OpenAI Operator: How Developers Can Use and Learn from It
What is an operator?
OpenAI’s Operator is an AI agent that interacts with websites like a human user, clicking, scrolling, typing, and filling forms via a remote browser.
It is powered by OpenAI’s Computer‑Using Agent (CUA) model built on GPT‑4o and later upgraded to o3 in mid‑2025.
Operator launched on January 23, 2025, and became available to ChatGPT Pro users in the U.S. in research preview from February 1, 2025, before expanding internationally later.
How Operator works
It “sees” webpages via screenshots and identifies elements like buttons or input fields to decide actions.
It uses a loop of perception, reasoning, action, and self‑correction, enabling navigation across websites without APIs.
When encountering CAPTCHAs, login prompts, or payment steps, the Operator pauses and asks you to take over (“takeover mode”) to maintain security and accuracy.
You can save reusable task templates (e.g., “book a reservation,” “shop groceries”) for repeat execution.
Operator use cases for developers
1. Automate Repetitive Tasks
Repetitive browser actions—like filling out web forms, placing orders, or booking reservations—can be time-consuming and mentally draining. OpenAI’s Operator is designed to take over these tasks, enabling developers to:
- Fill web forms automatically
- Navigate websites without manual clicks
- Perform multi-step sequences in online platforms
This automation allows developers to focus on higher-value activities, such as coding new features, optimizing performance, or tackling complex problem-solving.
For example, businesses like Instacart, DoorDash, OpenTable, and Uber already integrate similar automation to handle high-frequency workflows, proving the potential of AI-powered process execution.
2. Streamline Workflows
Workflows often involve jumping between multiple tools, performing the same sequence of actions over and over. Operator helps by:
- Automating cross-platform tasks
- Executing repeatable steps with minimal human oversight
- Reducing time spent on low-priority actions
Imagine being able to set a sequence once—such as exporting product data from one platform and uploading it to another—and letting Operator handle it reliably every time.
This not only saves hours of manual work but also ensures consistency and accuracy across repetitive processes.
3. Integrate with Existing Systems
While OpenAI’s Operator currently works within a virtual browser, its principles can inspire developers to build agent-based systems that work alongside existing applications.
By studying how Operator:
- Interprets visual information
- Recognizes UI components
- Navigates between steps
- Recovers from unexpected errors
Developers can create custom automation agents tailored to their tools—whether that’s for SaaS platforms, internal business dashboards, or client-facing solutions.
4. Enhance Accessibility and Onboarding
Not all users are equally familiar with complex digital interfaces. Operator can act as a guide for less-experienced users by automating navigation and providing step-by-step assistance. For example:
- In corporate settings, Operator can help new employees get started on multiple internal tools without overwhelming them.
- In public services, it can simplify online applications for people unfamiliar with digital forms.
By bridging the gap between human intent and digital execution, Operator enhances inclusivity and reduces learning curves.
5. Assist in Research and Content Planning
Beyond simple automation, Operator is also useful for information gathering and structuring. It can:
- Browse multiple websites to collect relevant data
- Organize research into topic-based outlines
- Assist content teams in building blog or product pipelines
This makes it especially valuable for marketers, product teams, and researchers who need structured information quickly, without switching between dozens of browser tabs.
6. Learn from Its Approach
For developers aiming to build their own automation or AI agents, Operator provides an excellent model. Studying its approach can reveal:
- How to analyze visual cues in a browser environment
- How to interact with dynamic UI elements
- How to recover from errors and adapt to unexpected changes
By understanding these principles, developers can design smarter, more resilient AI-driven tools.
7. Explore New Possibilities
Experimenting with Operator can lead to new, unexpected use cases. Developers might discover ways to:
- Automate niche workflows unique to their industry
- Combine Operator’s automation with APIs for hybrid solutions
- Build completely new products inspired by its capabilities
The more you explore, the more you can uncover innovative opportunities that push beyond traditional automation.
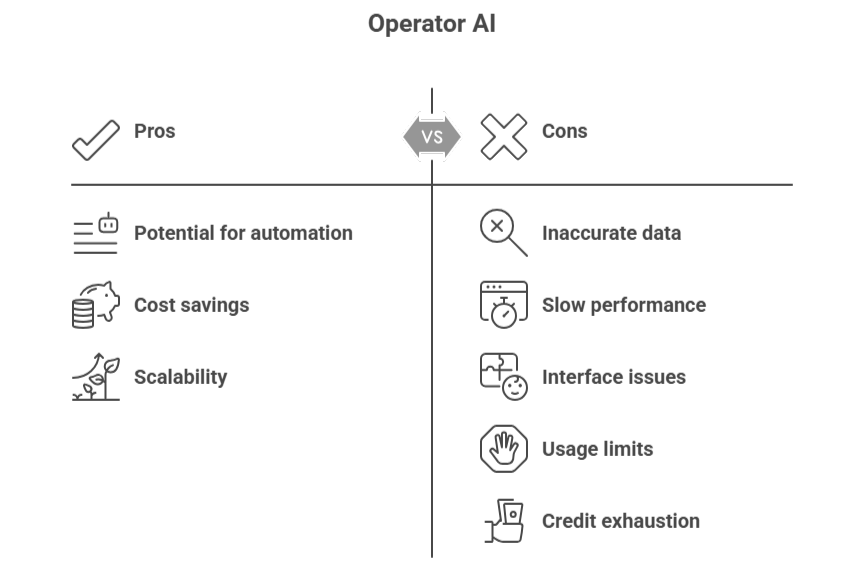
Limitations of the OpenAI operator every developers should know
Accuracy and reliability
- Independent reviewers noted frequent hallucinations and fabricated content when asked to gather influencer data or emails.
- One tester spent 10 minutes getting only 18 valid entries, and many were incorrect.
- The operator invented LinkedIn profiles and emails in one case.
Speed and efficiency
- Users report Operator is often slower than manual browsing.
- Tasks like flight booking or data gathering can take 3× longer than doing them yourself manually, sometimes with worse results.
Complexity of interfaces
- The operator struggles with non-standard web interfaces, dashboards, dynamic pages, and complex workflows.
- It also cannot reliably handle multi-step tasks like flight bookings or advanced calendar navigation yet.
Rate limits and usability
- The operator imposes usage limits even for paying Pro-tier users, which can affect prolonged testing or repeated workflows.
- There’s also credit exhaustion and training resets reported by users.
Recent improvements as of mid‑2025
Model upgrade: The underlying CUA model switched to o3 (May 23, 2025), improving persistence and task accuracy, especially on benchmarks like OSWorld and WebArena.
Task completion dialogue: Operator now prompts users at the end of a run to confirm whether the task succeeded, making feedback easier
Global availability: Starting February 2025, Operator became available beyond the U.S., including India, Brazil, Canada, Australia, the UK, and more, accompanied by new language support in over 60 languages.
Integration into ChatGPT: By July 17, 2025, Operator is being migrated into the ChatGPT agent interface. The standalone site will be deprecated soon
Practical guidance for developers
If you’re a developer building workflows or internal tools, here’s how to think about Operator:
Looking ahead
Operator is an early milestone in agentic AI, moving from chat-only modeling toward agents that can perform real-world web tasks.
As agent models like O3 improve and integration into ChatGPT becomes smoother, Operator may become a reliable assistant for repetitive or template workflows.
However, more tuning, interface adaptability, and model safety enhancements are needed before it's ready for complex mission-critical automation
