Introduction to Computer Vision
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables machines to interpret and make sense of visual data. By mimicking human vision, computers can analyze images and videos to recognize patterns, objects, and even emotions. From self-driving cars to medical imaging, computer vision is revolutionizing various industries. This guide explores the fundamentals, applications, and future of computer vision.
Understanding Computer Vision
At its core, computer vision involves processing and understanding visual information through machine learning and deep learning techniques. The goal is to extract meaningful insights from images and videos, enabling machines to perform tasks such as:
Object detection and recognition
Image classification
Facial recognition
Motion tracking
Scene reconstruction
How Computer Vision Works
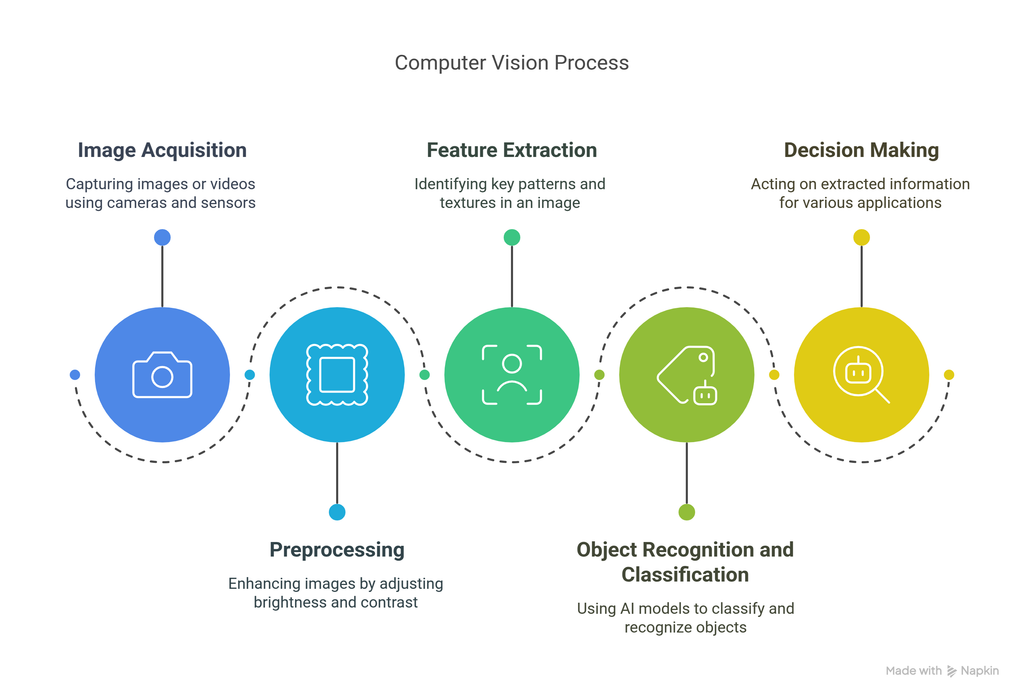
Computer vision systems typically follow these steps:
Image Acquisition: Capturing images or videos using cameras, sensors, or other imaging devices.
Preprocessing: Enhancing images by adjusting brightness, contrast, and noise reduction.
Feature Extraction: Identifying key patterns, edges, and textures in an image.
Object Recognition and Classification: Using AI models to classify and recognize objects.
Decision Making: Acting on the extracted information, such as guiding autonomous vehicles or detecting defects in manufacturing.
Applications of Computer Vision
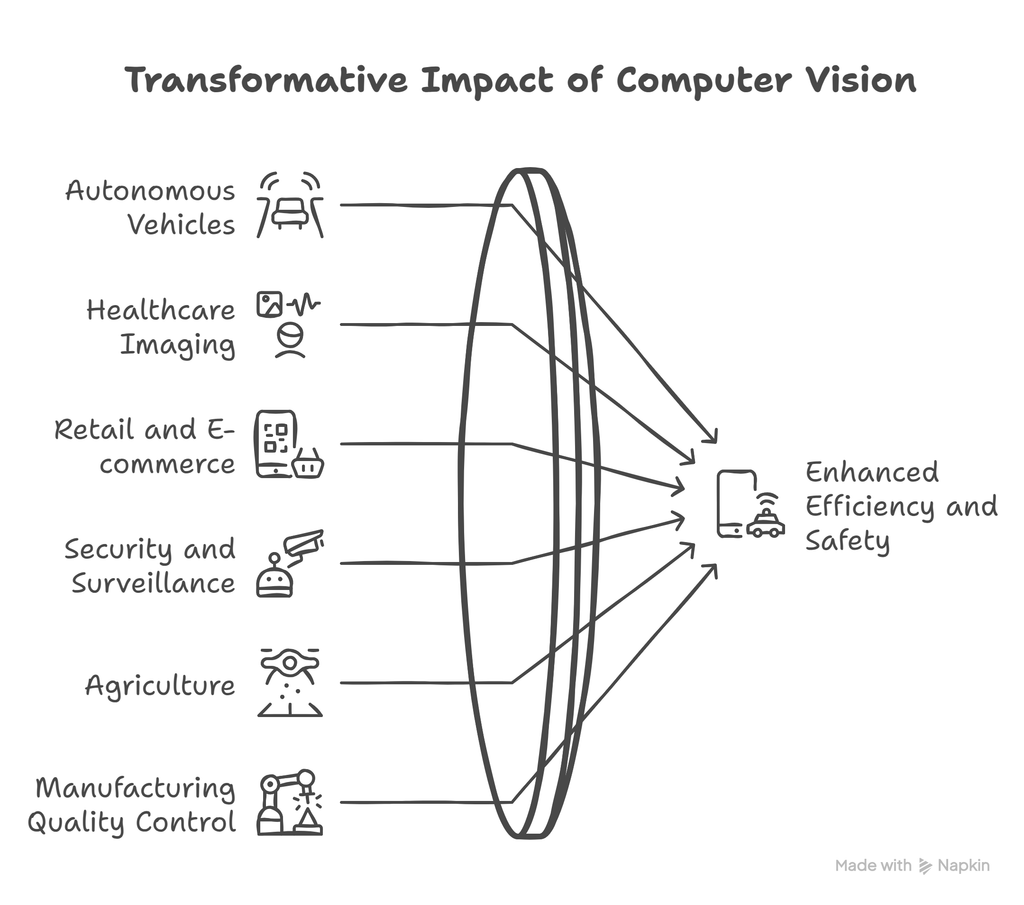
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on computer vision to detect road signs, lane markings, pedestrians, and obstacles, ensuring safe navigation.
2. Healthcare and Medical Imaging
Computer vision assists in diagnosing diseases by analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. AI-powered image analysis enhances early detection of conditions like cancer and neurological disorders.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Retailers use computer vision for inventory management, cashier-less stores, and personalized shopping experiences through visual search.
4. Security and Surveillance
Facial recognition and anomaly detection help enhance security by identifying threats and unauthorized access in real-time.
5. Agriculture
Farmers use computer vision for monitoring crop health, detecting pests, and optimizing irrigation through satellite imagery and drones.
6. Manufacturing and Quality Control
Automated inspection systems detect product defects, ensuring high-quality standards in industries such as automotive and electronics.
Technologies Behind Computer Vision

Computer vision is powered by various technologies and frameworks, including:
Deep Learning: Neural networks like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze visual data with high accuracy.
OpenCV: An open-source computer vision library used for real-time image processing.
TensorFlow and PyTorch: AI frameworks for building and training computer vision models.
Edge AI: Running computer vision models on edge devices like smartphones and IoT cameras for real-time processing.
Challenges in Computer Vision
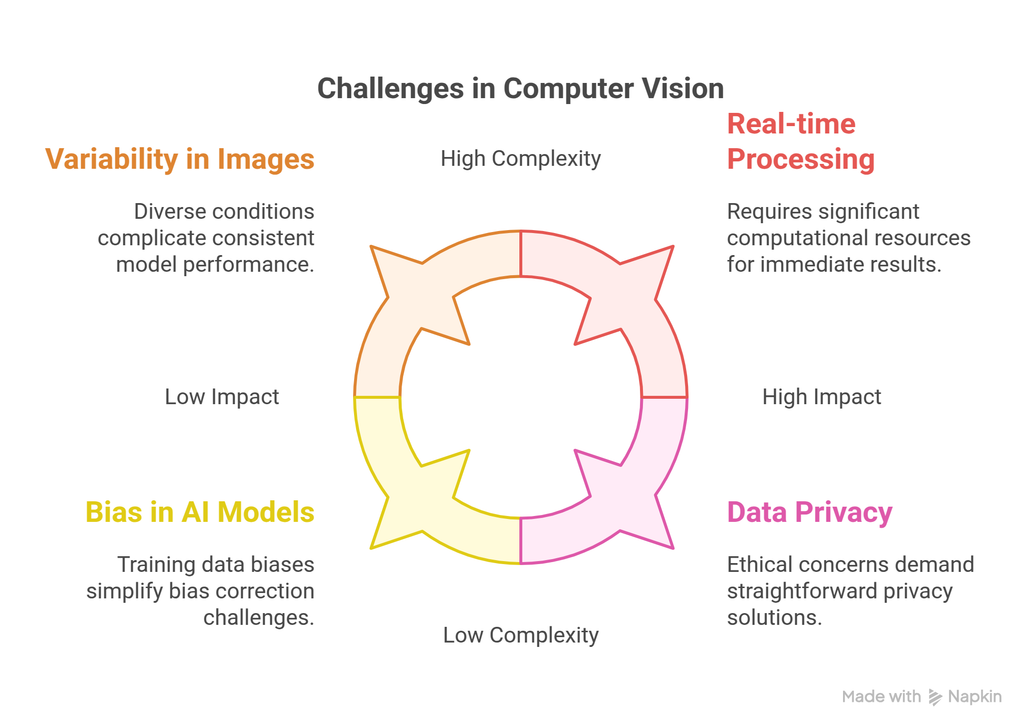
Despite its advancements, computer vision faces challenges such as:
Data Privacy: Ethical concerns over facial recognition and surveillance.
Bias in AI Models: Training data biases can lead to inaccurate or unfair predictions.
Real-time Processing: High computational power is required for real-time image analysis.
Variability in Images: Differences in lighting, angles, and backgrounds can affect model accuracy.
The Future of Computer Vision
As AI and hardware technology advance, computer vision is expected to become more accurate, efficient, and widely adopted. Some emerging trends include:
AI-powered Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing AR experiences with real-time object recognition.
Edge Computing in Vision: Reducing latency by processing images on edge devices.
Generative AI for Image Synthesis: Creating realistic images for entertainment and design.
Human-like Vision Systems: Enabling AI to understand visual data with reasoning and context awareness.
Conclusion
Computer vision is transforming the way machines interpret and interact with the world. With applications spanning multiple industries, this technology continues to drive innovation. As research progresses, we can expect even more groundbreaking developments, making computer vision an integral part of our daily lives.
