A Complete Guide to Master Cloud FinOps

Blog overview
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Cloud FinOps, a crucial discipline for managing and optimizing cloud spending.
It delves into the core principles, key practices, and practical strategies necessary to effectively control costs, improve resource utilization, and drive business value in cloud environments.
Whether you're a seasoned cloud professional or just beginning your journey, this guide offers actionable insights to help you master Cloud FinOps.
Fundamentals of Cloud FinOps
Cloud FinOps, short for Cloud Financial Operations, is an evolving cloud financial management discipline and cultural practice that brings financial accountability to the variable spending model of the cloud, enabling distributed teams to make informed decisions.
It's about more than just cost cutting; it's about maximizing the business value of your cloud investments.
The core principles
FinOps is built on a set of guiding principles that shape its approach to cloud financial management:
Collaboration: FinOps requires close collaboration between engineering, finance, and business teams. This ensures that everyone is aligned on goals and understands the financial implications of their decisions.
Data-driven decisions: FinOps relies on accurate and timely data to inform decision-making. This includes cost data, usage data, and performance data.
Centralized governance, decentralized execution: A central FinOps team sets policies and provides guidance, while individual teams are empowered to make decisions about their own cloud spending.
Real-time visibility: FinOps emphasizes the importance of having real-time visibility into cloud costs. This allows teams to identify and address potential issues quickly.
Accountability: FinOps promotes accountability for cloud spending at all levels of the organization. This ensures that everyone is aware of their responsibilities and takes ownership of their costs.
Taking advantage of the variable cost model of the cloud: FinOps encourages teams to leverage the flexibility and scalability of the cloud to optimize costs. This includes using techniques such as right-sizing instances, using spot instances, and automating resource management.
The FinOps lifecycle
The FinOps lifecycle is a continuous process that involves three key phases:
Inform: This phase focuses on gathering and analyzing data to understand cloud spending patterns. It involves identifying cost drivers, tracking key metrics, and creating reports that provide insights into cloud usage.
Optimize: This phase focuses on identifying and implementing opportunities to reduce cloud costs. It involves techniques such as right-sizing instances, using reserved instances, and automating resource management.
Operate: This phase focuses on establishing processes and controls to ensure that cloud spending remains optimized over time. It involves setting budgets, monitoring costs, and enforcing policies.
Key practices for effective Cloud FinOps
Implementing FinOps effectively requires a combination of tools, processes, and cultural changes.
Here are some key practices to consider:
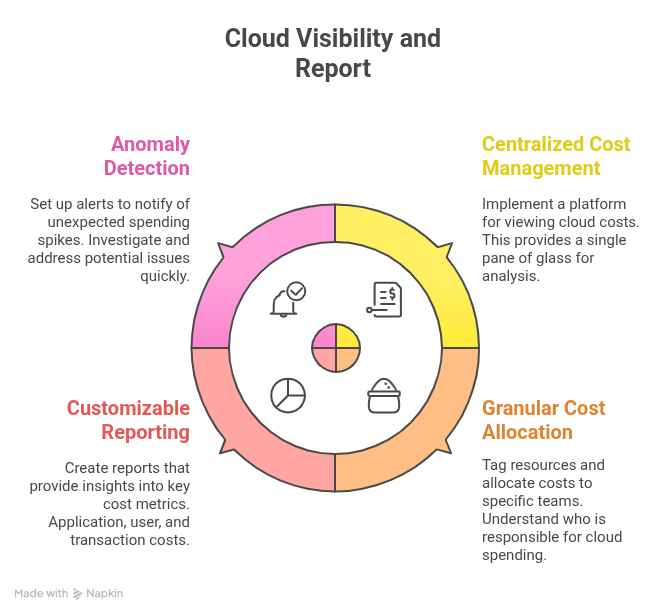
Cost visibility and reporting
Gaining clear visibility into your cloud spending is the first step toward effective FinOps.
This involves:
Centralized cost management tools: Implement a cloud cost management platform that provides a single pane of glass for viewing and analyzing cloud costs.
Granular cost allocation: Tag resources and allocate costs to specific teams, projects, or business units. This allows you to understand who is responsible for cloud spending and identify areas for improvement.
Customizable reporting: Create reports that provide insights into key cost metrics, such as cost per application, cost per user, or cost per transaction.
Anomaly detection: Set up alerts to notify you of unexpected spikes in cloud spending. This allows you to investigate and address potential issues quickly.
Budgeting and forecasting
Effective budgeting and forecasting are essential for controlling cloud costs and ensuring that you stay within your financial targets.
This involves:
Setting realistic budgets: Work with teams to set realistic budgets for their cloud spending based on their business needs and expected usage.
Forecasting future costs: Use historical data and predictive analytics to forecast future cloud costs. This allows you to identify potential budget overruns and take corrective action.
Monitoring budget performance: Track your actual cloud spending against your budget on a regular basis. This allows you to identify areas where you are overspending or underspending.
Variance analysis: Investigate any significant variances between your actual spending and your budget. This helps you understand the root causes of cost overruns and identify opportunities for improvement.
.png)
Optimization strategies
Optimizing your cloud resources is crucial for reducing costs and improving efficiency.
This involves:
Right-sizing instances: Analyze your instance utilization and right-size your instances to match your actual needs. This can significantly reduce your compute costs.
Reserved instances and savings plans: Purchase reserved instances or savings plans to get discounted pricing on your compute resources. This can save you a significant amount of money over the long term.
Spot instances: Use spot instances for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions. Spot instances offer significant cost savings compared to on-demand instances.
Automated resource management: Automate the provisioning, scaling, and decommissioning of your cloud resources. This can help you optimize resource utilization and reduce waste.
Storage optimization: Optimize your storage usage by deleting unused data, compressing data, and using tiered storage options.
Data transfer optimization: Minimize data transfer costs by optimizing your network architecture and using caching techniques.
.png)
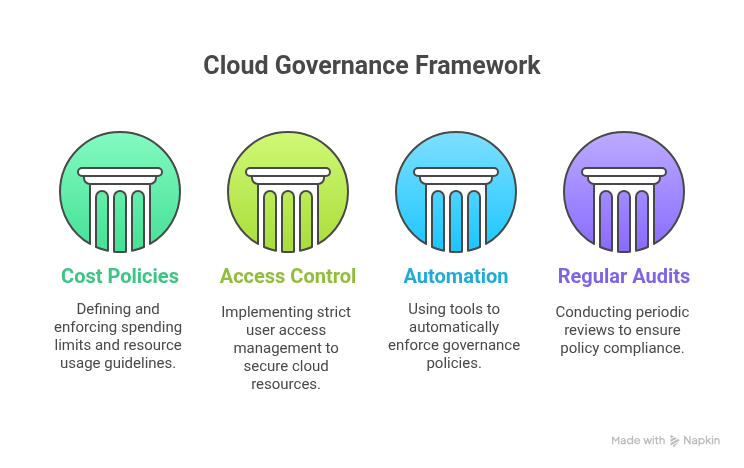
Governance and policy enforcement
Establishing clear governance policies and enforcing them consistently is essential for maintaining control over your cloud spending.
This involves:
Cost policies: Define policies for cloud spending, such as maximum instance sizes, approved regions, and tagging requirements.
Access control: Implement strict access control policies to ensure that only authorized users can provision and manage cloud resources.
Automation: Automate the enforcement of your governance policies using tools such as AWS Config, Azure Policy, or Google Cloud Policy Controller.
Regular audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure that your governance policies are being followed.
Fostering a FinOps culture
FinOps is not just about tools and processes; it's also about culture. To be successful with FinOps, you need to foster a culture of cost awareness and accountability throughout your organization.
This involves:
Training and education: Provide training and education to your teams on FinOps principles and best practices.
Communication: Communicate regularly about cloud costs and optimization opportunities.
Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between engineering, finance, and business teams.
Incentives: Align incentives to reward cost-saving behavior.
-5.png)
Tools and technologies for Cloud FinOps
A variety of tools and technologies can help you implement and manage your FinOps program.
These include:
Cloud provider cost management tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Cost Management provide basic cost visibility and reporting capabilities.
Third-party finOps platforms: CloudHealth by VMware, Apptio Cloudability, and Flexera Cloud Management Platform offer more advanced features, such as cost optimization recommendations, budget management, and policy enforcement.
Open-source tools: Kubecost and Cloud Carbon Footprint are open-source tools that can help you monitor and optimize your Kubernetes costs and track your cloud carbon footprint.
Automation tools: Terraform, Ansible, and Chef can be used to automate the provisioning, scaling, and decommissioning of your cloud resources.
-5.png)
Overcoming common challenges
Implementing FinOps can be challenging, but by understanding the common pitfalls and taking proactive steps to address them, you can increase your chances of success.
Some common challenges include:
Lack of visibility: Difficulty in gaining clear visibility into cloud spending.
Data silos: Lack of collaboration between engineering, finance, and business teams.
Complexity: The complexity of cloud pricing models and resource configurations.
Resistance to change: Resistance to adopting new processes and technologies.
Lack of expertise: A shortage of skilled FinOps professionals.
.png)
Conclusion
Mastering Cloud FinOps is essential for organizations looking to maximize the value of their cloud investments.
By understanding the core principles, implementing key practices, and leveraging the right tools and technologies, you can effectively control costs, improve resource utilization, and drive business value in the cloud.
Embrace the FinOps culture, foster collaboration, and continuously optimize your cloud spending to achieve long-term success.


.svg)