligence (BI) software
BI software is designed to help organizations collect, process, and analyze data to make informed business decisions. These tools provide data visualization, reporting, and analytics capabilities, enabling businesses to gain insights from their data. Examples of BI software include Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik Sense.
Launched:
- Microsoft Power BI was officially launched in 2015, and has quickly become one of the most widely used BI tools due to its integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem and user-friendly interface.Global
Ranking:
- Power BI is consistently ranked as one of the top BI solutions globally, particularly recognized for its ease of use, affordability, and strong integration with Microsoft products.
Key Features:
- Data visualization, dashboards, reporting, and data modeling.
- Integration with Excel, Azure, and other Microsoft tools.
- Cloud-based service with options for on-premises with Power BI Report Server.
- Real-time data monitoring and interactive dashboards.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop features.
- Seamless integration with other Microsoft products.
- Affordable pricing with a free tier available.
- Strong community support and frequent updates.
Cons:
- Limited advanced analytics capabilities compared to other tools.
- Performance can be an issue with very large datasets.
- Some advanced features require premium licenses.
- Customization can be limited compared to more complex BI tools.
Launched:
- Tableau was founded in 2003 and has since become a leading BI tool known for its powerful data visualization capabilities and ease of use.
Global Ranking:
- Tableau is one of the top-ranking BI solutions globally, particularly praised for its advanced data visualization, intuitive interface, and ability to handle complex data sets.
Key Features:
- Advanced data visualization, dashboards, and reporting.
- Drag-and-drop interface for creating interactive visualizations.
- Integration with various data sources, including cloud databases and spreadsheets.
- Strong focus on visual analytics and storytelling.
Pros:
- Powerful and flexible data visualization capabilities.
- Easy to use with minimal technical expertise required.
- Strong community support and extensive online resources.
- Integration with a wide range of data sources.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to some other BI tools.
- Limited data preparation and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) features.
- Can require additional tools or expertise for advanced analytics.
- Performance can slow down with very large or complex data sets.
Launched:
- Qlik Sense was launched in 2014 as a next-generation BI tool, building on the success of QlikView with a focus on self-service data discovery and visualization.
Global Ranking:
- Qlik Sense is highly regarded in the BI space, known for its powerful data discovery capabilities, associative data engine, and robust data integration features.
Key Features:
- Self-service data discovery, visualization, reporting, and analytics.
- Associative data engine that enables users to explore data from any angle.
- Integration with a wide range of data sources, both on-premises and cloud-based.
- Advanced analytics, including AI-driven insights and predictive analytics.
Pros:
- Powerful data discovery and associative engine for exploring data.
- Flexible and scalable for organizations of all sizes.
- Strong data integration capabilities with various sources.
- Advanced analytics and AI-driven insights.
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve compared to some other BI tools.
- Higher cost, particularly for larger deployments.
- Customization can be complex and may require specialized skills.
- Performance can be affected by very large or complex data sets
Human Capital Management (HCM) Software
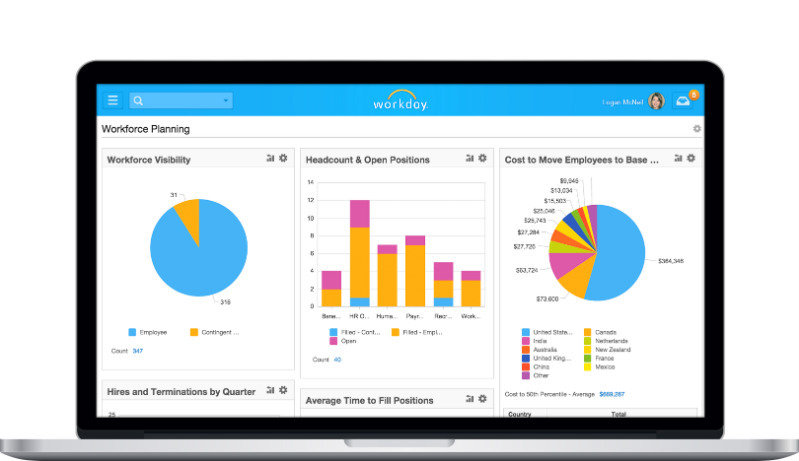
HCM systems are designed to manage and optimize an organization’s human resources functions, including recruiting, onboarding, payroll, performance management, learning and development, and employee engagement. Examples of HCM software include SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle HCM Cloud, and Workday HCM.
Launched:
- SAP SuccessFactors was founded in 2001 and later acquired by SAP in 2011, becoming a key part of SAP’s cloud-based HCM offerings.
Global Ranking:
- SAP SuccessFactors is one of the leading HCM solutions globally, particularly known for its strong integration with SAP’s broader enterprise suite and its comprehensive HR features.
Key Features:
- Core HR and payroll, talent management, learning and development, workforce analytics, and employee experience management.
- Integration with SAP ERP and other SAP solutions.
- Cloud-based with real-time data analytics and reporting.
- Strong focus on employee experience and engagement.
Pros:
- Comprehensive and modular system covering all HR processes.
- Strong integration with SAP’s ERP and other enterprise solutions.
- Scalable for large global enterprises.
- Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
Cons:
- High implementation and maintenance costs.
- Complexity in customization and configuration.
- Steep learning curve, particularly for non-SAP users.
- Long implementation times for complex deployments.
Launched:
- Oracle HCM Cloud was launched as part of Oracle’s broader cloud-based application suite in 2011, building on Oracle’s extensive experience in enterprise software.
Global Ranking:
- Oracle HCM Cloud is a top-tier solution, frequently ranked among the best HCM software for its comprehensive features, cloud-native architecture, and strong integration with Oracle’s other enterprise applications.
Key Features:
- Core HR, talent management, workforce management, payroll, and benefits administration.
- Cloud-based architecture for easy scalability and updates.
- Advanced analytics and AI-driven insights.
- Strong integration with Oracle ERP and other enterprise solutions.
Pros:
- Comprehensive HR solution with a cloud-native approach.
- Regular updates and innovations, especially in AI and machine learning.
- Strong focus on data security and compliance.
- Flexible and scalable for organizations of various sizes.
Cons:
- Complex implementation process, especially for large enterprises.
- Customization can be challenging and may require specialized expertise.
- Higher ongoing subscription costs for extensive use.
- Licensing and pricing models can be complex.
Launched:
- Workday was founded in 2005, and its HCM solution quickly gained popularity for its innovative cloud-based approach, with the first version launched in 2006.
Global Ranking:
- Workday HCM is one of the most highly regarded HCM solutions globally, particularly known for its user-friendly interface, cloud-native architecture, and strong focus on employee experience.
Key Features:
- Core HR, talent management, payroll, workforce planning, and learning management.
- Cloud-based with a focus on mobile accessibility and user experience.
- Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
- Strong focus on employee engagement and experience.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface and strong mobile accessibility.
- Cloud-native with real-time updates and innovations.
- Scalable for both mid-sized businesses and large enterprises.
- Strong focus on employee experience and engagement.
Cons:
- Higher upfront costs compared to some competitors.
- Customization can be limited compared to more traditional, on-premises solutions.
- Integration with non-Workday products can be more challenging.
- Some users may find it less suited for highly complex or unique HR processes.
Content Management System (CMS)
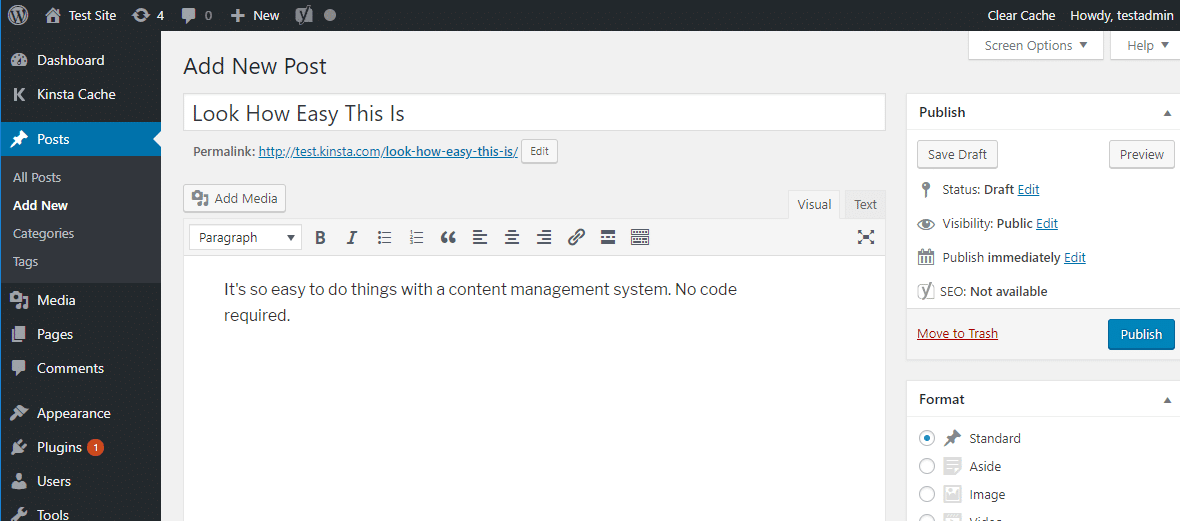
A Content Management System (CMS) is a software application that helps users create, manage, and modify digital content in a centralized platform. It simplifies website creation and content management, enabling non-technical users to collaborate and publish content efficiently.
- WordPress was launched in 2003 by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little. It started as a blogging platform but has since evolved into a full-fledged CMS.
Launched:
- WordPress is the most popular CMS globally, powering over 40% of websites on the internet. It is known for its flexibility, extensive plugin ecosystem, and ease of use.
Global Ranking:
- Flexible and user-friendly interface for content management.
- Thousands of themes and plugins for customization.
- SEO-friendly with various plugins like Yoast.
- Supports blogs, e-commerce (via WooCommerce), portfolios, and more.
- Open-source and community-driven with strong developer support.
Key Features:
- Easy to use and widely adopted, with extensive resources and community support.
- Highly customizable through plugins and themes.
- Suitable for a wide variety of websites, from small blogs to large enterprise sites.
- Large plugin marketplace for adding features like SEO, security, and e-commerce.
Pros:
- Vulnerability to security risks if not regularly updated.
- Can become slow or bloated with too many plugins or poor-quality themes.
- Requires additional plugins for advanced functionality, which can increase complexity.
- High-performance hosting may be necessary for large sites.
Cons:
Launched:
- Drupal was initially released in 2001 by Dries Buytaert as an open-source CMS and framework, focusing on flexibility and scalability.
Global Ranking:
- Drupal is popular among large organizations and enterprises, known for its robust security and flexibility, especially for complex websites and applications.
Key Features:
- Highly flexible and scalable for complex content architectures.
- Strong focus on security, suitable for government and enterprise use.
- Customizable content types, taxonomies, and access control.
- Multilingual capabilities built into the core.
- Integrates with various enterprise systems, including CRM and e-commerce platforms.
Pros:
- Extremely customizable, making it ideal for complex, large-scale projects.
- Strong security features, used by government organizations.
- Large developer community offering thousands of modules for added functionality.
- Flexible content modeling and structure for various use cases.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve, especially for non-developers.
- Requires technical expertise for setup, customization, and maintenance.
- Fewer themes and modules compared to WordPress.
- Development costs can be higher due to its complexity.
- Joomla was launched in 2005 as a fork of Mambo CMS and quickly gained popularity for its balance between ease of use and flexibility.
Launched:
- Joomla is a widely-used CMS, especially popular for building community and portal websites due to its built-in features for user management and content organization.
Global Ranking:
- Advanced user and content management features.
- Built-in multilingual support without the need for extensions.
- Supports multiple templates and layouts for different pages.
- Extensive plugin ecosystem with modules, components, and plugins for added functionality.
- Suitable for small to large websites, including e-commerce and social networking.
Key Features:
- Offers more flexibility out-of-the-box than WordPress for advanced users.
- Strong user management, suitable for community or membership-based sites.
- Built-in support for multiple languages.
- Good balance between usability and customization.
Pros:
- Smaller plugin and theme ecosystem compared to WordPress.
- Requires more technical knowledge for customization and optimization.
- Updates and maintenance can be more complex than WordPress.
- Less popular than WordPress, meaning fewer resources and support.
Cons:
Project Management Software
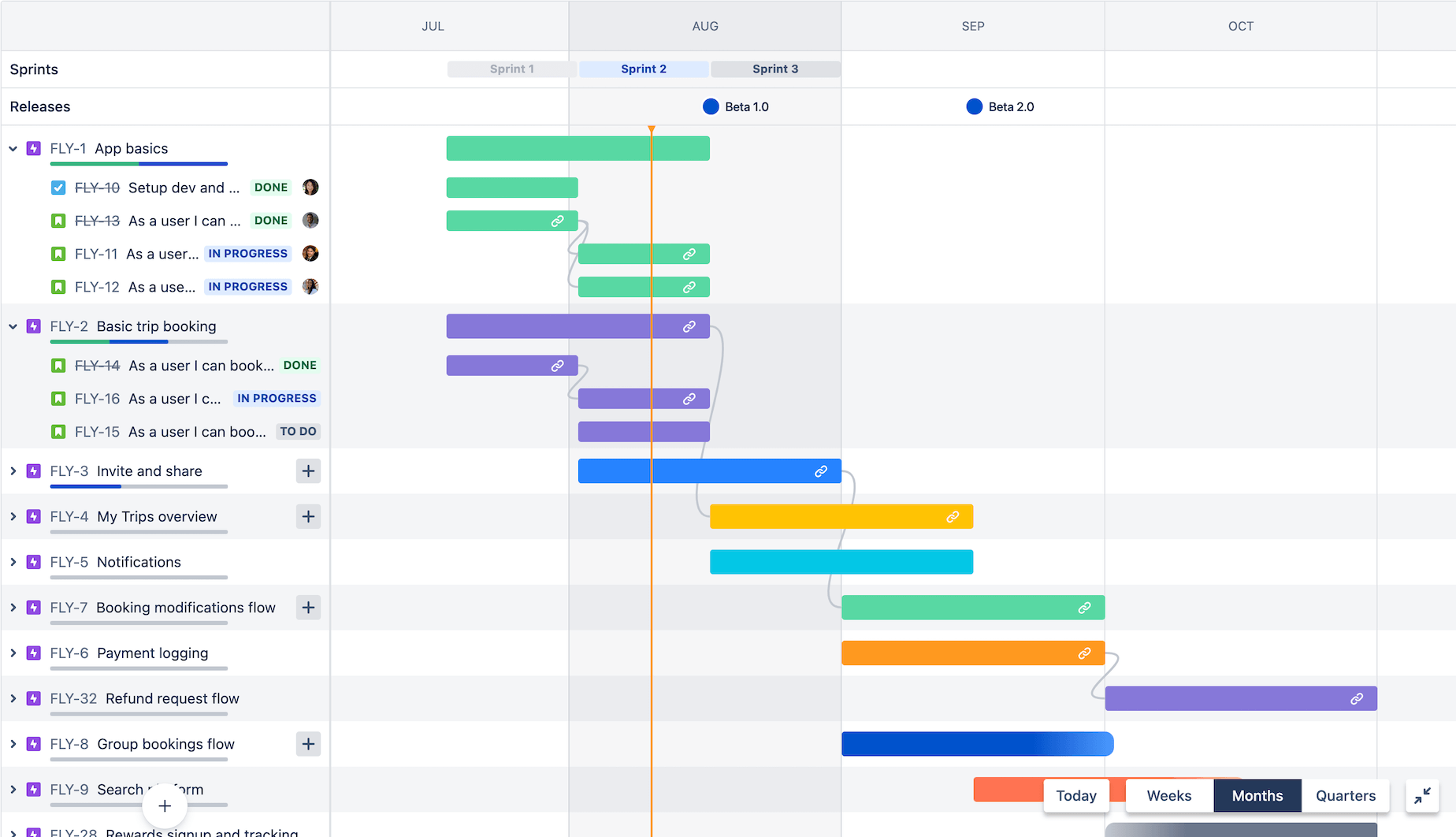
Project management software assists individuals and teams in planning, organizing, and executing projects effectively. Similar to an ERP system, it centralizes essential functionalities for a specific purpose: project success.
- Asana was founded in 2008 by Dustin Moskovitz and Justin Rosenstein, former Facebook executives, and officially launched to the public in 2011.
Launched:
- Asana is one of the most popular project management tools globally, known for its user-friendly interface and flexibility in managing tasks, projects, and workflows for teams of all sizes.
Global Ranking:
- Task and project tracking with customizable boards, lists, and timelines.
- Workflow automation, dependencies, and task assignment.
- Integration with over 100 apps, including Slack, Google Drive, and Microsoft Teams.
- Reporting, goal tracking, and workload management.
- Collaboration tools such as comments, file attachments, and shared dashboards.
Key Features:
- Easy to use with an intuitive interface, making it suitable for teams of all sizes.
- Versatile for both simple task management and complex project workflows.
- Strong integration with many other collaboration and productivity tools.
- Excellent for remote and distributed teams with real-time collaboration features.
Pros:
- Limited native time tracking (requires third-party tools).
- Customization options for complex workflows can be limited.
- Can get expensive with scaling for larger teams and enterprise use.
- Lacks advanced budgeting and resource management features compared to some competitors.
Cons:
- Trello was launched in 2011 by Fog Creek Software and later acquired by Atlassian in 2017.
Launched:
- Trello is widely popular for its simplicity and visual board-based project management, often favored by small teams and individuals.
Global Ranking:
- Kanban-style boards for task management.
- Drag-and-drop functionality for organizing tasks into lists and cards.
- Power-Ups (integrations) for adding features like time tracking, automation, and reporting.
- Collaboration features like comments, file attachments, and checklists.
- Mobile-friendly with a strong emphasis on usability across devices.
Key Features:
- Very easy to use, with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
- Great for visual task tracking and collaboration on small projects.
- Flexible for simple workflows and customizable through Power-Ups.
- Free tier available with sufficient features for small teams or personal use.
Pros:
- Limited functionality for complex project management needs (e.g., Gantt charts, advanced reporting).
- Not ideal for managing large projects with many dependencies or resource planning.
- Some Power-Ups (integrations) require paid plans.
- Lacks native time tracking, budgeting, or detailed reporting features.
Cons:
- Jira was launched by Atlassian in 2002 as a bug-tracking tool, but it has since evolved into a comprehensive project management platform, especially popular among software development teams.
Launched:
- Jira is highly regarded in the software development industry and is one of the top tools for agile and technical project management.
Global Ranking:
- Agile project management (scrum and kanban boards).
- Issue and bug tracking with customizable workflows.
- Sprint planning, backlog management, and release tracking.
- Integration with development tools like GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab.
- Extensive reporting, including burndown charts and velocity tracking.
Key Features:
- Ideal for software development teams following agile methodologies.
- Highly customizable workflows, permissions, and reporting features.
- Strong integration with development tools for seamless dev-ops.
- Robust tracking of bugs, issues, and project progress.
Pros:
- Steep learning curve, particularly for non-technical users.
- Can be overkill for non-software projects or small teams.
- Customization can be complex, requiring admin expertise.
- Pricing can be high for larger teams with advanced needs.
Cons:
Business Process Management (BPM) Software
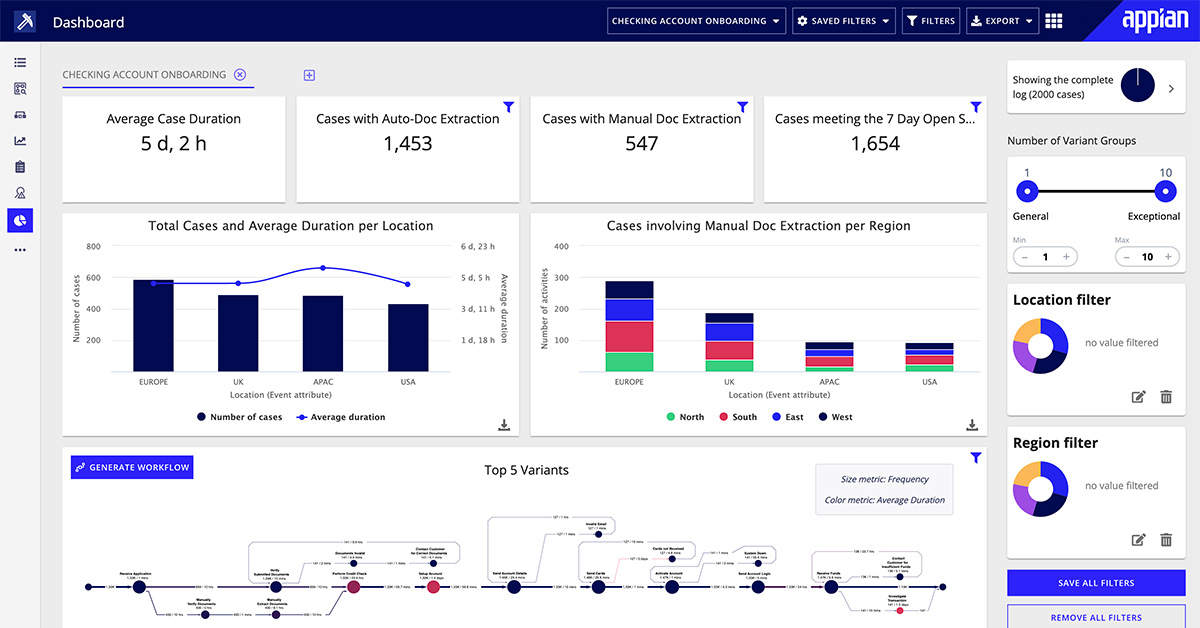
BPM or Business Process Management software helps organizations design, automate, optimize, and manage their business processes. It provides a framework to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and achieve strategic goals.
IBM Business Automation Workflow
- IBM Business Automation Workflow (BAW) is part of IBM's extensive suite of process management and automation tools, with roots going back to IBM’s acquisition of Lombardi Software in 2010.
Launched:
- IBM BAW is recognized as one of the most powerful BPM tools, especially favored by large enterprises for its robust integration with IBM’s cloud services and AI-driven process automation.
Global Ranking:
- Workflow management and business process automation.
- Process modeling, tracking, and optimization with BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation).
- Integration with IBM’s AI services for process insights and automation.
- Case management, human task management, and business rules.
- Scalable cloud-based and on-premise solutions.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive features for process automation and case management.
- Strong integration with other IBM products, including AI and analytics.
- Suitable for complex, large-scale enterprise environments.
- Robust security and compliance features.
Pros:
- High complexity and steep learning curve.
- Expensive, especially for small to medium-sized organizations.
- Implementation can be time-consuming and require deep expertise.
- May be overkill for simpler BPM needs.
Cons:
- Appian was founded in 1999, and its BPM platform quickly gained recognition for combining process automation with low-code development, enabling faster deployment of business solutions.
Launched:
- Appian is one of the leading BPM tools, particularly known for its low-code development platform, making it accessible for both technical and non-technical users.
Global Ranking:
- Low-code process automation for rapid app development.
- BPMN 2.0-based process modeling and automation.
- Workflow and task management with built-in AI and analytics.
- Integration with enterprise applications like SAP, Salesforce, and Oracle.
- Case management, document management, and data reporting.
Key Features:
- Low-code platform enables faster deployment and process automation.
- Strong process modeling and management capabilities.
- AI and machine learning integration for smarter process optimization.
- Easy to integrate with existing enterprise systems.
Pros:
- Licensing and usage costs can be high for large organizations.
- Complex workflows may still require advanced coding knowledge.
- Limited customization compared to more traditional BPM platforms.
- Time-consuming for scaling complex processes.
Cons:
- Pega was founded in 1983 and has evolved into a leader in BPM, with its Pega Platform offering an end-to-end solution for process automation and case management.
Launched:
- Pega is a top-tier BPM tool, especially strong in industries such as finance, insurance, and healthcare, where complex workflows and rules-based automation are critical.
Global Ranking:
- Business process automation and case management.
- AI-driven decision-making and workflow optimization.
- Integration with CRM, ERP, and legacy systems.
- Case management and BPMN-based process modeling.
- Low-code development tools for rapid automation deployment.
Key Features:
- Strong AI and machine learning capabilities for decision-making automation.
- Built-in case management for complex workflows.
- Powerful for handling compliance-heavy and rules-based industries.
- Low-code platform accelerates time to market for automation solutions.
Pros:
- High cost, especially for large enterprises with extensive process automation needs.
- Requires a high degree of customization for complex processes.
- Can have a steep learning curve for users new to BPM.
- Implementation and configuration can be time-intensive.
Cons:
Choose the Right Enterprise Software for Your Business
- Start with goals: What issues do you need to solve? What improvements do you seek?
- Budget matters: Set a realistic limit including implementation and support.
- Compare options: Research features, industry fit, and user feedback.
- Key aspects: Scalability, integrations, security, and vendor support matter most.
- Speak to users: Get real-world insights from references and online reviews.
- Read the fine print: Negotiate the contract, understanding costs and terms clearly.
Conclusion
From managing customers (CRM) and resources (ERP) to analyzing data (BI) and streamlining projects, there's a wide range of enterprise software to tackle various business needs. Consider goals, budget, features, and user feedback to choose the right tool for your organization, ensuring efficiency, better decisions, and growth.
