What are the phases of DevSecOps

Introduction
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, security can no longer be an afterthought. Traditional DevOps practices often focus on streamlining development and operations, leaving security concerns to be addressed at the end, sometimes resulting in vulnerabilities slipping through. This is where DevSecOps steps in, embedding security at every phase of the development lifecycle.
DevSecOps isn't just about adding security to DevOps, it’s about making security everyone's responsibility. In this blog, we’ll explore the phases of DevSecOps, outlining how security integrates into each step and the tools and best practices that ensure secure and reliable software delivery.
What is DevSecOps?
DevSecOps stands for Development, Security, and Operations. It builds upon the principles of DevOps, which aim to bridge the gap between development and operations teams, and adds a crucial third element: security. The goal is to integrate security throughout the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC) from planning and coding to deployment and beyond.
In traditional software development, security checks are often performed at the end of the process, which can lead to vulnerabilities being discovered late in the game, causing delays and increasing costs. DevSecOps shifts security left, meaning security is embedded right from the start, alongside development and operations tasks.
The Importance of Security in DevOps
With the rise of cyber threats, security has become a top concern for organizations. High-profile security breaches can lead to data loss, financial damage, and a tarnished reputation. In traditional DevOps, security is usually considered late in the process, but DevSecOps changes that by making security an integral part of the entire development cycle.
By addressing security early in the process, organizations can:
- Identify and fix vulnerabilities sooner, saving time and resources.
- Reduce the overall cost of development by catching issues early, before they propagate through the system.
- Improve collaboration between development, operations, and security teams, ensuring everyone is aligned on security goals.
Phases of DevSecOps
Now, let’s dive into each phase of DevSecOps, showing how security is integrated into the development process from start to finish.
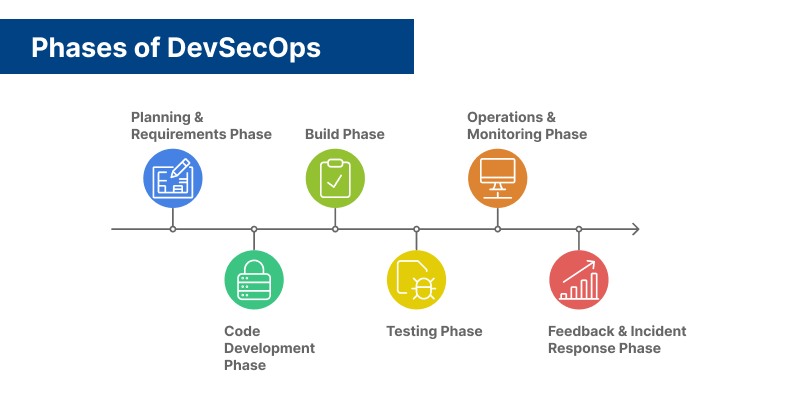
1. Planning & Requirements Phase
The journey to secure software begins in the planning phase. It’s crucial to consider security from the moment you start gathering requirements. In this phase, you need to:
- Define security requirements alongside functional requirements.
- Identify potential risks and develop a plan to address them early.
- Create security policies to guide the development and deployment processes.
Best Practices:
- Use threat modeling to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors. Tools like the Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool can help you visualize and mitigate risks before development starts.
- Clearly define security roles and responsibilities for your team members.
2. Code Development Phase
Once the planning phase is complete, the next step is coding. In DevSecOps, developers need to write secure code from the start. This means following secure coding guidelines and using tools that help prevent vulnerabilities.
Key actions during the coding phase:
- Implement secure coding practices (e.g., avoiding SQL injection and cross-site Scripting).
- Run static code analysis (SAST) to catch vulnerabilities as you code. This can be automated to scan code for security issues before it’s committed to the repository.
Tools/Practices:
Use tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx for static analysis to ensure code quality and security.
Follow best practices like OWASP Secure Coding Guidelines to avoid common vulnerabilities.
3. Build Phase
In the build phase, the code is integrated and compiled. Security checks should be automated within the continuous integration (CI) process to catch any issues that might arise. Here, it’s essential to ensure the integrity of your code and manage dependencies properly.
Key actions during the build phase:
- Automatically scan for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies.
- Ensure the build pipeline includes security tests alongside traditional unit and integration tests.
Tools/Practices:
- Use tools like OWASP Dependency-Check or Snyk to automatically scan for vulnerable dependencies.
- Integrate security checks into your CI tools, such as Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitLab CI.
4. Testing Phase
In this phase, security testing takes center stage. The goal is to identify any vulnerabilities that may have slipped through the earlier phases, using both automated and manual testing techniques.
Types of security testing in this phase:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyzes the code for vulnerabilities before execution.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Tests the application during runtime to catch issues that only surface when the app is running.
- Penetration Testing: Manual testing to simulate real-world attacks and uncover hidden vulnerabilities.
Tools/Practices:
- Use DAST tools like OWASP ZAP or Burp Suite to simulate attacks on your application.
- Consider interactive testing with tools like Contrast Security to provide real-time feedback during both static and dynamic phases.
5. Operations & Monitoring Phase
Once your application is live, continuous monitoring is essential to detect and respond to security threats in real-time. Security in production involves maintaining visibility into your environment and preparing for quick responses to any incidents.
Key actions in the operations phase:
- Set up real-time monitoring for security events and anomalies.
- Implement logging and auditing to track all activity in your system for later analysis in case of an incident.
Tools/Practices:
- Use SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools like Splunk or ELK Stack to gather and analyze logs.
- Set up real-time alerts with tools like Prometheus or Grafana to notify you of suspicious activity.
6. Feedback & Incident Response Phase
No security process is complete without learning from past mistakes. The final phase of DevSecOps focuses on collecting feedback from security incidents and continuously improving the system.
Key actions in the feedback phase:
- Analyze security incidents to perform a root cause analysis and improve future processes.
- Implement continuous feedback loops to share learnings across the development, operations, and security teams.
Best Practices:
- Develop a detailed incident response plan that outlines the steps to take when a security breach occurs.
- Use tools for post-incident analysis and make improvements to your SDLC to prevent similar issues from arising.
Best Practices for Implementing DevSecOps
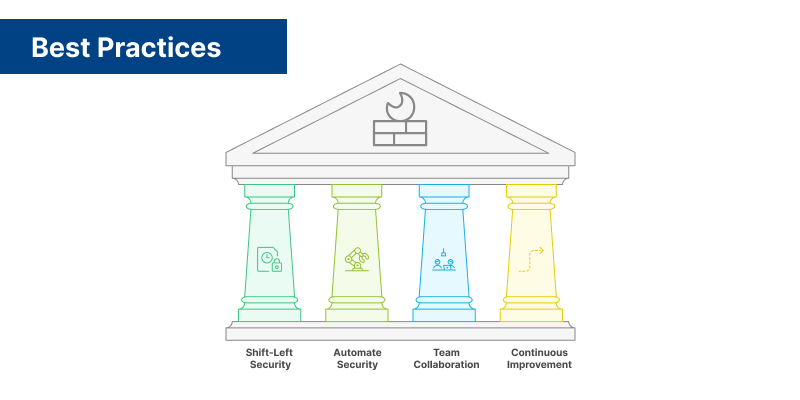
- Shift-left security: Move security checks to earlier phases of the SDLC to catch vulnerabilities early.
- Automate security: Automate as many security tasks as possible using CI/CD pipeline integrations.
- Collaborate across teams: Ensure development, operations, and security teams work together closely to achieve shared security goals.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly update and improve your security practices based on incidents, feedback, and emerging threats.
Conclusion
Adopting DevSecOps isn’t just about adding security into your DevOps pipeline it’s about fostering a culture where security is part of everyone’s responsibility. By embedding security into each phase of the SDLC, organizations can reduce vulnerabilities, improve response times, and build trust with their users.
The future of software development lies in proactive security, and DevSecOps is the key to staying ahead of potential threats. So, whether you're just starting or already have a mature DevOps process, it’s time to integrate security and make your software safer for everyone.
