How Much Does it Cost to Develop a Mobile Banking App?

Most banking apps in 2025 cost between $50,000 and $300,000 to build a serious MVP. Enterprise banking platforms that support advanced security controls, AI-driven features, and multi-region regulatory compliance can exceed $1 million.
That gap exists because a banking app today can refer to many different product types. According to recent mobile banking statistics published by Coinlaw, more than 2.17 billion people were using mobile banking services by the end of 2025, and in markets like the United States, nearly three out of four adults now rely on mobile banking for daily financial activity.
As mobile banking becomes the primary channel, even early-stage apps are expected to handle identity verification, fraud prevention, regulatory reporting, and integrations with payment networks. Each requirement adds engineering effort and long-term cost. Understanding these cost drivers upfront is essential before finalizing scope, timelines, or development strategy.
What counts as a banking app?
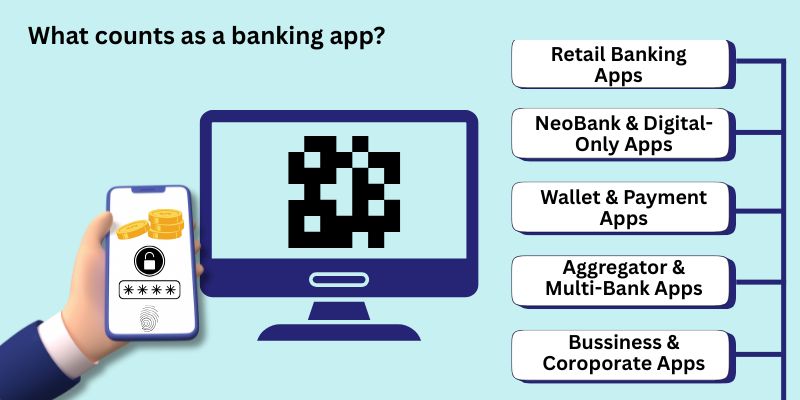
The term “banking app” is often used broadly, but in practice it covers several distinct product types. Each type comes with different functional expectations, regulatory requirements, and development costs. Understanding which category your product falls into is essential before estimating budget or timelines.
Below are the most common types of banking applications businesses develop today.
Retail banking apps
Retail banking apps are built for traditional banks and credit unions to serve individual customers. These apps typically support account management, transfers, bill payments, card controls, notifications, and customer support. Because they must integrate with legacy core banking systems and meet strict regulatory requirements, development costs are usually higher than basic fintech products.
Neobank and digital-only banking apps
Neobanks operate without physical branches and rely entirely on digital channels. Their apps often include faster onboarding, in-app KYC, spending insights, card issuance, and integrations with third-party financial services. While these apps may launch with a focused feature set, expectations around security and compliance remain high, which directly influences development cost.
Wallet and payment apps
Wallet-based apps focus on payments rather than full banking services. Common features include peer-to-peer transfers, QR payments, merchant transactions, and card linking. These apps typically have lower initial development costs but may require extensive integrations with payment gateways, fraud monitoring tools, and identity verification services as they scale.
Aggregator and multi-bank apps
Aggregator apps allow users to view and manage accounts from multiple banks in one place. They rely heavily on third-party APIs and open banking frameworks to retrieve and sync data. While these apps can be less complex on the surface, integration reliability and data security significantly affect development effort and long-term maintenance costs.
Business and corporate banking apps
Business banking apps are designed for SMBs or enterprises. They often support multi-user access, role-based permissions, approvals, payroll, invoicing, and advanced reporting. These requirements increase backend complexity and compliance overhead, making development more expensive than consumer-only banking apps.
Each of these app types involves a different balance of features, integrations, and regulatory exposure. As a result, two products both labeled “banking apps” can have vastly different development costs, even before features are finalized.
Key factors that influence banking app development cost
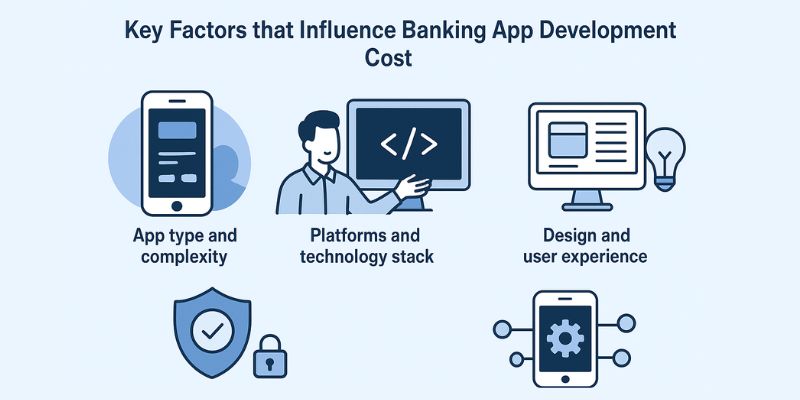
Banking app development cost is shaped by several structural and operational factors, not just the number of features included. Decisions around compliance, integrations, technology, and delivery approach have a measurable impact on both initial build cost and long-term expenses. Understanding these factors early helps teams plan budgets more accurately and avoid scope-related overruns during development.
Cost estimates also depend on whether development is led by general app development teams or specialists familiar with regulatory controls, transaction security, and compliance-driven workflows.
Below are the factors that most directly influence the cost of developing a banking application.
App type and complexity
The type of banking app being developed sets the baseline for cost and effort. A payment or wallet-based app typically requires fewer backend systems and regulatory checks than a retail or corporate banking platform. As complexity increases through multi-account handling, lending workflows, or cross-border transactions, development effort expands across backend logic, testing, and compliance review.
Cost impact increases with:
- Multiple account types or currencies
- Lending, investment, or business banking features
- Support for cross-border transactions
Platforms and technology stack
The choice between native development and cross-platform frameworks affects development time, team size, and maintenance effort. Native apps usually require separate development for iOS and Android, increasing cost. Cross-platform frameworks can reduce initial development effort but may introduce additional work for platform-specific behavior and long-term upgrades.
For teams evaluating cross-platform frameworks, planning early for developing a cross-platform app helps balance upfront savings with long-term maintenance and integration effort in banking applications.
Technology decisions also affect how easily the app integrates with:
- Core banking systems
- Payment gateways
- Compliance and reporting tools
Design and user experience
Banking apps must balance clarity with complexity. User journeys often include onboarding, identity verification, payments, and approvals, all of which require careful UX planning. Design costs include user research, wireframing, interface design, and usability testing.
While deeper design work increases upfront investment, it often reduces rework, support queries, and post-launch fixes.
Security and compliance requirements
Security and compliance obligations are a major cost driver in banking app development. Requirements such as encrypted data storage, secure authentication, audit trails, and regulatory reporting add engineering and testing effort.
Costs rise further when the app must meet:
- Multiple regional regulations
- Ongoing compliance audits
- Industry security standards
Third-party and core banking integrations
Most banking applications rely on third-party services for functions such as identity verification, payment processing, notifications, and credit checks. Integration work includes API configuration, error handling, and testing under different transaction scenarios. This effort increases further when card networks and settlement systems are involved, where careful payment API setup is required to ensure secure transaction flows.
Apps that integrate with legacy core banking systems often require additional development time due to system constraints and data synchronization needs.
Team composition and development location
Development cost varies based on the team structure and geographic location. Rates differ significantly across regions, and projects that require security specialists, QA engineers, or compliance expertise typically involve larger teams.
Teams building regulated products often reduce long-term delivery and compliance risk by relying on fintech app development solutions built to handle regulatory validation and integration complexity early in the development lifecycle.
Cost considerations include:
- In-house versus outsourced teams
- Team size and role specialization
- Coordination and delivery overhead
Maintenance, updates, and operational support
Banking app development does not end at launch. Ongoing costs include bug fixes, platform updates, infrastructure management, security patches, and compliance reviews. These recurring efforts should be factored into any realistic estimate of total ownership cost.
Feature-wise cost breakdown
The overall cost of building a banking app increases primarily with the number, complexity, and security requirements of the features included. Each feature adds development effort through backend logic, integrations, testing, and compliance checks. For this reason, feature selection plays a central role in controlling banking app development cost.
Below is a breakdown of commonly implemented banking app features along with typical cost ranges based on development complexity and integration effort.
Core banking features
These features form the foundation of most banking applications and are usually included in an initial release.
Account Management and Fund Transfers ($10,000–$20,000)
Covers balance checks, transaction history, and internal or external transfers. These are baseline features for any banking app and follow established development patterns, keeping costs relatively predictable.
Customer Support ($10,000–$25,000)
Includes in-app messaging, FAQs, and ticket-based support. Costs depend on whether support is custom-built or integrated with an existing customer service platform.
Security Features ($50,000–$100,000+)
Includes secure authentication, encrypted data handling, and transaction protection measures. Costs increase as additional layers such as biometric access or transaction validation flows are added.
Advanced and value-added features
These features are typically added after the core functionality is in place and can significantly influence the overall budget.
Personal Finance Management ($20,000–$50,000)
Budgeting tools, spending breakdowns, and financial insights require additional data processing and custom interfaces, increasing both frontend and backend effort.
Investment Services ($50,000–$150,000)
Stock trading and portfolio management involve third-party integrations, regulatory oversight, and careful handling of financial data, making these among the more expensive features to implement.
Loan Management ($30,000–$80,000)
Loan applications, approval workflows, and repayment tracking require integrations with lending systems and strict handling of customer data.
Feature selection and budgeting considerations
Feature costs can rise quickly when apps target multiple regions, connect to legacy banking systems, or require extensive compliance checks. To manage budgets effectively, many teams focus on launching with essential features first and expanding functionality in later stages.
From a planning perspective, it is often more efficient to:
- Identify which features are mandatory at launch
- Defer high-complexity features to post-launch phases
- Align feature scope with the intended app type and market
This feature-level view provides a clearer link between functionality and budget, which sets the stage for evaluating cost based on overall app complexity.
Banking app development cost by complexity level
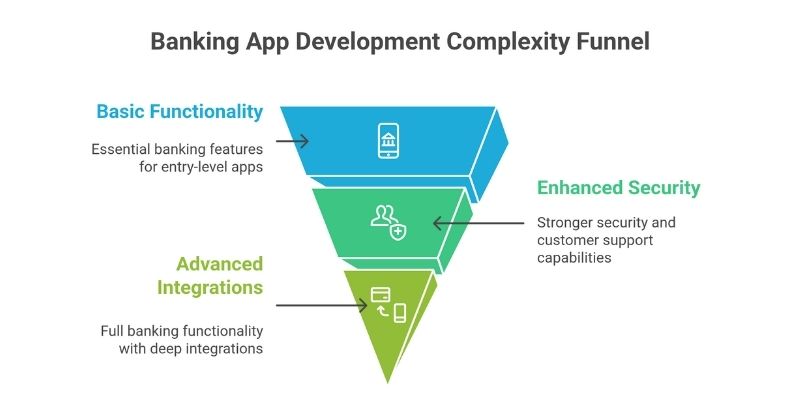
Banking app development cost scales with the overall complexity of the product rather than individual features alone. Complexity is defined by the depth of functionality, number of integrations, security requirements, and regulatory exposure. Most banking applications fall into one of three categories: basic, mid-level, or advanced.
Understanding these levels helps teams estimate costs more realistically before committing to scope or timelines.
Basic banking app
Estimated cost: $50,000-$100,000 Typical build time: 3-4 months
Basic banking apps focus on essential banking functionality and are often used as entry-level products or internal extensions of existing systems.
Common features include:
- User registration and authentication
- Balance viewing and transaction history
- Basic transfers within the same bank
- Simple notifications
- Foundational security controls
Best suited for: Small financial institutions, regional banks, or startups looking to launch a limited-scope product before expanding functionality.
Mid-level banking app
Estimated cost: $100,000-$300,000 Typical build time: 5-8 months
Mid-level apps support a broader range of banking activities and introduce stronger security and customer support capabilities.
Common features include:
- Multiple account management
- Inter-bank transfers and scheduled payments
- In-app customer support
- Alerts and notifications
- Identity verification workflows
- Entry-level personal finance tools
Best suited for: Growing banks or fintech companies targeting active retail users with a more complete mobile banking experience.
Advanced banking app
Estimated cost: $300,000-$1,000,000+ Typical build time: 9-15 months
Advanced banking apps are built for organizations that require full banking functionality, deep integrations, and extensive compliance support.
Common features include:
- Complex account structures
- Investment and lending modules
- Business or corporate banking workflows
- Multiple third-party and core banking integrations
- Data analytics and reporting
- Advanced security and fraud prevention systems
Best suited for: Enterprise banks and financial institutions operating across regions with strict regulatory obligations.
How complexity influences cost
As app complexity increases, costs rise due to:
- Larger development teams
- Deeper integrations
- Longer testing cycles
- Greater compliance and security requirements
This tier-based view helps bridge the gap between feature planning and realistic budgeting.
Example cost and timeline for a mid-level banking app
Scenario overview
This example outlines the development scope, timeline, and cost for a mid-level retail banking application designed for individual users in a single primary market. The application supports common day-to-day banking activities, includes standard security controls, and integrates with external payment and identity verification services.
Target audience: Retail banking customers Supported platforms: iOS and Android Application type: Retail / digital banking Regulatory scope: Single-region compliance requirements
Functional scope
The application includes functionality commonly expected in a mid-level banking product:
- Secure user registration and authentication
- Account balance visibility and transaction history
- Inter-bank transfers and scheduled payments
- Identity verification and onboarding workflows (KYC)
- Transaction alerts and push notifications
- In-app customer support channels
- Core security mechanisms, including encrypted storage and protected sessions
Estimated development timeline:
Total estimated timeline: 5-8 months
Actual timelines may vary based on integration depth, regulatory review cycles, and feedback incorporated during testing.
Estimated total development cost: $150,000–$300,000
Factors that commonly increase cost
Several elements can push development costs beyond the ranges outlined above:
- Expansion to multiple regulatory regions
- Support for business or corporate banking users
- Integration with legacy or non-standard core banking systems
- Feature additions after development has begun
- Extended testing cycles driven by compliance or audit requirements
Developer rates by region and their impact on banking app development cost
Why developer location matters
Labor cost is one of the largest contributors to banking app development cost. Developer rates vary widely by region due to differences in market demand, cost of living, and availability of specialized skills. For banking applications, this impact is even more pronounced because teams often require expertise in security, integrations, and regulatory compliance.
Choosing a development location affects:
- Hourly and monthly development rates
- Overall project budget
- Team composition and size
- Ongoing maintenance and support costs
Average developer rates by region
The following ranges reflect commonly observed hourly rates for mobile and backend developers involved in banking and fintech projects. Actual rates may vary based on experience, specialization, and project complexity.
These rates usually apply to experienced developers. Teams with specialized roles such as security engineers, QA specialists, or compliance consultants may command higher rates.
Hidden and overlooked costs in banking app development
Why these costs are frequently underestimated
Many banking app cost estimates focus only on design and development. In practice, a significant portion of the budget often comes from operational, compliance-related, and post-launch requirements. These costs tend to surface only after development has begun, leading to timeline extensions or budget adjustments.
Understanding these hidden cost areas early helps teams plan more accurately and avoid surprises later.
Licensing and regulatory-related expenses
Depending on the markets served and the services offered, banking apps may need to comply with financial regulations and licensing requirements. These obligations often involve legal consultation, documentation, and periodic verification.
Typical cost considerations include:
- Regulatory compliance assessments
- Legal review and documentation
- Third-party compliance tools or reporting services
While these costs may fall outside pure development work, they directly affect project timelines and budgets.
Ongoing security audits and compliance reviews
Banking applications are subject to recurring security checks and compliance reviews. These processes ensure the application continues to meet regulatory and security standards over time.
Associated costs may include:
- Periodic security testing and vulnerability assessments
- Compliance reviews triggered by regulatory updates
- Remediation work following audit findings
These expenses are recurring rather than one-time and should be budgeted annually.
Infrastructure and hosting costs
Banking apps rely on secure backend infrastructure to manage user data, transactions, and integrations. Infrastructure-related costs often scale with user growth and usage volume.
Common infrastructure expenses include:
- Cloud hosting and database services
- Monitoring and logging systems
- Backup and data retention services
As transaction volume increases, infrastructure costs tend to rise accordingly.
Third-party service fees
Many banking app features depend on external services, such as payment processors, identity verification systems, and notification services. While integration work is accounted for during development, ongoing service fees are sometimes overlooked.
Typical examples include:
- Per-transaction fees for payment processing
- Charges for identity verification or credit checks
- API usage fees based on request volume
These costs accumulate over time and can materially affect operating expenses.
Post-launch maintenance and support
After launch, teams must account for ongoing maintenance work. This includes fixing bugs, addressing performance issues, updating dependencies, and supporting new OS versions.
Maintenance-related costs are influenced by:
- Frequency of updates
- Complexity of integrations
- Compliance-driven changes
For many banking apps, annual maintenance costs range between 15% and 25% of the initial development cost.
Why accounting for these costs matters
Ignoring hidden costs can result in underfunded projects or delayed releases. A complete view of banking app development cost includes both the upfront build and the recurring expenses required to operate and maintain the application safely and compliantly.
How regional rates affect total project cost
To illustrate the difference, consider a mid-level banking app requiring approximately 4,000-5,000 development hours across backend, mobile, design, testing, and integrations.
- North America / Western Europe: Higher hourly rates increase overall cost but may offer closer timezone alignment and local regulatory familiarity.
- Eastern Europe: Often selected for a balance between cost efficiency and technical experience in financial software.
- India and Southeast Asia: Lower hourly rates can significantly reduce development cost, though projects may require more process oversight and documentation.
The difference in team location alone can shift total development cost by hundreds of thousands of dollars without changing feature scope.
Team structure and specialization considerations
Beyond geography, team composition also influences cost. Banking app projects typically involve:
- Mobile developers (iOS and Android)
- Backend engineers
- UI/UX designers
- QA and testing specialists
- Security and compliance experts
Projects that require dedicated security or compliance resources will generally have higher costs, regardless of development location.
Choosing the right delivery model
Many organizations adopt a hybrid delivery model, combining local product oversight with offshore or nearshore development teams. This approach allows teams to manage cost without compromising on security, quality, or regulatory alignment.
When evaluating development teams, cost should be considered alongside:
- Experience with banking or fintech systems
- Familiarity with regulatory requirements
- Communication practices and documentation standards
When you need your own license vs using Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Understanding the role of licensing in banking apps
A banking app’s licensing requirements depend on the financial services it provides. Full banking operations, such as accepting deposits or issuing loans, generally require a formal banking or financial services license. Obtaining and maintaining these licenses involves regulatory approval, legal review, capital requirements, and ongoing reporting obligations.
For many organizations, licensing represents a significant cost and time commitment that sits outside core application development.
When obtaining your own license is required
Organizations typically pursue their own financial license when they intend to operate as a regulated financial institution. This approach is more common for established banks or fintech companies with long-term regulatory and regional expansion plans.
Obtaining a license may be appropriate if:
- The app offers deposit, lending, or savings products
- The business operates independently of an existing bank
- Long-term control over compliance and operations is a priority
- The organization plans to expand across multiple jurisdictions
While this approach offers full control, it also introduces higher upfront costs, longer timelines, and ongoing compliance obligations.
Using Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Banking-as-a-Service allows businesses to build banking apps on top of an existing licensed institution’s infrastructure. Instead of securing their own license, app owners rely on a regulated banking partner to handle compliance, account management, and certain operational responsibilities.
BaaS models are often used by:
- Startups entering the market
- Companies testing new financial products
- Businesses focused on user experience rather than regulation
This approach can significantly reduce initial development time and regulatory overhead.
Cost and timeline implications
The choice between licensing models directly affects both budget and delivery speed.
Using a BaaS provider typically:
- Reduces legal and regulatory setup costs
- Shortens time to market
- Shifts some compliance responsibilities to the partner
Pursuing a standalone license generally:
- Increases upfront and ongoing operational costs
- Extends launch timelines
- Requires dedicated compliance resources
However, long-term operating costs may balance out depending on transaction volume, revenue structure, and partnership terms.
Key considerations before choosing an approach
Before committing to either model, teams should evaluate:
- Target markets and regulatory jurisdiction
- Types of financial services offered
- Expected transaction volume and growth plans
- Internal capacity to manage compliance and reporting
The licensing path chosen early in the project has a lasting impact on banking app development cost and operational complexity.
Conclusion
Banking app development cost depends primarily on app complexity, compliance scope, security requirements, integrations, and team structure. While a focused MVP typically falls in the $50,000-$300,000 range, enterprise-grade banking platforms with advanced functionality and multi-region compliance frequently exceed $1 million. These variations are expected, given the regulatory and operational demands of modern banking applications.
A reliable cost estimate starts with defining the type of banking app being built, limiting initial feature scope, and accounting for long-term maintenance and compliance needs. Treating banking app development as an ongoing operational investment rather than a one-time build helps teams set realistic budgets, timelines, and expectations from the outset.
