What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing & Why Should you Migrate
Introduction
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has become essential for businesses and individuals alike.
It enables the storage, management, and processing of data over the internet, offering flexibility, convenience, and accessibility from anywhere.
As more organizations move to the cloud, it has proven to be a vital tool for staying competitive and agile in an increasingly fast-paced technological world.
Before diving into the benefits of cloud computing, it’s important to understand what cloud computing actually is.
What is Cloud computing ?
Cloud computing is a way to access and use services like storage, software, and data over the internet instead of relying on local devices.
This means you can store files, run apps, and work with others from anywhere, without needing expensive hardware or complicated systems.
The cloud takes care of the heavy lifting, making it easier, more flexible, and cost-effective for individuals and businesses to manage their data and resources.
History of Cloud Computing
Early Beginnings
Time-Sharing in the 1960s:
- The concept of cloud computing can be traced back to the 1960s with the idea of time-sharing. This allowed multiple users to access a single computer system simultaneously, making computing resources more efficient and accessible1.
- In 1963, MIT’s Project MAC received funding to develop technology for multiple users to share a computer, laying the groundwork for cloud computing1.
Evolution
Development of ARPANET:
- In 1969, ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) was created, which was a precursor to the internet. It allowed computers to communicate with each other over long distances1.
- J.C.R. Licklider, a key figure in ARPANET’s development, envisioned an “Intergalactic Computer Network” where everyone could access data from anywhere1.
Rise of the Internet and Virtualization:
- The internet’s growth in the 1990s made it possible to connect computers globally, which is essential for cloud computing1.
- Virtualization technology emerged, allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. This made computing resources more flexible and efficient1.
Modern Era
Emergence of Major Cloud Service Providers:
- In 2002, Amazon launched Amazon Web Services (AWS), offering cloud-based services like storage and computing power2.
- Microsoft introduced Azure in 2010, providing a wide range of cloud services for businesses2.
- Google followed with Google Cloud Platform, offering scalable and reliable cloud solutions2.
These developments have made cloud computing a cornerstone of modern technology, enabling businesses and individuals to access powerful computing resources over the internet.
Evolution of Cloud Computing
Technological Advancements
High-Speed Internet:
- The widespread availability of high-speed internet has been crucial for cloud computing. Faster internet speeds allow for quicker data transfer and more reliable access to cloud services1.
Advanced Data Centers:
- Modern data centers are the backbone of cloud computing. They use cutting-edge hardware and software to provide scalable, efficient, and reliable services. Innovations like solid-state drives (SSDs) and advanced cooling systems have significantly improved data center performance1.
Improved Security Protocols:
- Security has always been a major concern for cloud computing. Advances in encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems have made cloud services much more secure1.
Adoption Trends
Businesses:
- Initially, small and medium-sized businesses adopted cloud solutions to reduce costs and improve flexibility. Over time, even large enterprises have moved to the cloud to take advantage of its scalability and advanced features2.
- Cloud computing has enabled businesses to innovate faster, as they can quickly deploy and scale applications without investing heavily in physical infrastructure2.
Individuals:
- Cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and iCloud have become integral to daily life, offering convenient storage and access to personal data from any device2.
- The rise of remote work, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, has accelerated the adoption of cloud-based collaboration tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams2.
Timeline of Cloud Adoption
2002: Amazon Web Services (AWS) launches, offering cloud storage and computing services3.
2006: Google introduces Google Docs, one of the first cloud-based office suites3.
2010: Microsoft launches Azure, expanding the cloud market with a wide range of services3.
2011: Apple introduces iCloud, bringing cloud storage to the masses3.
2014: Google Cloud Platform (GCP) becomes a major player in the cloud market3.
2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates cloud adoption as businesses and individuals rely heavily on cloud services for remote work and collaboration3.
These advancements and trends have made cloud computing an essential part of modern technology, driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors.
Types of Cloud Delivery Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- What it is: IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. This includes virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- How it works: Instead of buying physical servers, businesses can rent virtual servers and storage from an IaaS provider. This allows them to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- What it is: PaaS offers a platform that allows customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
- How it works: Developers can focus on writing code and deploying applications, while the PaaS provider handles the servers, storage, and networking. This simplifies the development process and speeds up deployment.
- Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services, and Heroku.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- What it is: SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications via a web browser without needing to install or maintain them.
- How it works: The SaaS provider hosts and manages the software, ensuring it is always up-to-date and available. Users simply log in and use the software as needed.
- Examples: Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft Office 365, and Salesforce.
These delivery models offer different levels of control, flexibility, and management, catering to various needs and preferences in the cloud computing landscape.
Key Breakthroughs in Cloud Computing
Virtualization:
- Enables multiple virtual machines on a single physical server.
- Maximizes resource use and reduces hardware costs.
Containerization:
- Packages applications and dependencies for consistent deployment.
- Improves scalability and portability.
Serverless Computing:
- Eliminates server management for developers.
- Offers cost efficiency and rapid deployment.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
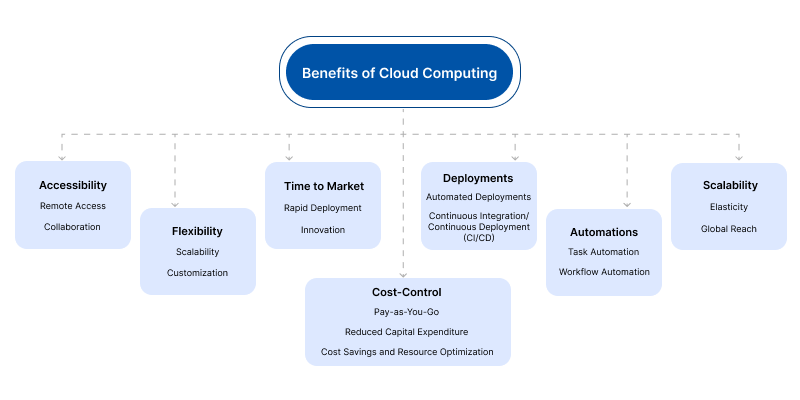
Accessibility
a. Remote Access:
- Cloud computing allows access to applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This means you can work from home, a coffee shop, or even while traveling, as long as you have internet access.
- Enables access to the latest versions of files and applications, ensuring you always work with the most up-to-date information.
- Supports remote troubleshooting and IT support, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
b. Collaboration:
- Cloud solutions enable real-time collaboration among teams. Multiple people can work on the same document or project simultaneously, making teamwork more efficient and seamless.
- Facilitates communication through integrated tools like chat, video conferencing, and shared calendars.
- Enhances project management with tools that track changes, assign tasks, and monitor progress.
Flexibility
a. Scalability:
- Cloud services can easily scale resources up or down based on demand. If your business needs more computing power or storage, you can quickly adjust without having to buy new hardware.
- Supports seasonal or temporary increases in workload without long-term commitments.
- Provides automatic scaling features that adjust resources in real-time to meet demand.
b. Customization:
- Cloud services can be tailored to meet specific business needs. You can choose the features and services that best suit your requirements, making it a flexible solution.
- Allows integration with existing systems and software, providing a seamless workflow.
- Offers customizable security settings to meet compliance and regulatory requirements.
Cost-Control
a. Pay-as-You-Go:
- The pay-as-you-go pricing model means you only pay for the resources you use. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- Reduces waste by eliminating the need to over-provision resources.
- Provides predictable billing, making it easier to manage budgets.
b. Reduced Capital Expenditure:
- Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant upfront investment in hardware. Instead of buying expensive servers and equipment, you can rent them from a cloud provider.
- Lowers maintenance costs as the cloud provider handles hardware upkeep and upgrades.
- Frees up capital for other strategic investments.
c. Cost Savings and Resource Optimization:
- Cloud computing optimizes resource usage by allocating resources as needed. This reduces overall costs and ensures efficient use of computing power and storage.
- Minimizes energy consumption and physical space requirements.
- Offers cost-effective disaster recovery solutions.
Time to Market
a. Rapid Deployment:
- Cloud services enable faster deployment of applications and services. You can launch new products or features quickly without the delays associated with setting up physical infrastructure.
- Reduces time spent on procurement and installation of hardware.
- Allows for quick scaling of development and testing environments.
b. Innovation:
- Cloud computing accelerates innovation by providing access to the latest technologies. Developers can experiment with new tools and services without worrying about infrastructure constraints.
- Encourages the adoption of emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT.
- Supports agile development practices, enabling faster iteration and improvement.
Deployments
a. Automated Deployments:
- Automated deployment processes in the cloud streamline the release of new software versions. This reduces manual errors and speeds up the deployment process.
- Ensures consistency and reliability across different environments.
- Facilitates rollback capabilities in case of deployment issues.
b. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
- CI/CD pipelines improve software development and deployment by automating testing and integration. This ensures that new code is quickly and reliably integrated into the main codebase.
- Enhances code quality through automated testing and validation.
- Reduces the time between development and production, enabling faster delivery of features.
Automations
a. Task Automation:
- Cloud platforms offer tools for automating routine tasks, such as backups, updates, and monitoring. This frees up time for IT staff to focus on more strategic activities.
- Improves consistency and reduces the risk of human error.
- Enhances system reliability and performance through regular automated maintenance.
b. Workflow Automation:
- Automating business workflows in the cloud improves efficiency and reduces the risk of human error. Tasks like data entry, approvals, and notifications can be automated to streamline operations.
- Increases productivity by reducing manual intervention.
- Provides better visibility and tracking of business processes.
Scalability
a. Elasticity:
- Cloud services can handle varying workloads efficiently. They automatically adjust resources to match the current demand, ensuring optimal performance.
- Supports burst workloads without performance degradation.
- Provides cost savings by scaling down resources during low-demand periods.
b. Global Reach:
- Cloud providers offer services across multiple geographic regions. This allows businesses to serve customers worldwide with low latency and high availability.
- Ensures data redundancy and disaster recovery through geographically distributed data centers.
- Complies with local data residency requirements.
c. Scalability and Elasticity:
- The ability to scale resources up or down and handle varying workloads is a key advantage of cloud computing. It ensures that businesses can meet demand without over-provisioning resources.
- Supports growth and expansion without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Enhances user experience by maintaining consistent performance during peak times.
These benefits highlight how cloud computing can transform the way businesses and individuals operate, offering flexibility, cost savings, and improved efficiency.
Benefits of Cloud-Based Software
Seamless Updates and Accessibility
- Automatic Updates: Cloud-based software ensures users always have access to the latest features and updates. Updates are automatically applied, so users don’t need to worry about manual installations.
- Accessibility from Any Device: Users can access cloud-based software from any device with an internet connection, ensuring they can work from anywhere.
- Reduced Downtime: Automatic updates minimize downtime, as updates are applied without interrupting user activities.
- Consistent User Experience: Ensures a consistent user experience across different devices and locations.
Increased Operational Efficiency
- Centralized Management: Cloud-based software allows for centralized management of applications and data, simplifying IT administration.
- Resource Optimization: Optimizes resource usage by dynamically allocating computing power and storage based on demand.
- Scalability: Easily scales to accommodate growing business needs without the need for additional hardware.
- Reduced Maintenance: The cloud provider handles maintenance tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
Enhanced Collaboration and Remote Work Capabilities
- Real-Time Collaboration: Cloud-based software facilitates real-time collaboration among team members, allowing multiple users to work on the same document or project simultaneously.
- Integrated Communication Tools: Often includes integrated communication tools like chat, video conferencing, and shared calendars, enhancing team communication.
- Remote Access: Supports remote work by providing secure access to applications and data from any location.
- Version Control: Ensures that all team members are working on the latest version of a document, reducing confusion and errors.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- Automated Backups: Cloud-based software often includes automated backup solutions, ensuring data is regularly backed up and can be quickly restored.
- High Availability: Ensures high availability and uptime, reducing the risk of downtime and data loss.
- Geographic Redundancy: Data is often stored in multiple geographic locations, providing additional protection against data loss.
User Experience and Support
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Cloud-based software typically features user-friendly interfaces, making it easy for users to navigate and use.
- Customer Support: Provides access to customer support and resources, helping users resolve issues quickly.
- Training and Resources: Often includes training materials and resources to help users get the most out of the software.
These additional points further highlight the comprehensive benefits of cloud-based software, making it a valuable solution for businesses and individuals alike
Practical Applications of Cloud Computing
.png)
Industry-Specific Uses
a. Healthcare:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Cloud computing allows healthcare providers to store and access patient records securely from any location.
- Telemedicine: Enables remote consultations and monitoring, improving access to healthcare services.
- Data Analytics: Helps in analyzing large datasets for research and improving patient outcomes.
b. Finance:
- Online Banking: Cloud services support secure online banking platforms, enabling customers to manage their finances remotely.
- Fraud Detection: Uses advanced analytics and machine learning to detect and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists financial institutions in meeting regulatory requirements by providing secure and compliant data storage solutions.
c. Education:
- E-Learning Platforms: Cloud-based platforms facilitate online learning and virtual classrooms, making education accessible to a wider audience.
- Collaboration Tools: Supports collaboration among students and teachers through shared documents and communication tools.
- Resource Management: Helps educational institutions manage resources efficiently, from student records to administrative tasks.
Real-World Examples
a. Netflix:
- Content Delivery: Uses cloud computing to stream content to millions of users worldwide, ensuring high availability and performance.
- Data Analytics: Analyzes viewer data to recommend personalized content and improve user experience.
- Scalability: Scales resources up or down based on demand, especially during peak viewing times.
b. Airbnb:
- Platform Management: Manages its global platform using cloud services, ensuring reliability and scalability.
- Data Security: Protects user data with advanced security measures provided by cloud providers.
- Innovation: Quickly deploys new features and updates to enhance the user experience.
c. Spotify:
- Music Streaming: Delivers music to users through a cloud-based platform, ensuring seamless streaming and high availability.
- Personalization: Uses data analytics to create personalized playlists and recommendations.
- Global Reach: Supports a global user base with low latency and high performance.
Future Trends
a. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
- Enhanced Services: Cloud platforms integrate AI and ML to offer advanced services like predictive analytics and automation.
- Personalization: Improves personalization in applications by analyzing user behavior and preferences.
- Efficiency: Increases operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and processes.
b. Internet of Things (IoT):
- Connected Devices: Supports the management and analysis of data from connected devices, enabling smart homes and cities.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time monitoring and control of IoT devices, improving efficiency and safety.
- Data Integration: Integrates data from various IoT devices for comprehensive analysis and decision-making.
c. Edge Computing:
- Reduced Latency: Brings computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving performance.
- Enhanced Security: Provides additional security by processing data locally before sending it to the cloud.
- Scalability: Complements cloud computing by handling data processing at the edge, reducing the load on central cloud servers.
These practical applications demonstrate how cloud computing is transforming various industries and driving innovation.
Why Should you Migrate ?
Migrating to the cloud offers numerous benefits, including greater flexibility and scalability, significant cost savings, and enhanced accessibility.
It provides robust security measures, supports disaster recovery, and accelerates innovation. Cloud migration also improves collaboration, ensures better resource optimization, and enhances competitive edge by enabling faster deployment of applications and services.
Overall, it transforms operations, making them more efficient, secure, and adaptable to changing needs.
Best Practices for Cloud Adoption
Here are some best practices for cloud adoption:
Planning and Strategy
- Assess Readiness: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure, applications, and team skills to determine cloud readiness.
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline your business goals and how cloud adoption aligns with them.
- Create a Roadmap: Develop a phased migration plan, prioritizing applications and workloads based on complexity and business impact.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from the beginning to ensure alignment and support throughout the adoption process12.
Security Best Practices
- Implement Strong Access Controls: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive data.
- Encrypt Data: Ensure data is encrypted both in transit and at rest to protect against unauthorized access.
- Regular Audits and Compliance Checks: Conduct regular security audits and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use security monitoring tools to detect and respond to threats in real-time12.
Cost Management
- Set Budgets and Alerts: Establish budgets for cloud spending and set up alerts to monitor usage and costs.
- Optimize Resource Usage: Use auto-scaling and right-sizing to ensure resources are used efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Leverage Reserved Instances: Take advantage of reserved instances and long-term commitments for predictable workloads to reduce costs.
- Regular Cost Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of cloud expenses and optimize based on usage patterns and business needs
Conclusion
Migrating to cloud computing offers a range of transformative benefits for businesses and individuals alike. By leveraging the cloud, organizations gain greater flexibility, scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced accessibility, enabling them to innovate faster and stay competitive.
Key advantages include streamlined deployments, automated processes, improved collaboration, disaster recovery, and access to advanced technologies like AI and IoT.
Cloud solutions enable efficient resource management, real-time collaboration, and global reach, making them essential for modern business operations.
For those seeking to optimize operations, reduce costs, and boost innovation, cloud migration is a strategic move.
