Enterprise Cloud Computing: Concepts, Platforms, and Use Cases
Enterprise systems support many digital operations, including customer platforms, internal business applications, data analytics, and large web services.
As these systems grow, many organizations struggle to manage rising infrastructure demands with traditional on-premise data centers. Hardware upkeep, capacity planning, and system upgrades often eat up significant time and resources.
This challenge has led to more cloud adoption, as businesses shift their workloads to cloud environments.
Gartner projects worldwide spending on public cloud services will reach over $723 billion in 2025. This figure points to large organizations' increasing reliance on cloud infrastructure for their business systems and enterprise applications.
The shift means cloud infrastructure is now a core part of modern enterprise technology and large-scale digital operations.
What Is Enterprise Cloud Computing?
Enterprise cloud computing refers to cloud environments designed to support the systems and operations of large organizations.
These environments provide the infrastructure and services required to run enterprise applications, store business data, and manage internal platforms used across different departments.
In an enterprise setting, cloud infrastructure supports a wide range of technology systems such as enterprise resource planning platforms, internal collaboration tools, customer-facing applications, and large data processing environments.
Organizations typically deploy these systems on cloud infrastructure provided by platforms like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
These platforms provide computing resources, storage systems, networking services, and cloud-based tools that enable enterprises to operate and manage large technology environments through cloud infrastructure.
Why Enterprises Are Moving From Traditional IT Infrastructure to Cloud
Enterprise technology environments have been growing tremendously as organizations depend on digital platform, enterprise software system, and large data environment to support operations of the business.
Previously used applications have now been utilized to provide support to customers, partners, and employees located in various locations.
Enterprise systems are becoming more complex to use and therefore, the infrastructure that is used should be able to accommodate more operational needs.
Growing Enterprise Systems
There is an enormous variety of digital systems in operation at modern enterprises, such as enterprise resource planning platforms, customer service applications, collaboration tools, and analytics platforms.
These systems handle large volumes of data while serving multiple departments and geographic locations, requiring efficient workload distribution through cloud load balancing.
The infrastructure needed to facilitate these systems increases as organizations increase their digital operations.
Limitations of On-Premise Infrastructure
Conventional on-premise infrastructure has meant that organizations have to implement physical servers, storage capabilities and networking appliances in data centers owned by the company.
To handle this environment, it includes purchasing of hardware and installing, maintaining, and upgrading it periodically.
With the increasing workloads of enterprises, IT teams need to constantly regulate the capacity of infrastructure and sustain systems to accommodate growing applications and data bases.
Cloud Infrastructure Approach
The cloud provides an opportunity to an enterprise to deploy applications and administer systems on a dispersed infrastructure instead of depending exclusively on internal data centers.
Cloud-based environments enable organizations to install enterprise software, handle business data as well as operate digital platforms using computing resources and infrastructure services delivered by externally controlled systems.
Enterprise Cloud Architecture and Infrastructure
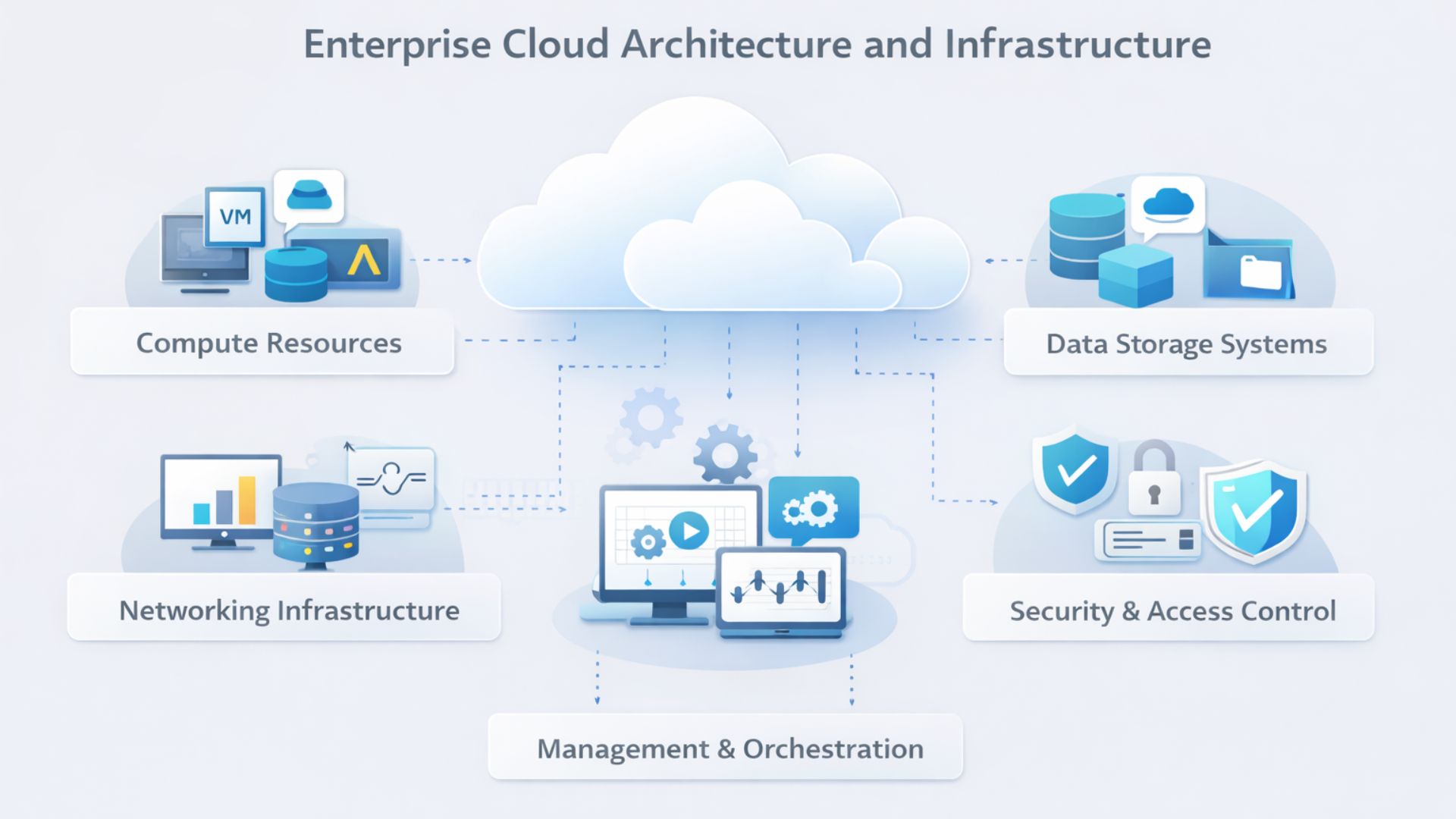
Enterprise cloud architecture is the definition of the structure of enterprise applications, data systems, and cloud infrastructure to enable business operations.
It explains the relationship between computing resources, storage systems, networking services, and management tools to execute enterprise software and digital platforms.
Most enterprise settings have users interfering with applications using web interface, in-house platform, or mobile tools whereas the processing, data storage, and infrastructure administration runs in the cloud.
Compute Resources
The computing resources are what offer the processing power to execute enterprise applications and business systems.
Typically, in cloud technologies, this involves virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing services used to run enterprise workloads, reflecting the advantages of containerization in modern application platforms.
Data Storage Systems
Enterprise cloud environments handle high amounts of business data created by applications and analytics systems as well as enterprise software platforms.
Cloud storage services can be applied to various kinds of storage, such as database storage of structured information, object storage of big data sets and backups, or file storage by enterprise applications.
Networking Infrastructure
Network infrastructure links applications, storage systems, and services in cloud environments.
This covers virtual networks, route systems, and load balancing services which facilitate communication between enterprise applications and users and other internal systems on distributed environments.
Security and Access Control
Security controls help safeguard enterprise applications and information stored in their cloud environments.
These controls include identity and access management systems, encryption tools, monitoring systems, and automated cloud security controls that regulate access to enterprise resources by users and services.
Management and Orchestration
Cloud environments in enterprises rely on management tools that enable teams to monitor infrastructure, deploy applications, and manage resources across enterprise cloud systems.
These systems assist the IT staff in monitoring enterprise platforms, system performance, and application operations within clouds.
All these elements collectively constitute the working infrastructure that sustains cloud-based environments of enterprises.
Enterprise applications execute on compute resources, business data is gathered and managed by storage systems, services and users are connected by networking, and access is controlled by security controls throughout the organization.
The management tools are used to organize these systems in order to allow the enterprise to implement applications, participate in internal platforms, and sustain the enterprise technology environments in cloud infrastructure.
Enterprise Cloud Service Models
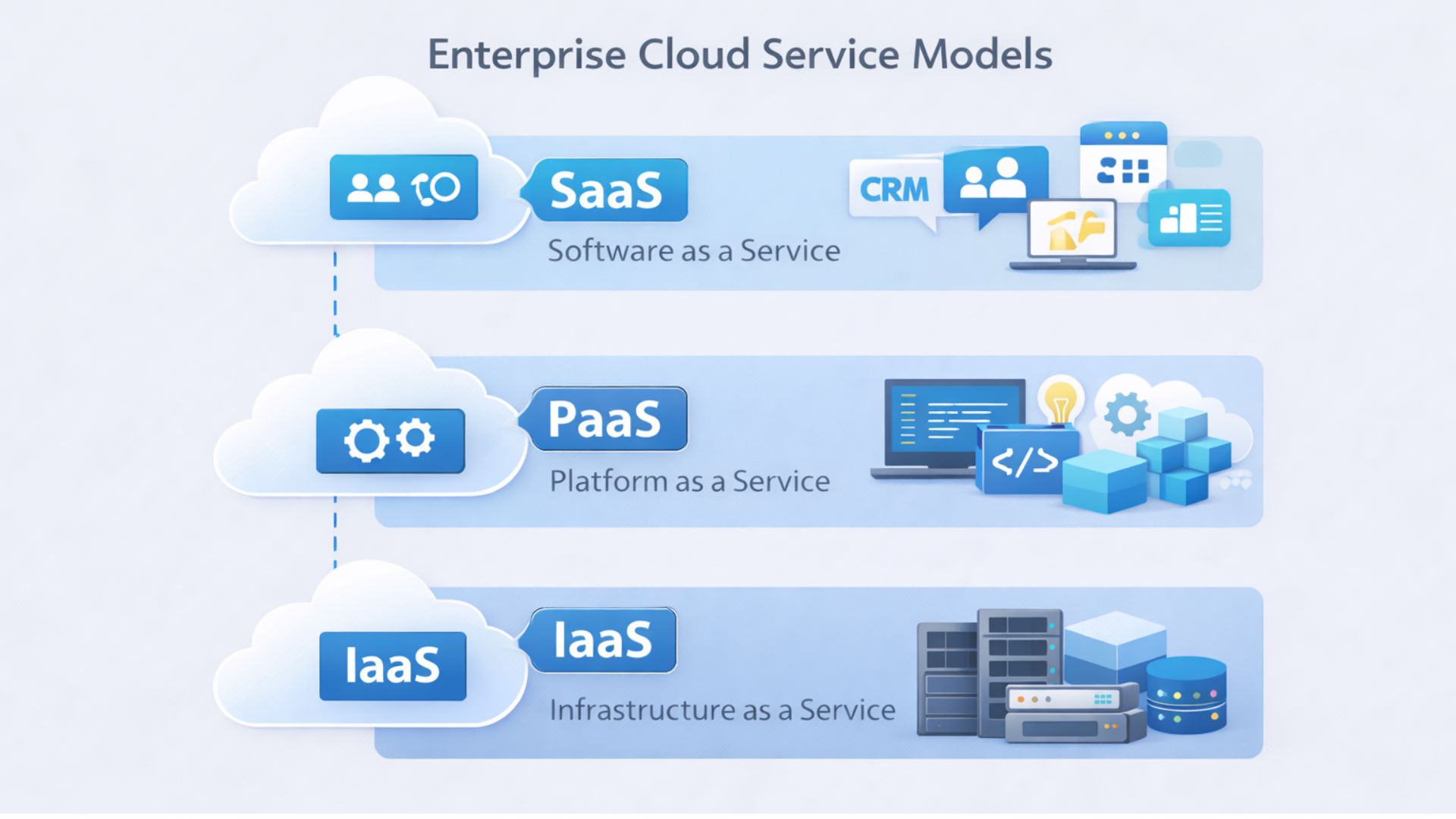
Enterprise cloud platforms deliver services through different layers that determine how organizations access software, build applications, and operate technology systems.
These service models define the level of control an enterprise has over applications, development environments, and infrastructure resources.
The three primary models used in enterprise cloud environments are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Types of Enterprise Cloud Service Models
Each model represents a different way enterprises interact with cloud platforms, depending on how much control they require over software, development environments, or infrastructure resources.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service offers web-based interfaces to enterprise software applications offered by organizations.
The cloud provider takes care of application infrastructure, software updates, and system maintenance letting the organizations concentrate on the usage of the software as opposed to managing it.
SaaS is typically used by enterprises in business applications that include customer relationship management applications, collaboration applications, human resource management applications, and project management applications.
These applications are relevant in the day to day running of businesses in various departments without having to have an internal infrastructure to execute the software.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service is the cloud based environments where one can build, test, and deploy applications.
These services consist of development tools, runtime environments, and deployment services enabling engineering teams to develop applications without having to control underlying infrastructure systems.
PaaS is commonly used to build internal business applications, customer platforms, and enterprise systems.
The teams of developers do not have to worry about their operating systems, runtime environments, or infrastructure services that are needed to run the applications and leave all these tasks to the cloud platform.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service offers basic computing facilities like data storage structures, virtual servers, and network infrastructure.
These resources can be configured to execute enterprise applications, databases, and business systems in the cloud environments by organizations.
They are used by enterprises that require more control over system environments, including running a large enterprise workload, data platform, or special applications requiring unique infrastructure settings.
Practically, organisations can hardly be satisfied with one model of service.
Organizations tend to combine cloud applications, development platforms, and infrastructure services to support various systems through multi-cloud & hybrid cloud strategies.
This multitiered strategy enables businesses to conduct business software, build in-house applications, and handle the complexity of enterprise workloads in the cloud.
Enterprise Cloud Deployment Models
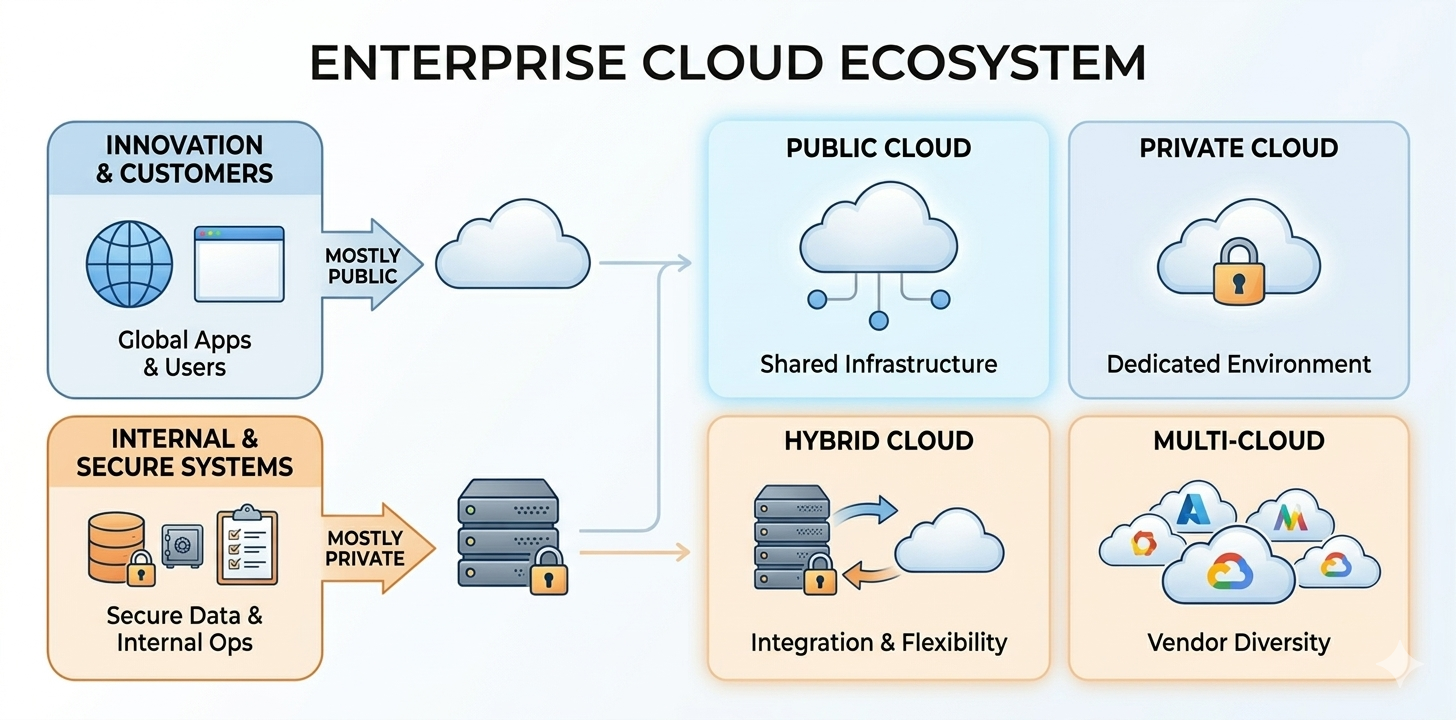
Enterprises do not adopt cloud infrastructure in a single uniform way. Different business systems, such as customer platforms, internal applications, and regulated data systems, often require different levels of control over infrastructure and data environments.
Cloud deployment models describe how organizations structure these environments and determine where enterprise applications and data systems operate within cloud infrastructure.
Public Cloud
Public cloud environments use infrastructure operated by external cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, where computing resources, storage systems, and networking services are delivered through shared cloud platforms.
Enterprises deploy applications and digital services on this infrastructure without operating their own data centers, including platforms used for building applications on Google Cloud.
This model is commonly used for customer-facing platforms, enterprise web applications built using modern cloud-native architectures, analytics environments, and other systems that require large computing capacity.
By using public cloud infrastructure, organizations can run enterprise workloads on externally managed environments rather than maintaining physical infrastructure internally.
Private Cloud
Private cloud environments are designed for a single organization and operate on dedicated infrastructure.
These environments can be hosted within a company’s own data centers or provided through managed cloud services designed for exclusive enterprise use.
Enterprises typically use private cloud environments when operating systems that handle sensitive business data or applications that require tighter control over infrastructure.
This model is often adopted by industries with strict regulatory requirements or internal policies governing data management and system access.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud environments combine private infrastructure with public cloud services. In this model, some enterprise systems operate within internal infrastructure while others run on public cloud platforms.
These environments allow organizations to integrate existing enterprise systems with cloud-based applications.
Enterprises often adopt hybrid cloud strategies when modernizing legacy systems or extending internal platforms with cloud services.
This approach allows organizations to gradually incorporate cloud infrastructure while maintaining certain systems within controlled environments.
Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud environments involve the use of multiple cloud providers within a single enterprise technology environment. Instead of relying on a single platform, organizations distribute applications and workloads across different cloud services.
Enterprises adopt multi-cloud strategies to support different technology requirements, deploy applications across multiple platforms, or maintain flexibility when operating enterprise systems.
This approach allows organizations to integrate various cloud services within one broader enterprise technology environment.
In practice, enterprise cloud environments are rarely limited to a single deployment approach. Organizations often run customer-facing platforms on public cloud infrastructure while maintaining internal or regulated systems within private environments.
Hybrid and multi-cloud architectures allow enterprises to integrate different platforms and distribute workloads across multiple cloud environments based on operational and technical requirements.
Business Benefits of Enterprise Cloud Computing
Enterprise cloud computing not only impacts infrastructure management. It transforms the way the organization creates applications, data processing, and support teams in the operation around the world.
These advantages in operation are the reasons why cloud infrastructure has become a fundamental element in the current enterprise technology strategies
Lower Infrastructure Costs
Cloud architecture eliminates excessive initial expenditures on server, data centers, and networking equipment. The organizations switch technology expenditure to service-based consumption as opposed to infrastructure-intensive consumption.
Faster Application Deployment
Applications and development environments can be quickly deployed on enterprise teams without having to wait to install hardware or to provide systems.
This enables organizations to publish digital services and internal tools more efficiently during enterprise software development workflows.
Improved Data Analytics
Cloud services are used to support high-scale data processing and analytics models. Cloud-based data platforms enable enterprises to analyze the data on their operations, customer behavior, and the performance of their business.
Support for Global Teams
The enterprise cloud platforms enable employees and partners to access the applications and internal systems at varying locations. This allows organizations to maintain dispersed teams and geographical cooperation.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Cloud infrastructure enables data and applications of the enterprise to be copied in more than one environment. This assists organizations in recovering systems and being operational in case of disruption in infrastructures.
Access to Advanced Technologies
Cloud environments make technologies like machine learning platforms available, analytics tools, and large data systems accessible without necessitating special hardware infrastructure.
Reduced Infrastructure Management
Some of the infrastructural maintenance activities taken by cloud platforms include server upgrade, capacity optimization, and reliability of hardware. This enables enterprise IT teams to concentrate more on the development of applications and improvement of the system.
Combined with these benefits, enterprise cloud infrastructure is a viable baseline of contemporary enterprise technology environments. Companies are able to run digital systems, handle big data, and support a globally distributed team without physically supporting complicated infrastructure.
Enterprise Cloud Cost Considerations
Enterprise cloud adoption changes how organizations approach technology spending.
Traditional infrastructure models often require large upfront investments in servers, storage systems, and data center facilities commonly referred to as capital expenditure (CapEx).
Cloud environments shift much of this spending toward operational expenditure (OpEx), where enterprises pay for infrastructure services based on actual usage rather than maintaining owned hardware environments.
Core Infrastructure Cost Drivers
These components form the primary sources of cloud infrastructure spending across enterprise environments.
Operational Cost Model
Cloud infrastructure replaces large upfront infrastructure purchases with service-based spending. Instead of maintaining excess hardware capacity, enterprises pay for infrastructure services as part of ongoing technology operations. This model allows organizations to adjust infrastructure usage without long-term hardware commitments.
Usage-Based Pricing
Most cloud platforms use consumption-based pricing, where organizations pay according to the resources their applications consume. Computing power, storage capacity, and network usage increase or decrease depending on operational demand. Because cloud infrastructure can scale up or down based on workload activity, infrastructure spending often adjusts alongside application usage.
Cloud Cost Management
Enterprises often monitor cloud usage through cost management and reporting tools that track how resources are consumed across systems and departments. These tools help organizations identify underutilized resources, adjust infrastructure capacity, and maintain visibility into cloud spending as enterprise systems scale.
Hidden Cost Factors
Certain operational factors can influence overall cloud spending if they are not monitored carefully. Data transfer between systems, long-running workloads, and premium support services can increase operational costs over time. Understanding these factors helps organizations manage infrastructure budgets and avoid unexpected expenses as cloud environments expand.
When managed effectively, enterprise cloud cost models provide organizations with greater control over how infrastructure resources are allocated, allowing technology spending to adapt to evolving operational demands.
Enterprise Cloud Applications and Use Cases
Enterprise cloud infrastructure hosts various operational systems used by enterprises. These operational systems include data analytics systems, application development environments, recovery environments, and digital services that must respond to changing workloads.
In addition to these operational use cases, cloud infrastructure has various applications within different industries that are utilized to run different sectoral applications such as financial transaction systems, healthcare data analytics systems, and e-commerce services.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Enterprises use cloud infrastructure to run data analytics systems that process large quantities of operational data as well as customer data.
These data analytics systems provide business intelligence reports that help organizations monitor their operations as well as predict operational patterns.
Software Development and Testing
Software developers use cloud infrastructure to provide temporary environments that are utilized by software developers to develop enterprise software applications.
These temporary environments allow software developers to launch development environments that are utilized to test new software features as well as remove testing environments when they are no longer necessary.
Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Cloud computing is used by enterprises in replicating applications and data in various infrastructure locations. These applications help in recovering applications and data in instances where the applications and data are inaccessible.
Infrastructure Scaling
Enterprise software applications require scaling up during times of increased workloads. Cloud infrastructure is utilized by various organizations to provide scalable infrastructure that is utilized by various software applications during times of increased workloads.
Industry Specific Use Cases
Enterprise cloud infrastructure supports both core technology functions and industry-specific platforms. Organizations apply cloud environments to run data systems, operate digital services, and manage business applications that support large-scale enterprise operations.
Challenges in Enterprise Cloud Adoption
The implementation of the enterprise cloud infrastructure is not just about relocating the applications to a different technology platform. The main issues that organizations have to control include technical, operational, and organizational aspects as the cloud platform becomes a part of the main IT systems of the organization.
Knowledge of these issues aids enterprises in developing cloud plans that tackle the complexity of the infrastructure, governance needs and long term management of operations.
System Migration Complexity
Cloud services can be scaled at a rapid rate with the introduction of new applications and services by teams.
In the absence of defined governance policies, the organization can experience disorganized security practices, a lack of control over use of resources, or even duplication of systems in various departments.
Setting up governance structures assists companies in retaining authority over the use of the cloud, infrastructure policies, and standards of operation.
Security and Regulatory Compliance
Businesses have to make sure that the cloud environment addresses both internal security and external regulatory standards.
Companies that manage sensitive data, including financial data, healthcare data, and customer data, should enforce tough access control, monitoring tools, and encryption measures while ensuring that they comply with industry regulations and laws of data protection.
Cloud Cost Management
Despite the flexibility of pricing models used in cloud infrastructure, it is not always easy to control the usage of cloud infrastructure in large enterprise settings.
There are several applications, groups, and services that can use infrastructure resources concurrently and it is hard to trace the pattern of spending. Monitoring tools and governance policies are usually needed by organizations to ensure they have visibility on cloud use and avoid wastage of resources.
Skills and Technical Expertise
Expertise in cloud architecture, cloud security, and automation of the infrastructure is required in enterprise cloud environments.
Lack of professionals with profound experience in these fields can hold an organization back, or even change more heavily on outside consultants and managed service providers.
Vendor Dependency
Migrating enterprise systems to a new provider may be a complicated process when the latter are developed based on a particular cloud platform.
The differences in platform services, infrastructure tools, and system configurations can be associated with a lot of redevelopment work. This is why long-term cloud approaches are frequently considered by enterprises before they commit to one of the providers.
Governance and Operational Control
Cloud services can be scaled at a rapid rate with the introduction of new applications and services by teams. In the absence of defined governance policies, the organization can experience disorganized security practices, a lack of control over use of resources, or even duplication of systems in various departments.
Setting up governance structures assists companies in retaining authority over the use of the cloud, infrastructure policies, and standards of operation.
Conclusion
Large organization cloud computing has now been a center to the current technology plans. Enterprise applications, data systems, and other digital platforms are only growing and therefore, cloud infrastructure offers the platform to make these environments functional at scale.
Enterprises rely on cloud systems to facilitate important business processes and changing digital services, on top of analytics platforms and development environments, as well as industry specific applications.
Simultaneously, successful cloud adoption needs careful planning. The cloud strategy requires associations to analyze infrastructure architecture, cost models, policy governance, and difficulty in operations.
With a simple and straightforward strategy, an enterprise cloud environment enables companies to run sophisticated technology environments and promote long-term innovation, data-driven decisions, and international digital operations.
