Design Patterns for Flutter Applications
In the world of mobile app development, creating scalable and maintainable applications is of paramount importance.
With the advent of cross-platform frameworks like Flutter, developers now have a powerful tool at their disposal to craft beautiful and functional apps for both Android and iOS platforms simultaneously.
However, as apps grow in complexity, maintaining code readability, scalability, and reusability becomes increasingly challenging.
This is where Flutter design and architecture patterns come into play.
These design patterns offer proven solutions to common problems encountered during mobile app development.
They provide a structured approach to organizing code, improving its maintainability, and making it easier to understand and modify.
Let's delve into some of the most useful design patterns for Flutter development and discuss how they can be applied to create robust and efficient apps.
1. MVC (Model-View-Controller)
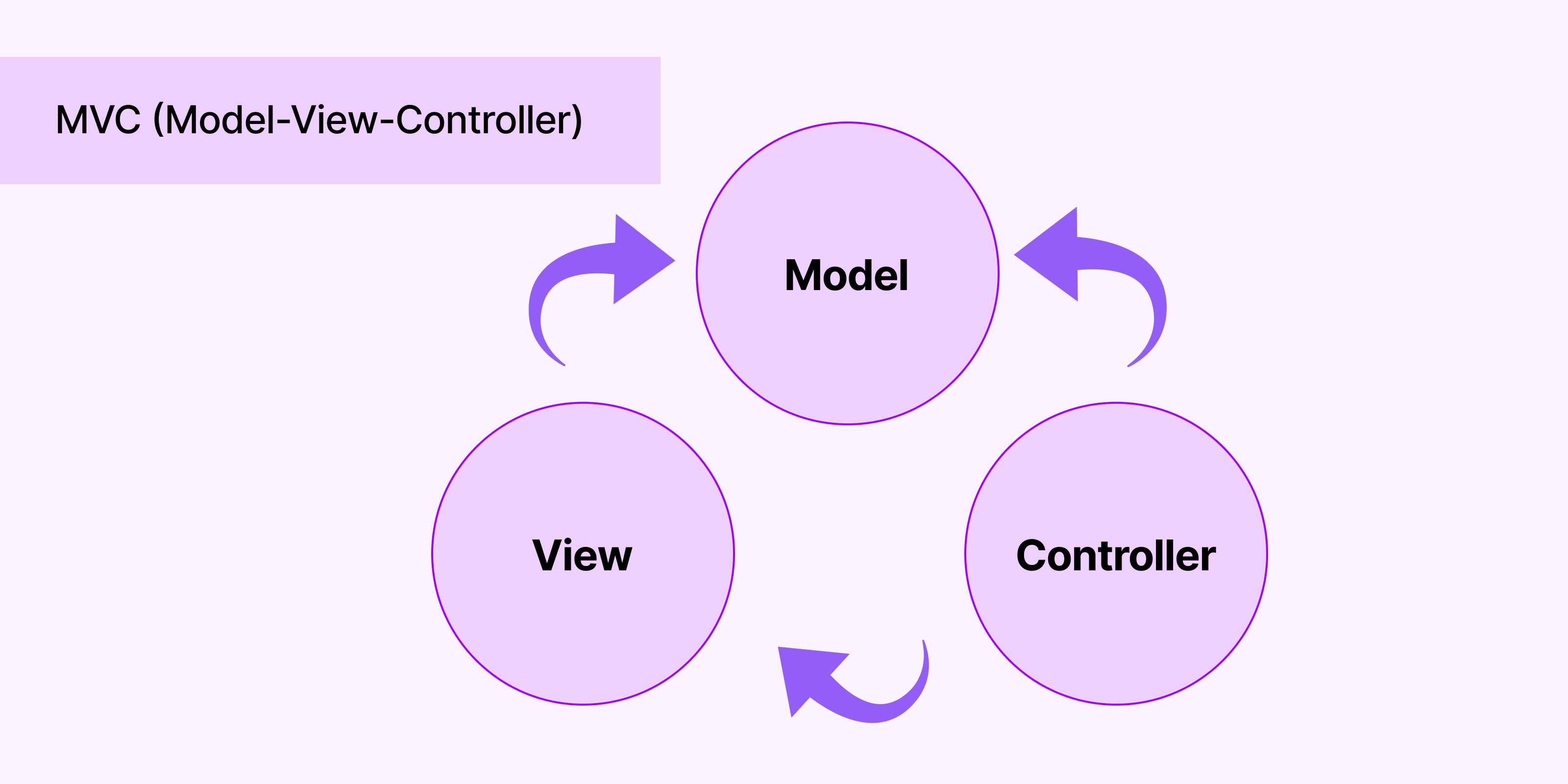
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a widely used architectural pattern that provides a structured way to organize code in an application.
MVC is often hotly debated and compared with Microservices, in the case of Flutter, MVC is chosen of the latter due to its various advantages.
MVC separates an application into three interconnected components:
- Model: This component represents the data and business logic of the application. It encapsulates the data structure and behavior.
- View: The view component is responsible for rendering the user interface and displaying data to the user. It presents information to the user in a visually appealing manner.
- Controller : The controller acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It handles user input, processes requests, and updates the model accordingly. It receives input from the user via the view, manipulates the model based on that input, and updates the view to reflect any changes in the model.
MVC's Application in Flutter
In Flutter, you can implement MVC by structuring your code into separate classes or modules for each component:
- Model: Model classes encapsulate the data and business logic. They define the structure of the data and contain methods to manipulate it.
- View: Widgets represent the view layer in Flutter. They are responsible for rendering the user interface and displaying data to the user. Widgets can be built using Flutter's extensive widget library.
- Controller: Controllers manage the application logic. They handle user input, interact with the model, and update the view accordingly. Controllers can be implemented using StatefulWidget or StatelessWidget, depending on whether they need to maintain state.
Example
Let's say you're building a simple to-do list app in Flutter using MVC. Your code structure might look something like this:
- Model: A To-do Model class that represents a to-do item with properties like title, description, and completion status. It also contains methods to add, remove, and update to-do items.
- View: A TodoView widget that renders the user interface. It displays the list of to-do items and provides UI elements for adding, removing, and updating todos.
- Controller: A TodoController class that manages the application logic. It handles user input from the TodoView, interacts with the TodoModel to perform CRUD operations on to-do items, and updates the TodoView to reflect any changes.
Benefits
- Separation of Concerns: MVC separates the presentation logic from the business logic, making the codebase more modular and easier to maintain.
- Reusability: Each component can be reused independently, allowing for better code organization and improved code reusability.
- Scalability: MVC promotes a structured approach to development, making it easier to scale the application as it grows in complexity.
MVC is a foundational design pattern in software development that provides a clear separation of concerns between the data, presentation, and application logic.
By implementing MVC in your Flutter projects, you can create well-organized, maintainable apps that are easier to understand and extend over time.
We have also listed down a few flutter based companies from India for an end to end fultter development project.
2. MVP (Model-View-Presenter)
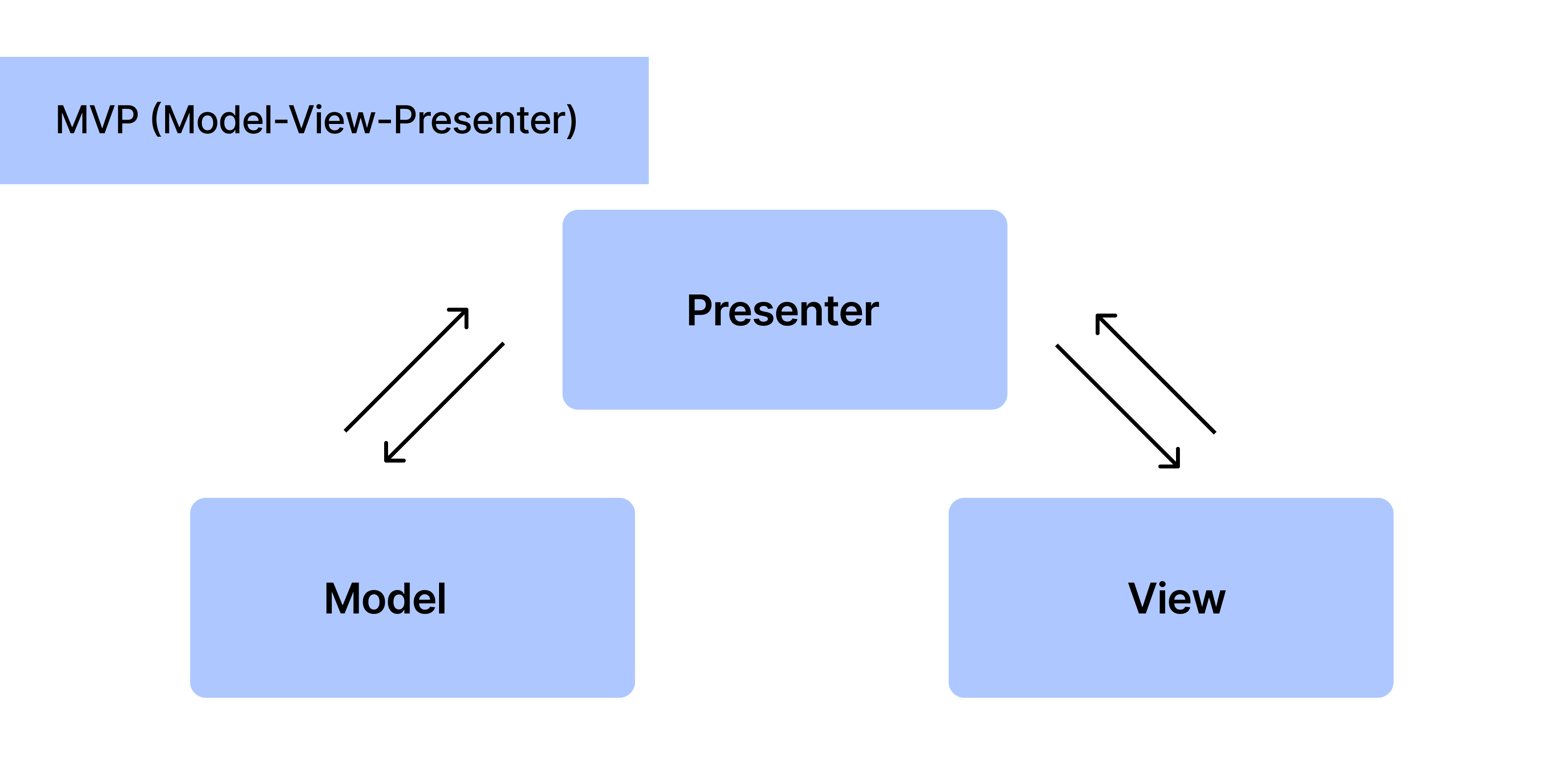
Model-View-Presenter (MVP) is an architectural pattern that shares similarities with MVC but places a stronger emphasis on separating concerns and keeping the view layer as "dumb" as possible.
- Model: The model component in MVP represents the data and business logic of the application, similar to MVC.
- View: Unlike MVC, the view in MVP is passive and does not contain any application logic. It is responsible for rendering the user interface but does not handle user input directly.
- Presenter: The presenter acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It receives input from the view, interacts with the model to perform business logic operations, and updates the view accordingly.
Application in Flutter:
In Flutter, MVP can be implemented by defining interfaces for views and presenters:
- Model: Model classes encapsulate the data and business logic, similar to MVC.
- View: Widgets represent the view layer in Flutter. However, in MVP, the view is passive and does not contain any application logic. Instead, it defines interfaces that the presenter can interact with.
- Presenter: Presenters manage the application logic. They handle user input from the view interfaces, interact with the model to perform business logic operations, and update the view interfaces to reflect any changes.
Example:
Continuing with the todo list app example, in MVP:
- Model: The todoModel class encapsulates the data and business logic for managing todo items.
- View: TodoViewInterface defines interfaces for rendering the user interface and receiving user input.
- Presenter: TodoPresenter class implements the logic for handling user input from the TodoViewInterface, interacting with the TodoModel to perform CRUD operations, and updating the TodoViewInterface accordingly.
Benefits:
- Separation of Concerns: MVP separates the presentation logic from the application logic, making the codebase more modular and easier to maintain.
- Testability: Since the view is passive and does not contain application logic, presenters can be easily unit tested without requiring UI testing frameworks.
- Flexibility: MVP allows for easier swapping of view implementations, making it suitable for cases where the same application logic needs to be used with different UI frameworks or platforms.
MVP is a variation of the MVC pattern that promotes a cleaner separation of concerns and enhances testability in Flutter applications. By implementing MVP, developers can create more maintainable and scalable apps with a clear separation between the presentation layer and the application logic.
3. MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel)
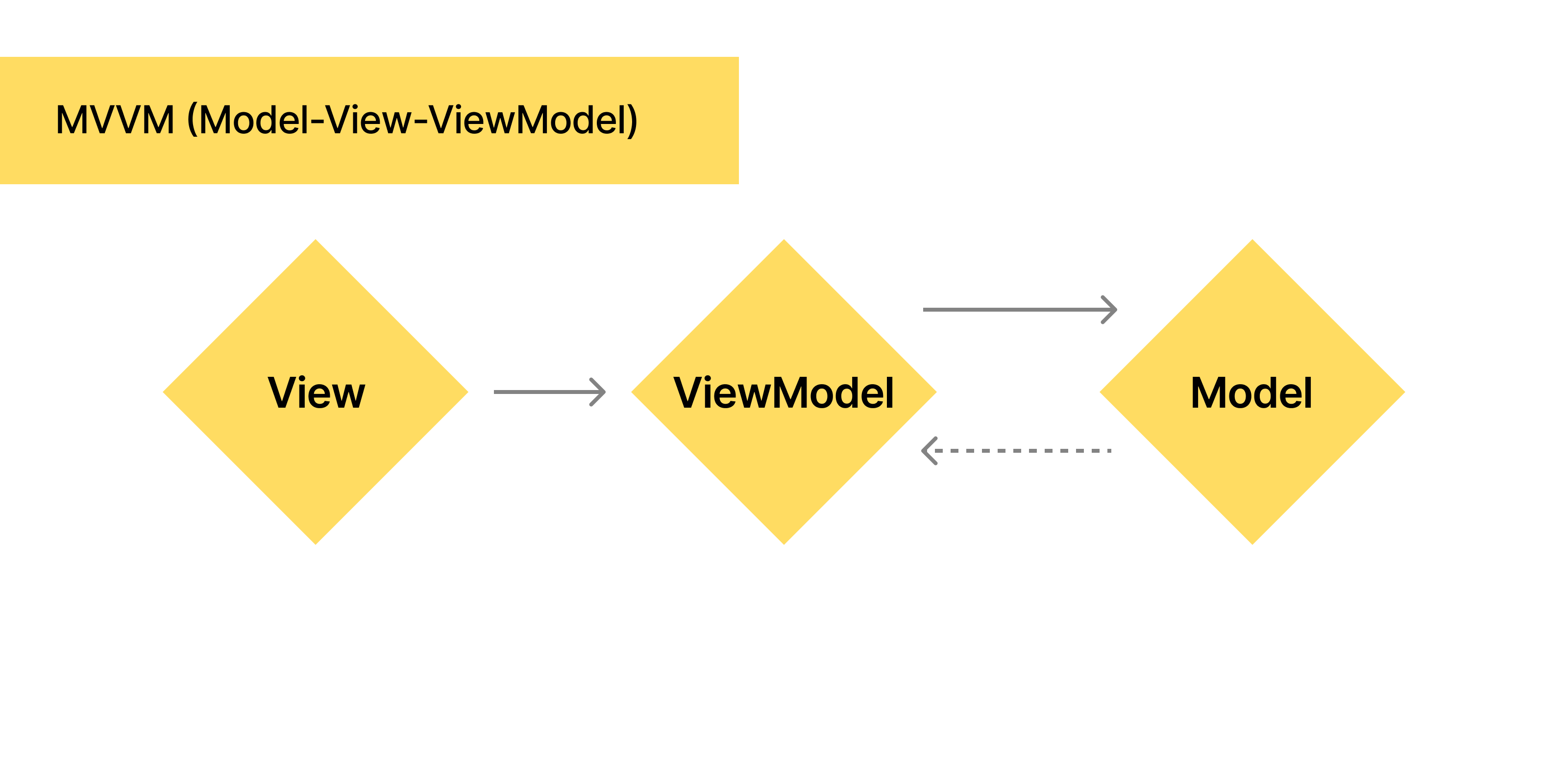
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) is a design pattern that further decouples the view layer from the business logic by introducing a view model.
- Model: Represents the data and business logic, similar to MVC and MVP.
- View: Renders the user interface and displays data, similar to MVC and MVP.
- ViewModel: Exposes data and commands from the model to the view, typically using data binding techniques. It contains presentation logic but does not have a direct reference to the view.
Application in Flutter
In Flutter, MVVM can be implemented using packages like Provider or Riverpod for state management and data binding:
- Model: Model classes encapsulate the data and business logic, similar to MVC and MVP.
- View: Widgets represent the view layer in Flutter. Views observe changes in the view model and update their UI accordingly.
- ViewModel: View models expose stateful data to the view layer using data binding techniques. They interact with the model to retrieve data and contain presentation logic for formatting data for display.
Example
In the todo list app example, in MVVM:
- Model: TodoModel class encapsulates the data and business logic for managing todo items.
- View: TodoView widget renders the user interface and observes changes in the TodoViewModel to update its UI.
- ViewModel: TodoViewModel exposes stateful data (e.g., list of todo items) to the TodoView and contains presentation logic for formatting todo items for display.
Benefits
Separation of Concerns: MVVM separates the view layer from the business logic, improving code maintainability and testability.
- Data Binding: MVVM utilizes data binding techniques to automatically update the UI when the underlying data changes, reducing boilerplate code.
- Testability: View models can be unit tested independently of the view, making it easier to write automated tests for UI-related logic.
MVVM is a design pattern that enhances code maintainability and testability by separating the view layer from the business logic using view models. In Flutter, MVVM can be implemented using state management solutions like Provider or Riverpod for data binding and state management. By adopting MVVM, developers can create more scalable and maintainable Flutter applications with a clear separation of concerns between the view and the business logic.
4. Singleton
The Singleton pattern ensures that a class has only one instance and provides a global point of access to it. This pattern is useful when there should be exactly one instance of a class available to the entire application.
Application in Flutter
In Flutter, singletons can be used to manage global state or provide access to shared resources such as database connections or network clients. For instance, you can use the Provider package to create singletons that hold application-wide state and share it between different parts of your app.
Example
Imagine you have a UserManager singleton class responsible for managing user authentication and session information throughout the app. This class ensures there's only one instance of UserManager, providing centralized access to user-related functionalities.
Benefits
- Global Access: Singletons provide a centralized point of access to resources or services, ensuring consistency and preventing multiple instances from being created.
- Resource Management: They facilitate efficient resource management by ensuring that resources are instantiated only when needed and shared across the application.
5. Factory
The Factory pattern is used to create objects without specifying the exact class of object that will be created. It encapsulates the object creation process and provides a centralized point for creating instances of classes.
Application in Flutter
In Flutter, factories can be employed to create instances of classes dynamically based on certain conditions or parameters. For example, you can create a factory method that returns different types of widgets depending on the platform or user preferences.
Example
Suppose you're developing a weather app where you need to display different types of weather cards based on the weather condition. You can implement a WeatherCardFactory that returns the appropriate weather card widget based on the weather data received from the API.
Benefits
- Decoupling: Factories decouple the client code from the concrete implementation of objects, allowing for flexibility and easier maintenance.
- Dynamic Object Creation: They enable dynamic object creation, allowing the creation of objects based on runtime conditions or configurations.
6. Observer
The Observer pattern is used to define a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
Application in Flutter
In Flutter, streams and the StreamBuilder widget can be used to implement the Observer pattern. Streams emit events whenever data changes, and the StreamBuilder widget automatically rebuilds parts of the UI in response to these events.
Example
Consider a chat application where multiple users are sending messages in real-time. Each user's message stream acts as an observable, and the UI components subscribed to these streams are observers. When a new message is received, the UI components are automatically updated to display the latest messages.
Benefits
- Loose Coupling: Observers are loosely coupled with the subject (observable), allowing for easier maintenance and modifications.
- Real-Time Updates: They enable real-time updates in the UI by automatically notifying observers of changes in the subject's state.
7. Repository
The Repository pattern abstracts away the details of data storage and retrieval, providing a clean and consistent interface for accessing data. It separates the logic for fetching and storing data from the rest of the application.
Application in Flutter
In Flutter, repositories encapsulate data access logic and provide a single point of entry for fetching data from different sources such as databases, web APIs, or local storage. This helps decouple the application logic from the underlying data storage implementation.
Also, get an understanding about how to set up and how does Payment APIs work
Example
Suppose you're developing a news app that fetches articles from both a remote API and a local database. You can implement a NewsRepository that handles data retrieval from both sources. The rest of the application interacts with the repository without needing to know the details of data storage.
Benefits
- Decoupling: Repositories decouple the application logic from the data storage implementation, making it easier to switch between different data sources or refactor the code.
- Abstraction: They provide a clean and consistent interface for accessing data, hiding the complexities of data storage and retrieval from the rest of the application.
Why are Design Patterns Important?
Design patterns are crucial in software development for several reasons:
Reusable Solutions
Design patterns offer proven solutions to common problems encountered during software development.
They encapsulate best practices and provide a blueprint for solving recurring design issues.
By leveraging design patterns, developers can reuse successful solutions, saving time and effort.
Maintainability
Design patterns promote code maintainability by enforcing a structured approach to organizing code.
They improve code readability and comprehensibility, making it easier for developers to understand and modify the codebase.
By following established patterns, developers can quickly grasp the architecture and design principles of a project, facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing among team members.
Refer to a dedicated guide on implementing integration and deployment for smooth project management
Scalability
Design patterns support application scalability by providing guidelines for building flexible and extensible software systems.
They encourage modular design and separation of concerns, allowing developers to add new features or modify existing functionality without disrupting the entire system.
With scalable architectures in place, applications can adapt to changing requirements and accommodate future growth effortlessly.
Performance Optimization
Certain design patterns, such as the Singleton pattern, can optimize performance by controlling the instantiation of objects and minimizing resource consumption.
By managing resources efficiently, design patterns contribute to better application performance and responsiveness.
Abstraction and Encapsulation
Design patterns promote abstraction and encapsulation, two fundamental principles of object-oriented programming.
Abstraction allows developers to focus on essential details while hiding unnecessary complexities, leading to cleaner and more maintainable code.
Encapsulation ensures that the internal workings of an object are hidden from external entities, enhancing code modularity and security.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
With the rise of cross-platform development frameworks like Flutter, design patterns play a crucial role in ensuring compatibility and consistency across different platforms.
By following standardized design patterns, developers can create applications that behave predictably across various operating systems and devices, delivering a seamless user experience.
Ease of Testing
Design patterns facilitate testability by promoting modular and loosely coupled architectures.
Components designed using patterns like MVC, MVP, or MVVM are easier to test in isolation, allowing for comprehensive unit testing and automated testing practices.
This leads to improved software quality and reliability, as bugs and issues can be identified and addressed early in the development process.
In summary, design patterns are essential tools for building robust, scalable, and maintainable software applications.
We also have an article on detailed pricing structure for flutter applications development.
By incorporating design patterns into their development practices, developers can streamline the development process, enhance code quality, and deliver superior user experience.
Check out our guide on React Design Patterns to understand the true nature of react architecture patterns.
Conclusion
Design patterns are indispensable tools for Flutter development, offering reusable solutions to common challenges and enhancing code maintainability, scalability, and readability.
By understanding and employing these patterns effectively, developers can build robust and efficient apps that are easier to maintain and extend over time.
Whether developing a small prototype or a large-scale production app, incorporating design patterns into Flutter projects can significantly enhance the quality and maintainability of the codebase.