The Role of AI in Modern Insurance
 (1).png)
Introduction
The insurance sector is undergoing a data-driven transformation powered by artificial intelligence.
As AI adoption surpasses 77% among global insurers, it’s becoming the foundation for risk assessment, pricing, and customer experience.
The AI in the insurance market, now valued at USD 10.24 billion, is projected to grow at a 32.8% CAGR, reflecting a decisive shift toward intelligence-led operations.
The adoption curve is steep
- The global AI-enabled insurance market is projected to grow from USD $7.71 billion in 2024 to USD $10.24 billion in 2025, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~32.8%.
- A survey by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) found that 84% of U.S. health insurers currently use AI/ML in some capacity.
- 90% of respondents report being in some stage of evaluating generative AI in insurance; 55% are already in early or full adoption.
- A global usage of AI in the insurance market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of ~35.1% between 2025 and 2029, adding around USD 30.07 billion in revenue.
Why are insurers rebuilding their data foundations?
Insurance runs on information policies, claims, risk models, customer conversations, compliance records; the list keeps growing.
But the real obstacle isn’t the volume of data.
The most relevant information stays scattered across legacy systems, old documents, and unstructured files, making it hard to bring everything into one workflow.
When data lives everywhere and connects nowhere, decisions slow down, underwriting depends on incomplete context, and insights that should guide pricing or fraud detection never surface.
Over the past few years, insurers have shifted from viewing AI as an “automation tool” to seeing it as the only practical way to unify the messy, distributed nature of insurance data.
- 77% of insurers are adopting AI technologies to automate and integrate their data workflows, improving accuracy and speed.
- 50–90% reduction in manual data tasks as AI systems handle metadata tagging, document classification, and data-quality checks.
- 80% of insurers say AI-powered analytics now help them make faster, more confident decisions.
AI and generative AI in underwriting
Underwriting is the core of every insurance business, and for decades, it depended on historical datasets and human judgment to understand risk.
Today, insurers are dealing with climate volatility, cyber exposure, shifting customer behavior, and entirely new categories of loss that don’t follow past trends. In that environment, static models fall short. They can’t interpret emerging variables fast enough or with the depth required for modern risk environments.
AI-driven underwriting tools are starting to fill this gap. These systems draw from IoT devices, telematics, behavioral signals, and external data sources to build a more current and connected understanding of each applicant or portfolio.
Recent results from global insurers show how quickly this shift is taking place.
Many teams report a 43% jump in risk-assessment accuracy and 31% faster underwriting on complex cases after adopting AI. Utilizing machine-learning models, insurers are able to fine-tune risk and pricing strategies, achieving up to a 54% improvement in underwriting accuracy. 81% of insurers worldwide plan to expand their AI investment specifically to strengthen underwriting.
A closer look at AI in claims operations
At the intake stage, AI-powered chatbots and self-service portals now capture customer details, photos, and videos directly, reducing paperwork and ensuring no critical information is missed.
During document verification, natural language processing (NLP) scans and compares claims forms, repair invoices, and policy documents in seconds, flagging inconsistencies or missing information that used to delay assessments.
For damage estimation, computer vision models trained on millions of accident or property images can now evaluate photos and generate near-instant repair cost estimates, dramatically cutting reliance on manual inspections.
AI also enhances fraud detection by analyzing patterns across historical claims, location data, and claimant behavior to identify anomalies that human adjusters might overlook.
Meanwhile, generative AI assists adjusters behind the scenes, drafting claim summaries, composing personalized status updates for customers, and even suggesting next steps based on claim context.
A recent McKinsey survey suggests:
- 50% faster claim-processing speeds. Insurers using AI for triage and routing have seen processing times cut in half, thanks to intelligent workflow automation.
- 30% reduction in claims costs. AI and straight-through automation are helping insurers significantly lower administrative and processing expenses.
- 80% of claims executives say AI and machine learning will be key to future value creation in claims management.
How AI Interprets Customer Intent
Insurers are using machine-learning systems to make sense of signals users generate across the customer lifecycle.
These systems analyze past claims, lifestyle indicators, digital behavior, and engagement patterns to anticipate needs before they’re expressed.
This allows insurers to recommend coverage adjustments, identify potential lapses, and provide support at the right moments, not just when prompted.
Generative AI’s Role in Customer Communication
GenAI builds a bridge between complex insurance language and customer-friendly clarity. It drafts personalized policy summaries in plain English, generates contextual updates, and supports call-center and agent teams by suggesting responses tailored to each customer’s situation.
A report by EY mentioned that nearly 70% of insurance organizations now deploy AI to personalize interactions, and 56% of executives cite front-office AI applications such as chatbots, targeted campaigns, and automated service as top GenAI investment priorities.
How AI Shapes Smarter Insurance Products
In insurance, the term "product" refers to the complete structure of coverage offered to a customer the policy type, pricing model, terms, exclusions, service components, and how the insurer manages risk behind it. Motor, health, property, liability, cyber, micro-insurance, and usage-based plans are all examples of insurance products.
Each product has to balance customer needs, regulatory requirements, distribution models, and actuarial risk calculations.
Why do traditional insurance product models struggle today?
Historically, designing a new insurance product required long cycles of market study, risk modeling, policy drafting, approvals, and pilot testing.
This process often took many months and relied heavily on past data.
How does AI identify emerging product opportunities?
Here, machine learning is used to detect emerging product opportunities by modeling shifts in customer behavior, claims frequency, and sensor-driven risk indicators.
This process depends on how raw data is cleaned, transformed, and represented before training, which directly influences a model’s ability to detect behavioral shifts, evolving risk exposures, and unmet coverage needs an approach rooted in effective data processing for machine learning.
Key machine-learning capabilities supporting this use case include:
- Pattern learning across heterogeneous data sources to surface recurring and non-obvious associations
- Temporal trend modeling to capture changes in customer behavior and loss frequency over time.
- Similarity-based segmentation to reveal underserved or emerging customer cohorts.
- Anomaly and distribution-shift detection to flag new risk scenarios requiring tailored products.
How does generative AI speed up product development?
Generative AI helps remove bottlenecks in the product lifecycle.
It can:
- Draft policy wording based on regulatory rules
- Simulate pricing scenarios using historical and live data.
- Create customer-friendly explanations for new coverage.
- Personalize marketing and communication templates.
This reduces the dependency on long manual drafting processes and supports more agile product iterations.
According to a recent industry research report,
Insurers can expect up to a 50% reduction in development time, as AI tools compress multiple phases of research and iteration.
The new compliance and performance standard
AI now influences underwriting decisions, pricing recommendations, fraud alerts, and claim evaluations. As models take on more judgment-heavy work, the risks shift from human error to algorithmic error.
This makes governance essential not for tradition’s sake but to ensure that automated decisions stay accurate, traceable, and fair as customer behavior and risk patterns evolve.
New internal controls insurers are establishing
- Setting up cross-functional AI governance committees.
- Running fairness and bias checks before releasing new models.
- Monitoring model drift to prevent performance degradation.
- Keeping human review in place for decisions with financial or legal weight.
Driving Growth with AI
AI in insurance is shifting from efficiency to growth. Insurers now use AI to spot new opportunities, forecast market trends, and make data-backed strategic decisions.
Machine learning models simulate the impact of inflation, regulation, or extreme weather before it happens, giving leaders early visibility into risk and return. Generative AI complements this by turning complex data into clear summaries, dashboards, and insights for faster decision-making also enables dynamic pricing and market expansion. Policies adjust to real behaviors, driving patterns, connected devices, or business resiliency, helping insurers offer fairer premiums, improve profitability, and strengthen loyalty.
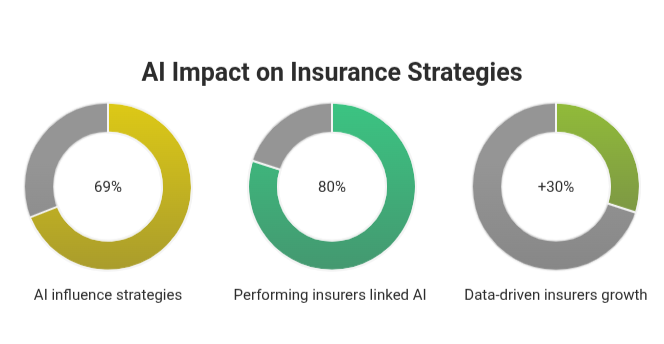
- 69% of insurance leaders say AI insights now directly influence core business strategies (BCG,2025)
- 80% of high-performing insurers have linked AI outcomes to profitability goals
- Data-driven insurers are growing 30% faster than peers still operating without AI insights
Conclusion - From AI Adoption to AI Advantage
AI and generative AI have moved from being optional innovations to becoming the insurance industry’s competitive backbone. What began as isolated automation, faster claims processing, improved data handling, and smarter pricing has now evolved into an intelligence-driven ecosystem where data and algorithms inform every decision, product, and customer interaction.
Insurers that treat AI as a strategic growth engine, not just a support tool, are already pulling ahead. The next phase will focus on scaling these gains responsibly, ensuring transparency, trust, and the ethical use of AI, while continuously innovating.
In 2025 and beyond, what will set insurers apart is how well they use AI.
External Sources
All data points and insights are drawn from the following sources.
CGI Voice of Our Clients, 2025
Retail Banker International, 2025
